Kingdoms of the Eastern and Western Franks
to explain why the Empire of Charles the Great broke up;
to describe the fate of the Carolingian dynastydynasty after the death of Charles the Great;
to indicate what influence the TreatyTreaty in Verdun had on the history and shape of Europe;
to characterize the beginnings of creation of the contemporary states – Germany, France and Italy.

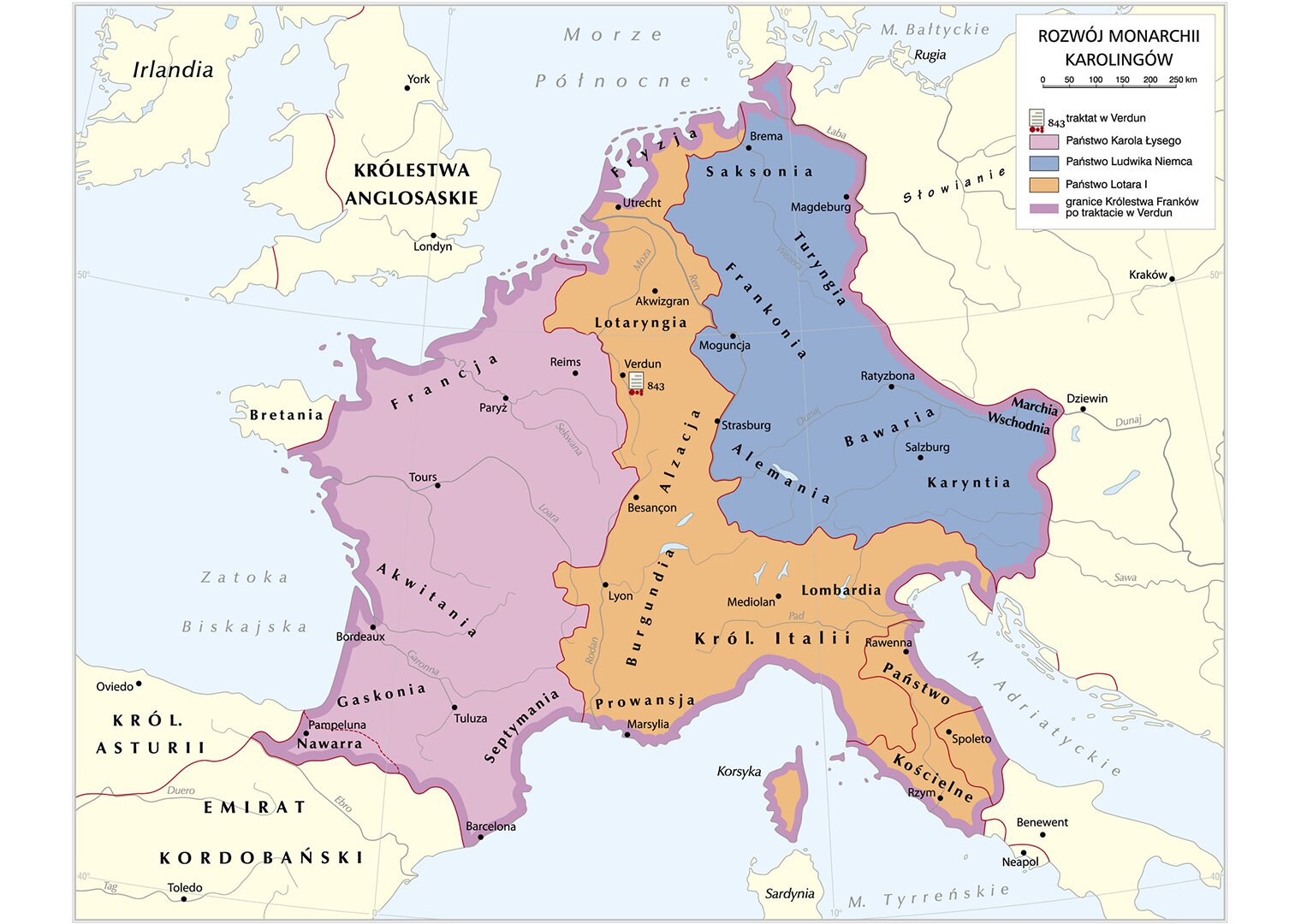
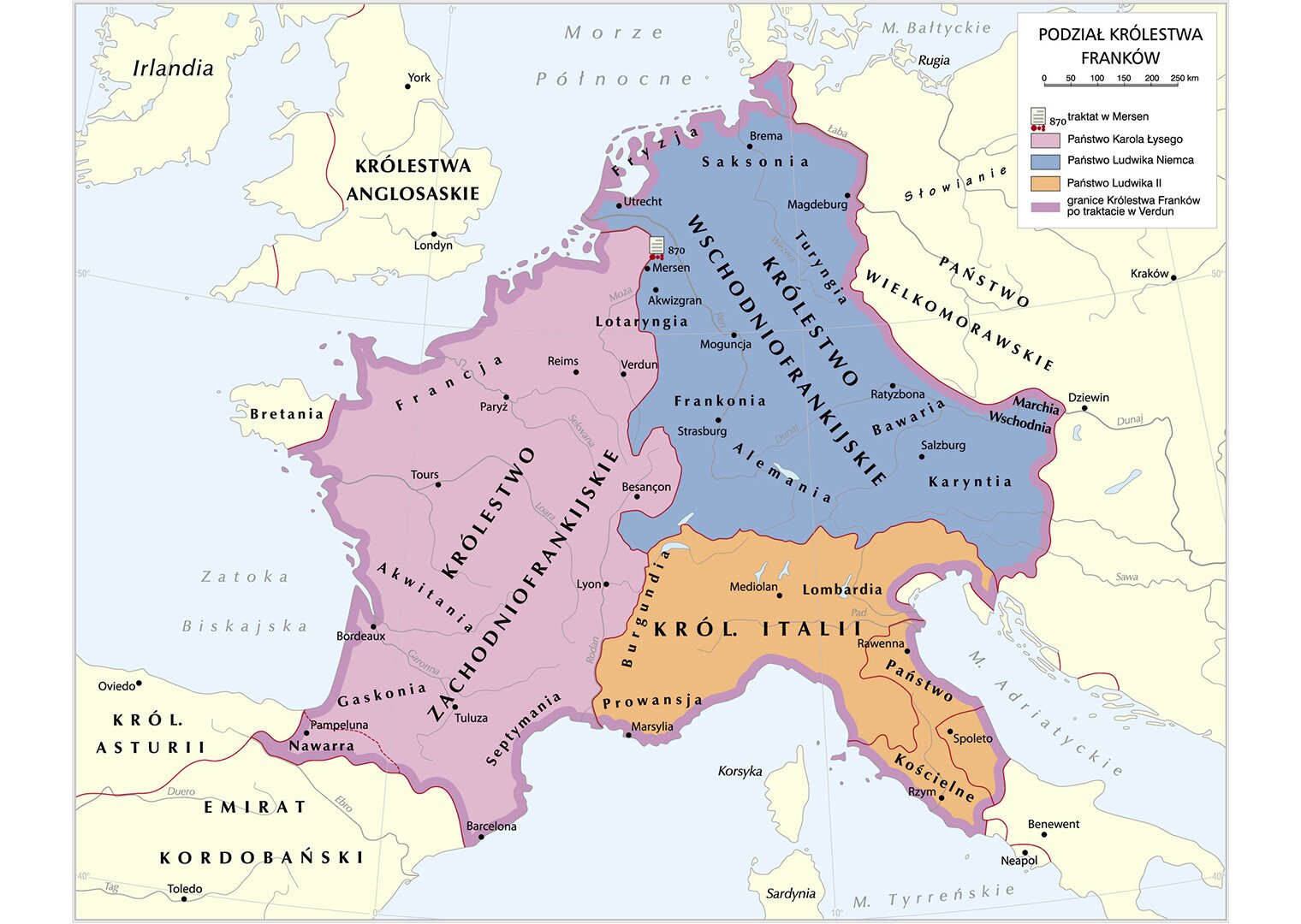
After the death of Emperor Charles the Great in 814, his successor became his son - Louis the Pious who unsuccessfully undertook actions aimed at maintaining the unity of the state and stopping the excessive ambitions of his sons. To strengthen his position, Louis the Pious worked closely with the church hierarchy. This led to an increase in the importance of the clergy and loss of the emperor's authority and completely changed the perception of the position of the ruler by the Church. From now on it was not the Church was part of the Christian monarchy, but itself started managing the monarchymonarchy. This way the emperor could no longer interfere in the affairs of the clergy, but he could even be assessed for morality. The results of this change have become visible very quickly. Statements of relatives, rebellions of his own sons led to total fall of the emperor's authority. The long lasting wars were finally ended by the Treaty in Verdun, adopted after the death of Louis the Pious in 843. He led to the irreversible division of the empire between his sons Lothair, Charles the Bald and Louis the German. Their lands became the origin of modern states: West Francia of Charles the Bald – France; East Francia of Louis the German – Germany; Middle Francia of Lothair – Italy. The imperial title, being only honorary leadership, was retained by the oldest of the sons - Lothair. His kingdom included the most developed and richest provinces of the Carolingian Empire. Unfortunately, their political and ethnic diversity quickly led to the disintegration of the kingdom. The former empire of Charles the Great was united for a short time in the second half of the ninth century by Charles the Fat, son of Louis the German. However also his reign did not last long. After only a few years, he was forced to abdicateabdicate and the state was finally divided. The position of the king in West Francia has been very week since the beginning and the ruling Carolingian dynasty could not keep the authority of the rulers. This was due to the weakness of the state in reactions for invasions of enemies what led to its disintegration into many independent counties and principalities. Finally, after the death of the last ruler of the Carolingian dynasty, the king of the Franks became Hugo Kapet from the line of Robertians. It initiated the reign of the new dynasty with future kings of France for over 300 years.

Eastern Frankish monarchy, whose founder was Louis the German, in the first decades of its existence, thanks to maintaining elements of the state organization from the time of Charles the Great and subordination of the powerful and clergy to royal authorities, avoided a deep crisis. However, in the 10th century, it fell into chaos and disintegrated into four duchies – Frankonia, Saxony, Bavaria and Swabia where princes became the rulers. Conrad I, the prince of Franconia, tried to save the broken country, however, realizing the weakness of his position and his own dynasty (The Conradines), he appointed the strongest ReichReich prince - Henry, the Saxon prince - as his successor. It was a breakthrough decision, because for the first time the authorities over the Franks was in the hands of a ruler not originating from this people. After taking the authorities in 919 as the king of Eastern Franks, he initiated a new period in history, giving origin to a later called German state.
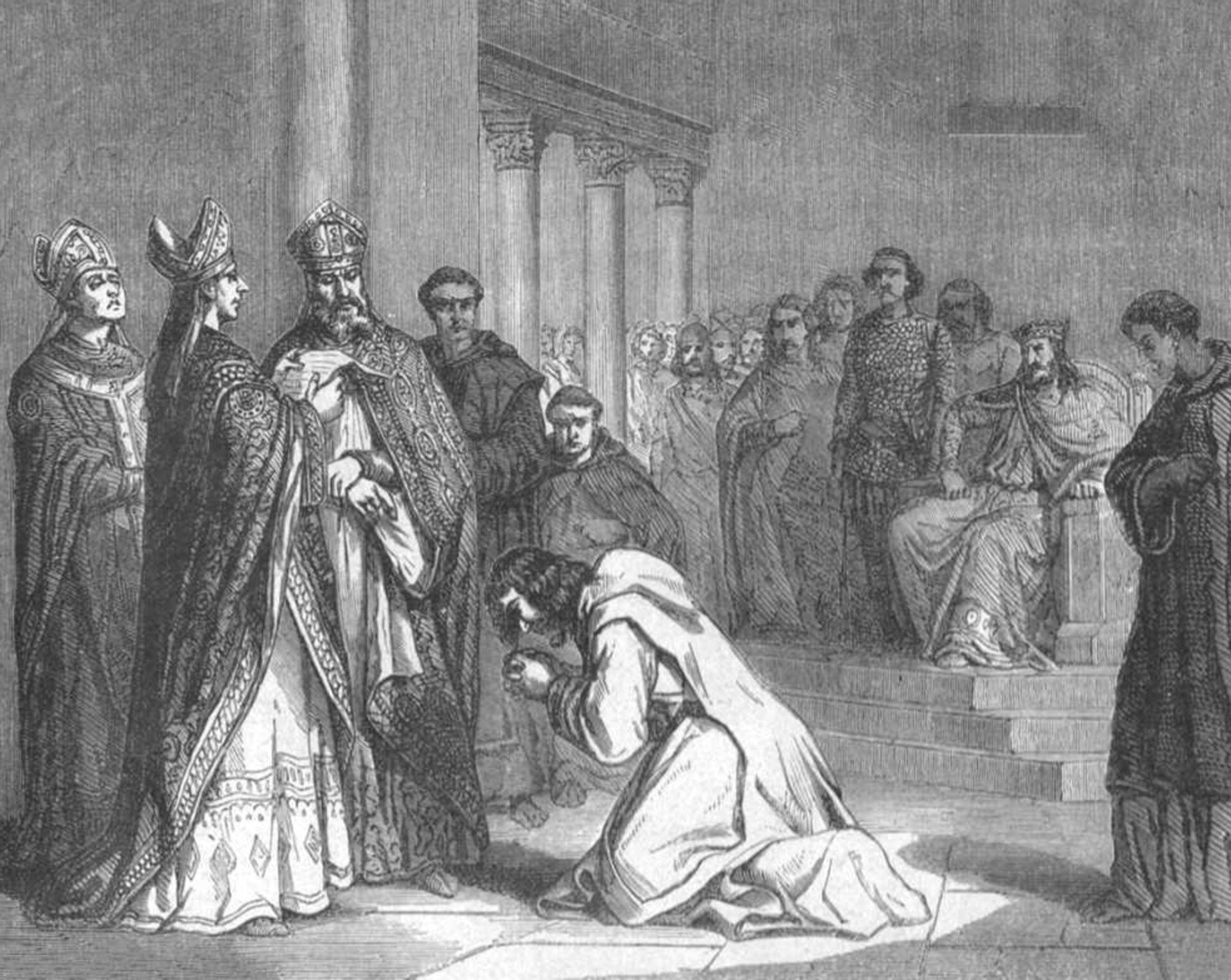

How the author introduced in the background of this scene, King Louis the German, son of Louis the Pious? Indicate the right answer.
- he is talking to his wife and eating a meal.
- he is proudly sitting on the throne as a king and looking mercifully at his father's humiliation.
- he feels sorry for his father and he can barely refrain from helping him.
Read the following text and indicate the rulers and their new kingdoms whose boundaries have been set as per the treaty.
Louis Charles the Bald Lothair
Annales Bertiniani about the Treaty in Verdun
Charles [the Bald] went to [his] brothers [Lothair and Louis] and joined them near Verdun. There [the empire] was divided into parts: Louis [the German] had all [lands] behind the Rhine, and in the Rhine region: Speier, Worms and Mainz with districts. Lothair [received lands] between the Rhine and Skalda extending from [the North] See, including Cambrai, Hainaut, Lomme and the counties lying on the Meuse to the place where the Seine connects with Rhone. Then along the Rhone to [the Mediterranean] Sea with the counties adjoining on both sides of the river. In addition, due to generosity of his brothers, Charles [the Bald] received the lands of the Atrebaty tribe [around Artois]. Rest of [lands] extending all the way to Spain, was passed under the rule of Charles [the Bald]. Having made sacred oaths, the brothers left.
Look at the line of the boundaries between the properties of the sons of Louis the Pious, established in the Treaty of Verdun (843). What do you think, considering the location of the lands of Emperor Lotar, the treaty had to lead to the collapse of his supremacy over the other Carolingians? List the arguments „for” and „against”, compare them with the answers of your colleagues. Try to find a common version of the answer to this question and a common list of arguments for it.
Key words
empire, Verdun, treaty, patrimonialismpatrimonialism, Reich, successionsuccession,
Glossary
Traktat – międzynarodowa umowa regulująca stosunki polityczne, gospodarcze lub podział jakiegoś terytorium między państwami.
Monarchia – forma rządów oparta na władzy stojącego na czele państwa monarchy (króla, cesarza itp.).
Monarchia patrymonialna – ustrój charakterystyczny dla wczesnego średniowiecza. U jego podstaw leżało przekonanie, że państwo jest prywatną własnością władcy i rozporządza on nim według uznania. Była charakterystyczna dla dynastii Karolingów.
Sukcesja – zasada przekazywania, dziedziczenia władzy monarszej następcy w przypadku śmierci, abdykacji lub w innych okolicznościach.
Rzesza – historyczne określenie państwa niemieckiego. W średniowieczu był to związek wielu, nawet kilkuset (w XIII w.) mniejszych autonomicznych księstw i państewek uznających zwierzchnictwo elekcyjnego króla niemieckiego.
Abdykacja – przedwczesne zrzeczenie się, ustąpienie ze stanowiska, panującego władcy. Może być dobrowolne, np. ze względu na stan zdrowia lub przymusowe, wymuszona przez okoliczności lub otoczenie.
Dynastia – ród, z którego pochodzą panujący władcy, np. królowie. Dynastie uznaje się za panującą jeśli co najmniej jej dwaj przedstawiciele panują bezpośrednio po sobie lub z niewielkimi przerwami.