Extinction of plants
the huge diversity of species makes it possible to survive in changing conditions;
a human directly and indirectly contributed to the extinction of numerous species;
many endeavours are undertaken in order to prevent extinction of further species.
to list and describe main reasons for extinction of plants;
to provide examples of extinct plants and endangered plants.
It is estimated that currently over 9 thousand plant species globally are at risk of extinction. They constitute approx. 3% of all described taxons. The most important causes for plant extinction are as follows: vanishing or transforming of natural habitats, environmental pollution, excessive utilisation of plants by humans, intentional elimination of species (e.g. destroying weeds), extinction mutualistic speciesmutualistic species, displacing by invasive species, and crossbreeding of rare species with common species.
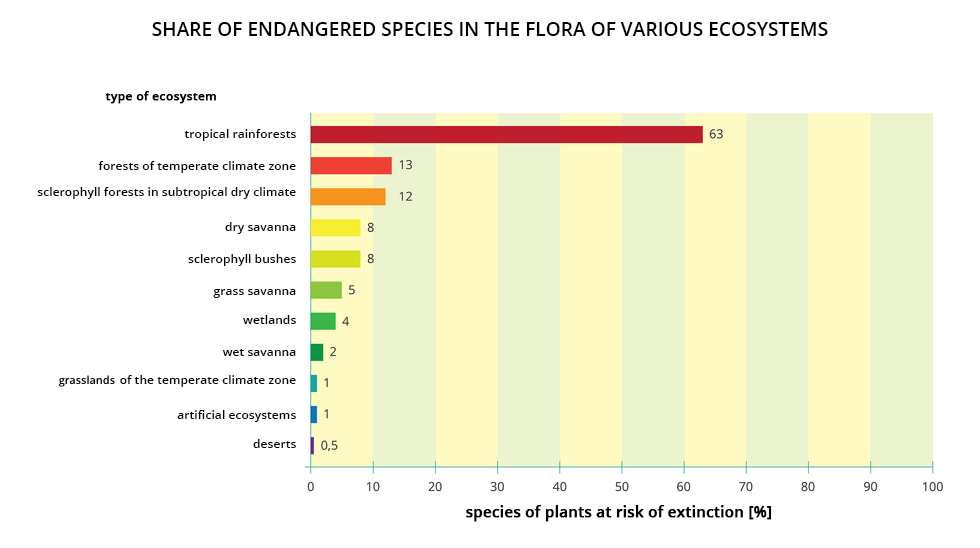
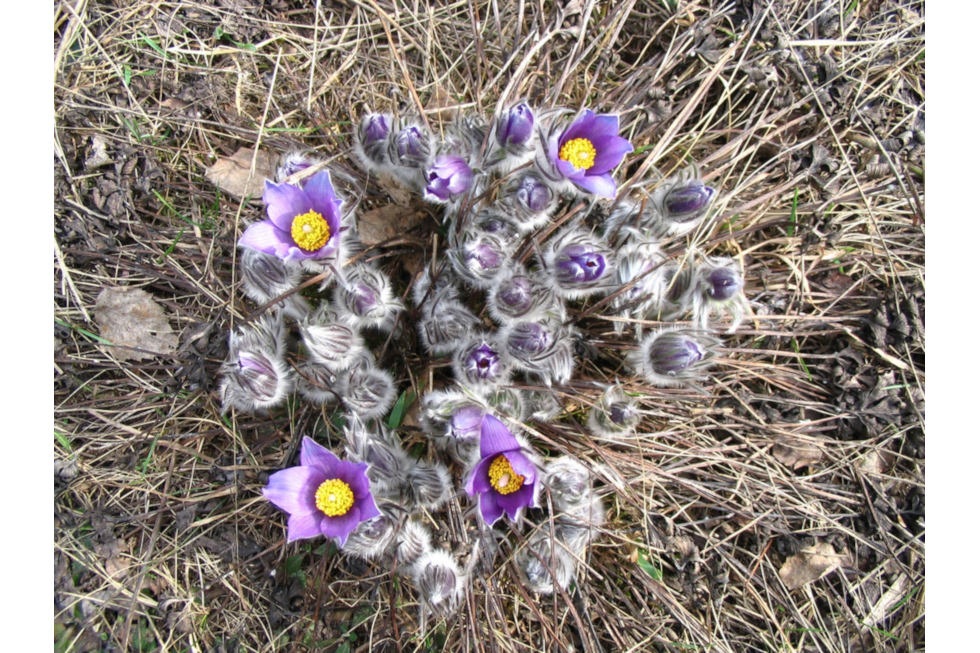
Over last 100–150 years, 44 species of vascular plants became extinct in Poland. Some of them are not irretrievable. Some of them can be found in natural habitats abroad, while the others, such as pasque flower (Pulsatilla vulgaris), are cultivated only in gardens.
It happens sometimes that species considered to be completely extinct are found in natural sites. These species are for example: strawberryleaf cinquefoil (Potentilla sterilis), found in 2008 in two sites in Lower Silesia, Veronica bellidioides, the appearance of which was reported in 2009 in Karkonosze, and Isolepis supina which was found in several sites in Lublin area in 2010.
There are quite a lot of vascular plants in Poland which at risk of becoming extinct: 506 species, which constitutes approx. 20% of the native flora. 74 species are considered to be critically endangered, which means that the size of their populations is extremely small. Usually, they are endemic species and relicts occurring in single sites.
In Muzeum Łąki (grassland museum) in Owczary, Lubusz voivodeship, a garden of weeds was established in 2004. Approximately 20 rare species of plants commonly destroyed in agriculture are cultivated there. Also their seeds are collected. What is the importance of such place for the maintenance of biodiversity?

In the list below, tick all human actions leading to extinction of rare plant species.
- cutting off the forests
- excessive collecting of wild growing plants
- improper farming activity
- introducing invasive species to ecosystems
- applying artificial fertilisers in private gardens
- composting plant residues
Move names of the plants into proper group
Viola tricolor, Common daisy (<em></em>), Northern red oak (<em></em>, Dwarf birch (<em></em><f/oreign>), Wood violet (<em></em>), Bug orchid (<em></em>), Scots pine (<em></em>), <em></em>, <em></em>, Eastern pasqueflower(<em></em>), <em></em>, Eyebright (<em></em>)
| Plants at risk of extinction within the area of Poland | |
|---|---|
| Plants not at risk of extinction within the area of Poland |
Put in the correct order the elements of the cause-and-effect chain, leading to the reduction of a population of plant living in symbiosis with a pollinator.
- reduction in a plant population
- reduction in population of a pollinator
- rarer seeds production by a plant
- pollution of the environment by insecticides
Summary
The main causes of plant extinction are as follows: vanishing of natural habitats, excessive acquiring of plants from the environment by humans, destroying plants considered to be undesirable, crossbreeding of close species, and changes in relationships between species in ecosystems.
Chose a rare plant species and indicate the reasons why it is endangered.
Keywords
extinction, plants, ecosystem
Glossary
mutualizm – jeden ze sposobów współżycia dwóch gatunków przynoszących sobie wzajemne korzyści, niezbędny dla ich istnienia