Metals – application, corrosion and passivation
what properties matter has in its various states;
what are symbols of chemical elements and how to use them;
how to identify and distinguish physical and chemical properties;
according to which criteria mixtures are classified;
what safety rules should be followed in the school chemical laboratory.
to show examples of the use of metals in everyday life;
to explain what the corrosion process is and suggest ways to prevent iron products from rusting;
to explain what the passivation process is and how it differs from the corrosion process.
Properties of metals and their application
Recall what are physical and chemical properties of metals. What do you think, which of these properties is used in many metal applications? Give examples.
Look at the table showing some metal applications and then do the exercise.
Name of the metal | Application |
lithium | addition to light metal alloys, used in lithium cells and batteries |
magnesium | component of compounds used for the production of objects' housing, car body elements, a component of low density alloys |
aluminium | cans, aluminum foil, a component of low density alloys |
copper | electrical wires, alloy components (including brass, bronze) |
argentum | jewellery, for the production of mirrors and Christmas balls |
mercury | filling in dentistry, phone batteries, fluorescent lamps, thermometers |
wolfram | filaments in bulbs, alloys’ components |
What is the corrosion process?
Before you watch the movie „Rust: Prevention and treatment”, formulate a research question and hypotheses. During the screening pay attention to what happens to the nails on various dishes. What does it mean?

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film prezentuje instrukcję przeprowadzenia doświadczenie, w którym w czterech próbówkach umieszczono metalowe gwoździe. Do każdej z próbówek dodano inne substancje, aby sprawdzić, jak zareaguje metal. Na filmie widoczne są instrukcje tekstowe w języku angielskim. Place an iron nail in four test tubes. Fill one with regular tap water until the nail is submerged. Fill another with regular tap water and add half a spoonful of sodium chloride – regular table salt. Shake from side to side to ensure that sodium chloride fully dissolves. Fill the third test tube with recently boiled water and add a thin layer of oil. When water is being boiled, any dissolved oxygen is removed. The layer of oil prevents more oxygen from dissolving. In the last test tube add a spoonful of calcium chloride. Calcium chloride removes any moisture. In the first tube the nail is exsposed to oxygen and moisture. In the second test tube the nail is exposed to oxygen, moisture and salt. In the third test tube the nail is exposed to water. In the fourth test tube the nail is exposed to oxygen. All four test tubes are covered with rubber bung. After a couple of days you will find that the nails in the first and second test tubes have rusted. The nail in the second test tube has rusted more than the nail in the first test tube and the rust has likely flaked off. The nails in the thrid and fourth test tubes have not rusted.
Consider these questions before discussing them with the teacher:
Do you know the experiment showing the phenomenon of corrosion? How can you experimentally show the course of corrosion? Do you know what the rustrust is?
What methods of corrosion prevention do you know? How do you protect metal parts from corrosion?
Where can you observe the corrosion process in your neighbourhood?
Do you think all metals undergo corrosion?
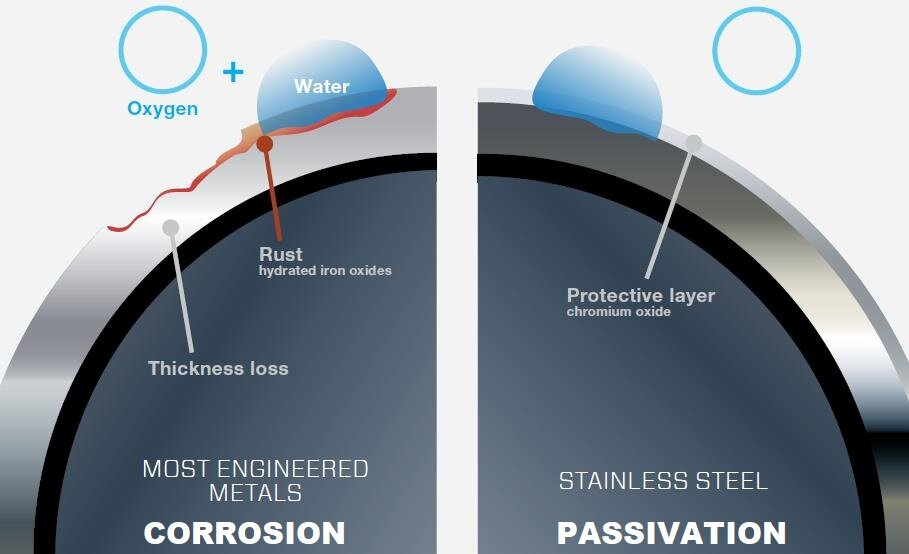
CorrosionCorrosion is a process of decaying materials caused by the action of air, water and other environmental factors. Destruction begins on the surface of the metal and progresses deeply, changing its properties. The most exposed to corrosion are seams with other metal, e.g. welding or soldering seams. Corrosion of iron and steel is called rusting. Objects made of copper, such as the roofs of historic buildings, over time are covered with a greenish coating called patinapatina, which protects copper from further decaying. This process is called passivationpassivation.

Passivation is therefore a process in which a certain chemical active substance in a given environment creates a protective coating on its surface – a passive layer. The coating is tight and resistant to further reactions with the environment – thus protecting the substance from decaying.
Passivation can be:
natural, resulting from properties of the metals in particular environment;
artificial, triggered by a deliberate reaction, e.g. the formation of a passive layer consisting of, for example, chromium oxides to protect steel alloys (a passive layer consisting of oxides, mainly chromium oxides).
The passivation phenomenon is used, for example, in the transport of concentrated nitric acid in aluminium cisterns. The aluminium reacts with the acid, forming a protective coating on the walls of the tanker by passivation. It prevents further chemical reactions and does not affect the physical and chemical properties of the acid.
Mark the factors that promote metal corrosion.
- moisture, water
- sunlight
- painted or varnished coating
- frequent temperature and pressure changes
- tension
- presence of impurities, solutions of some substances
Match the corrosion protection with an item.
enamelling, chroming, galvanizing, painting with oil paints
| Bathroom battery | |
|---|---|
| Steel pots | |
| Balcony railings | |
| Car bodies |
Summary
Metals by the definition are characterized by: metallic gloss, thermal conductivity, electric conductivity, tenacity, ductility.
Metals in a room temperature also have a constant state of matter (except mercury) and silvery‑white or silvery‑grey colour (with the exception of gold, copper).
All metals, except noble ones (e.g. gold, silver, platinum), are subject of corrosion.
Corrosion is the process of decomposition of materials caused by the action of air, water and other environmental factors.
Passivation is the process of coating formation, for example on copper, which protects the metal against further destruction.
Passivation concerns mainly metals and can be a natural process or caused intentionally by man.
Keywords
Corrosion, passivation, patina, properties of metals
Glossary
korozja – niszczenie materiałów (głównie żelaza) spowodowane wpływem czynników środowiska (wywołane jednoczesnym działaniem tlenu zawartego w powietrzu oraz wody, a nawet wilgoci); korozję przyspiesza obecność soli kamiennej
metale – substancje o metalicznym połysku, bardzo dobrze przewodzą ciepło i prąd elektryczny
rdza – krucha, żółtobrunatna warstwa pokrywająca wyroby z żelaza i stali, powstaje w procesie ich korozji (rdzewienia)
patyna – cienka, zielonkawa, szczelnie przylegająca warstwa związków chemicznych powstająca w wyniku działania czynników atmosferycznych na miedź
pasywacja – proces powstania na powierzchni metalu cienkiej, szczelnie przylegającej warstewki związku (*np. glin jest pokryty tlenkiem glinu), która chroni metal przed korozją