Protists
protists form one of the five kingdoms of organisms;
very diverse organisms were included in protists.
to describe autotrophic and heterotrophic protista;
to compare the structure and vital activities of slipper and euglena cells;
to show the positive and negative significance of protists for environment and human.
ProtistsProtists is the name of organisms that are neither bacteria nor fungi, nor plants or animals. So what are they and what distinguishes them? Protists are an artificially created group of weakly related organisms. There is evidence that protists lived on Earth 600 million years ago. Some probably gave rise to animals and fungi.
Protists and their lifestyle
The classification of protists causes biologists a lot of trouble. It is difficult to determine their characteristics, because they are very diverse and weakly related organisms. Most of them are microscopic single‑celled organisms, like Paramecium or diatoms, some of them, form clusters known as colonies. Among the protists there are also multicellular organisms, the length of which exceeds several dozen metres, such as a Laminaria.
Most of the protists live in water. Many of them are autotrophic algae inhabiting the oceans, ponds and lakes. These algae can also be found on land, but only where there is a lot of moisture. Their cells resemble plant cells, which is why they are called plant protists.
Heterotrophic protists – protozoa live in coastal waters, in moist soil or on fallen leaves. Some are predators hunting for microscopic prey, others prey on the bottom of tanks in dead debris forming silt. Still others parasite in organisms larger than themselves. The life style and body structure of protozoa caused that nowadays they are called animal protists.
A unique protist is a single‑celled euglena that changes its diet depending on food availability and lighting conditions. It can be autotrophic or heterotrophic.
Paramecium
Paramecium is an agile protozoan that lives in puddles and shallow ponds. Its body consists of just one cell that fulfills all life activities that can be observed in multicellular organisms. Paramecium moves with the help of wavy cilia, densely covering the cell membrane. It feeds on plant debris and bacteria, which it absorbs by means of a cell membrane cavity. At the bottom of the cavity, the food particles are surrounded by a cell membrane that forms vesicles called vacuoles. Food vacuoles first digest food found in them, and then, in a specific place of the body, connect to the cell membrane, remove undigested debris outside the cell. Paramecium breathes, collecting oxygen with the entire surface of its body. In its cytoplasm mitochondria are present, in which energy is released from nutrients. To regulate the amount of water and excretion of unnecessary and toxic substances, it is used by pulsating vacuoles, which relax and contract, expelling the fluid outside the body. Paramecium has two cell nuclei. The macronucleus controls life processes and the micronucleus participates in reproduction. Paramecium reproduces mainly by cell division.
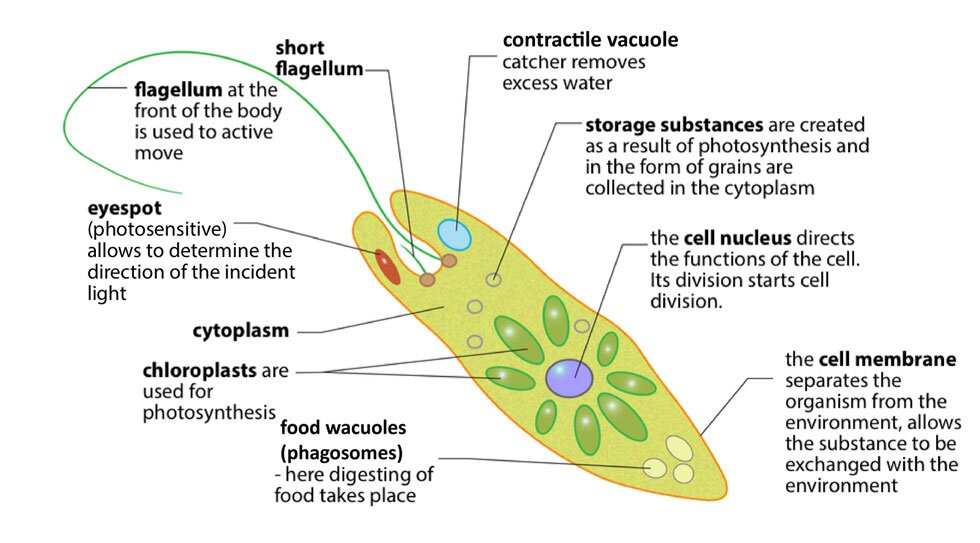
Euglena
Euglena is an amazing single‑celled organism with a dual lifestyle. It is found in ponds, puddles and lakes. Thanks to the fact that it has chloroplasts, it can be autotrophic. Most often, however, it is a predator hunting for bacteria or a saprobiont that feeds on plant debris. It digests the collected food in the same way as Paramecium, in vacuoles that are formed in the hollow of the body. Thanks to the photoreceptor, it reacts to light, and when it lacks food, it moves to illuminated places with a long flagella. The flexible cell coat allows it to change the shape while overcoming obstacles. Unnecessary metabolic products and excess water are released from the cell via pulsating vacuola vacuums. It reproduces through the longitudinal division of the cell.
Other protozoa
Single‑cell diatoms can occur individually or form colonies. Their cells look like carved boxes. The rigid cell wall, containing a lot of silica, forms a shell composed of a lid and a bottom. The appearance of the cell wall is a characteristic feature of the species. Diatoms are autotrophic, they live in fresh and salt waters. They float in water or settle at the bottom of water reservoirs, covering the stones with golden‑brown tarnum.
Protozoa have the ability to actively move. Some of them move with the help of long flagella (euglena), others use thousands of short and thickly distributed cilia (Paramecium) for movement. Still others crawl to form cytoplasmic protrusions of undefined shape. These include amoebas, for example. They are freshwater protozoa taking different shapes. They move with the use of pseudopodia, which also serve to gain food. They feed on smaller microorganisms, e.g. bacteria.
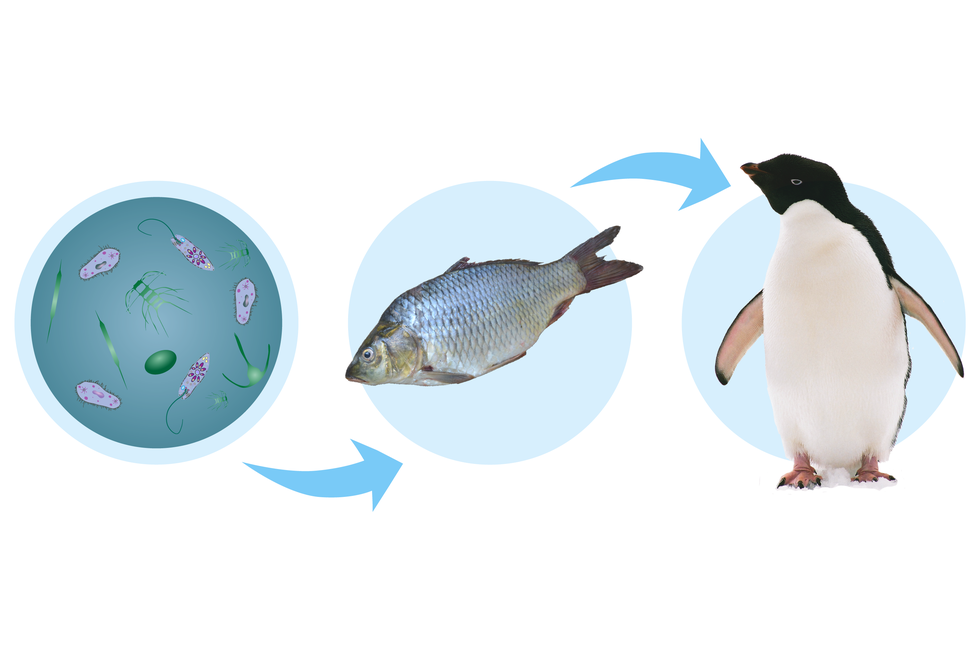
The importance of protists
Single‑celled plant and animal protists are a component of planktonplankton that floats on the surface of the water. Plankton, along with algae inhabiting water reservoirs, provides food for fish and other animals living in this environment. Autotrophic protists enrich water with oxygen, producing it during photosynthesis.
Heterotrophic protists together with bacteria and fungi break down the remains of plants and animals and contribute to the circulation of matter on Earth. Some species of protists inhabit the gut of termites and herbivorous animals. They help them digest food containing hard to decompose cellulose.
Among the parasitic single‑cell protists there are species that cause human diseases. Ameba causes a dangerous disease called dysentery. Trichomonas vaginalis is the cause of sexually transmitted disease - trichomoniasis. Toxoplasma causes toxoplasmosis - a disease particularly dangerous to the developing fetus. One can get infected from cats and other domestic animals. Malaria transmitted by mosquitoes of the Anopheles maculipennis causes malaria, a disease often occurring among people living in the tropic zone. Trypanosoma brucei transmitted by the tse‑tse fly is the cause of African coma.
Organize the elements of organisms’ characteristics starting from the top.
- External structure of organisms
- Life activities
- Representatives of this group and their short description
- Life environment of organisms
- Meaning of organisms in the environment and human life
Put fragments of the characteristics of the euglena in appropriate boxes.
Euglena occurs in sweet waters: ponds, puddles, lakes., Euglena is counted among protists., It is a single-cell organism. The cell has a spindle-like shape and has 2 flagella to move. It does not have a cell wall but only a thick cell membrane., In the light it is a producer of oxygen and organic matter, in the dark it absorbs dead organic matter from water, causing purification of water., Euglena feeds itself in the light by photosynthesis and is predatory in the dark. It distinguishes the light from the dark with the help of photoreceptor. In search of food, it moves with the help of flagella. It respires aerobically and takes oxygen with the entire surface of its body. It reproduces by cell division.
| Life environment of an euglena | |
|---|---|
| Systematic affiliation | |
| External structure of euglena | |
| Euglena's life activities | |
| The meaning of euglena in nature |
Organize the feeding stages of the paramecium.
- feeding
- digestion in the food vacuole (phagosome)
- penetration of nutrients from the food vacuole (phagosome) to the cytoplasm
- excretion of undigested remains
Organize stages of nutrition of the
- creating vesicle (food vacuole)
- digestion in the food vacuole (phagosome) with the participation of digestive enzymes
- absorption of digested food into the cytoplasm
- joining the food vacuole with a cell membrane and removing undigested debris outside the cell
- nutritional molecules absorbed by the cavity of the cell membrane
Summary
Protists are a diverse group of nuclear organisms with single‑cell, colony or multicellular structure.
Autotrophic protista are named algae.
The cells of heterotrophic protists show similarity to the cells of animals.
Euglena is a unique protist which, depending on the access to light and food resources, can be an autotrophic or heterotrophic organism.
Protists play an important role in nature as producers, saprobionts and parasites.
Single‑cell protists played an important role in the processes of building the earth's crust.
Keywords
protista, slipper, euglena, plankton
Glossary
plankton – niewielkie organizmy biernie unoszone w powierzchniowych warstwach wody.
protisty – niejednorodna grupa organizmów jądrowych, których nie można zaliczyć ani do roślin, ani do zwierząt, ani do grzybów, ani do bakterii; są wśród nich organizmy samożywne i cudzożywne.
wodniczka pokarmowa (fagosom) – błoniasty pęcherzyk w cytoplazmie komórek protistów, w którym zachodzi trawienie pokarmów.
wodniczka tętniąca – błoniasty pęcherzyk w cytoplazmie prostistów słodkowodnych, za pomocą którego wydalane są produkty przemiany materii i nadmiar wody.