Proteins - structure
how amino acids are built;
that amino acids can bind together to form peptides.
you name the binding found in the structure of proteins;
you will provide the elemental composition of the peptide bond;
you will draw a structural formula for the peptide bond;
discuss the construction of proteins.
Protein structure
Proteins are macromolecular compounds constructed from amino acid residues. The variety of proteins is huge, although protein amino acids only number around twenty. It is important which amino acids are included in the protein and how they are combined with each other.
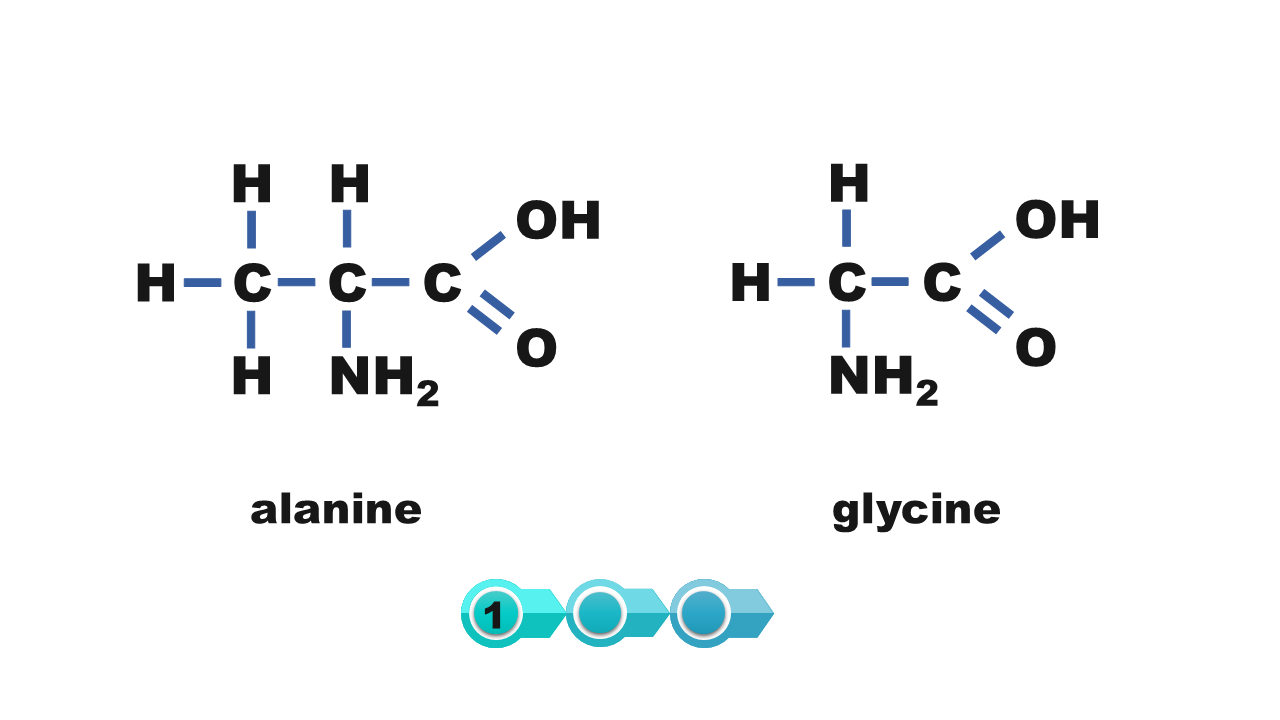
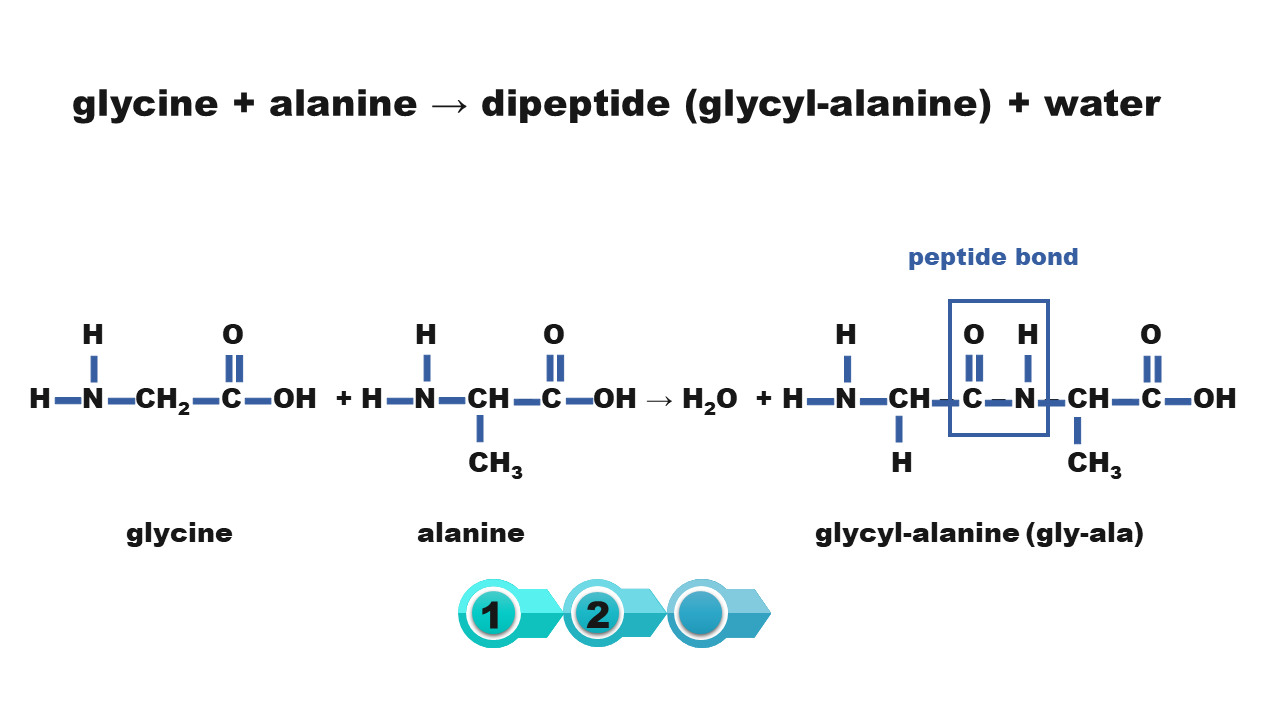
Amino acids can be joined by a peptide bondpeptide bond. Remind yourself of how to combine two molecules of the amino acid into the simplest construction – glycine.
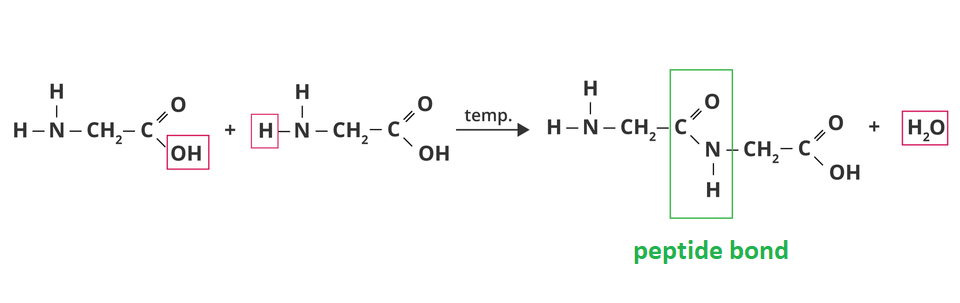
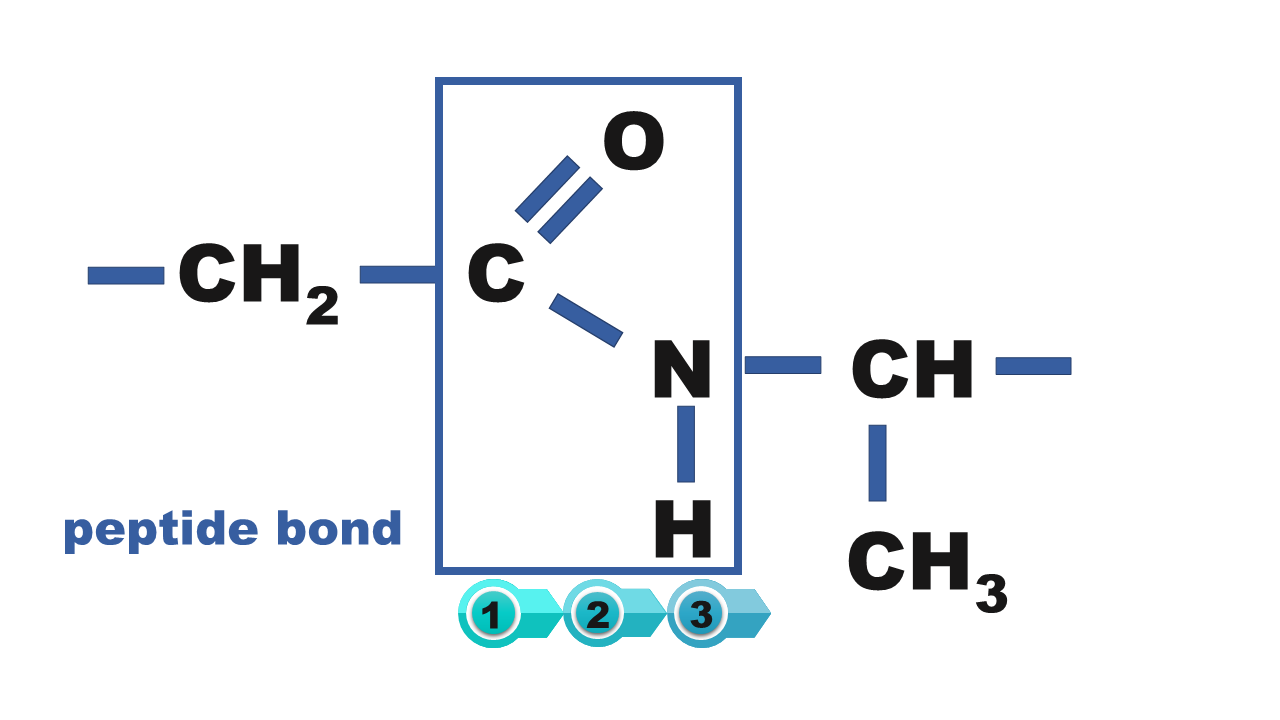
1. peptide bond
Watch the presentation „The formation of a dipeptide in the reaction of glycine with alanine”
Proteins are conventionally called compounds whose chain contains more than 100 amino acid residues, and shorter chain compounds are included in the polypeptides.
The protein chain can be described by the general formula:
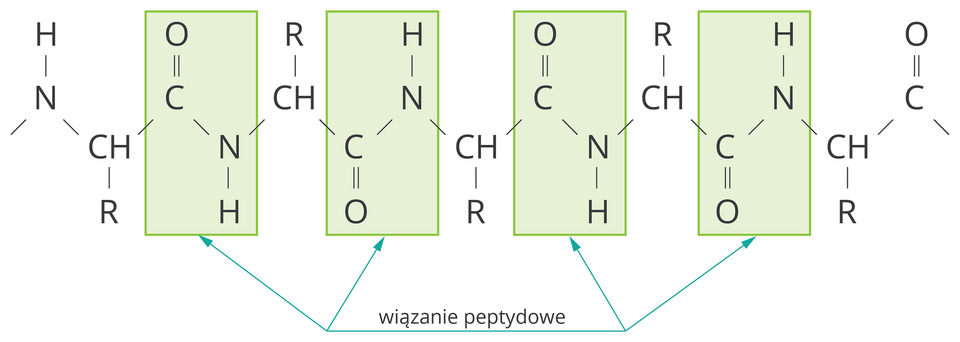
1. peptide bonds
Protein chains may have a different spatial structure, e.g. they twist in spirals or ribbons.
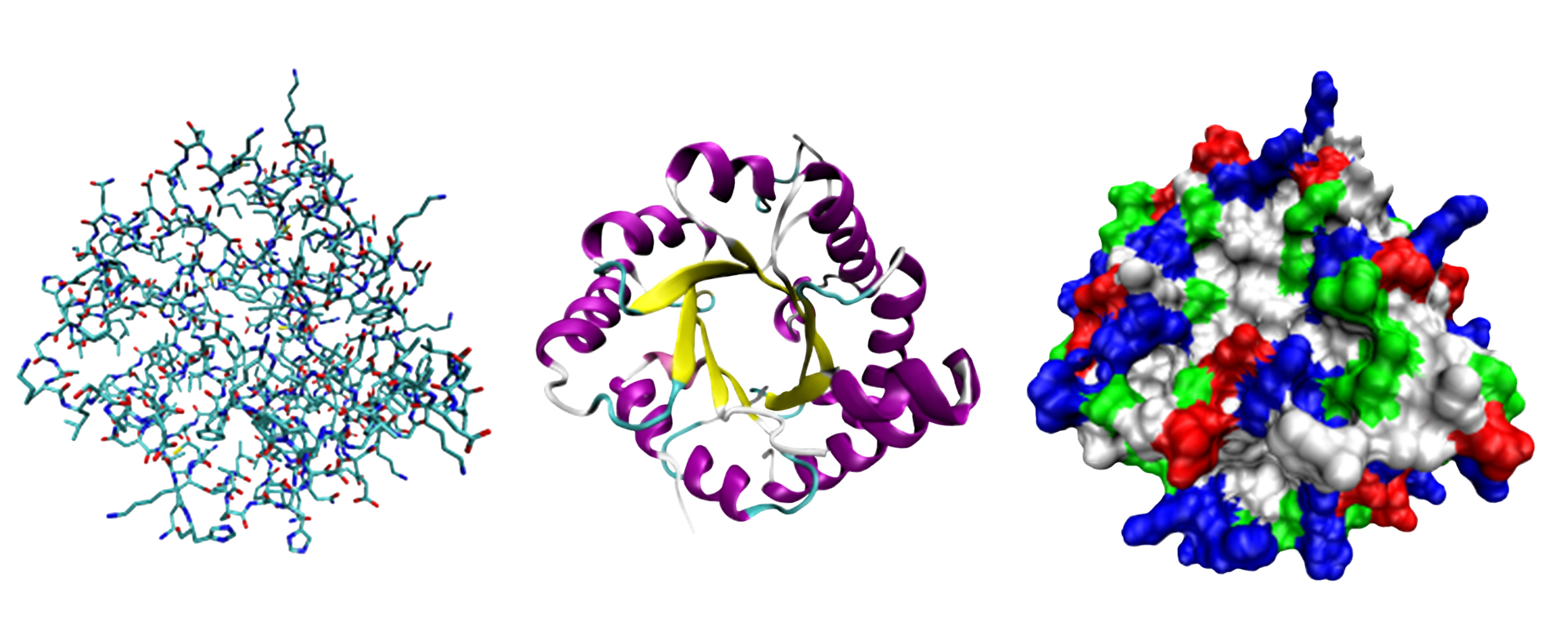
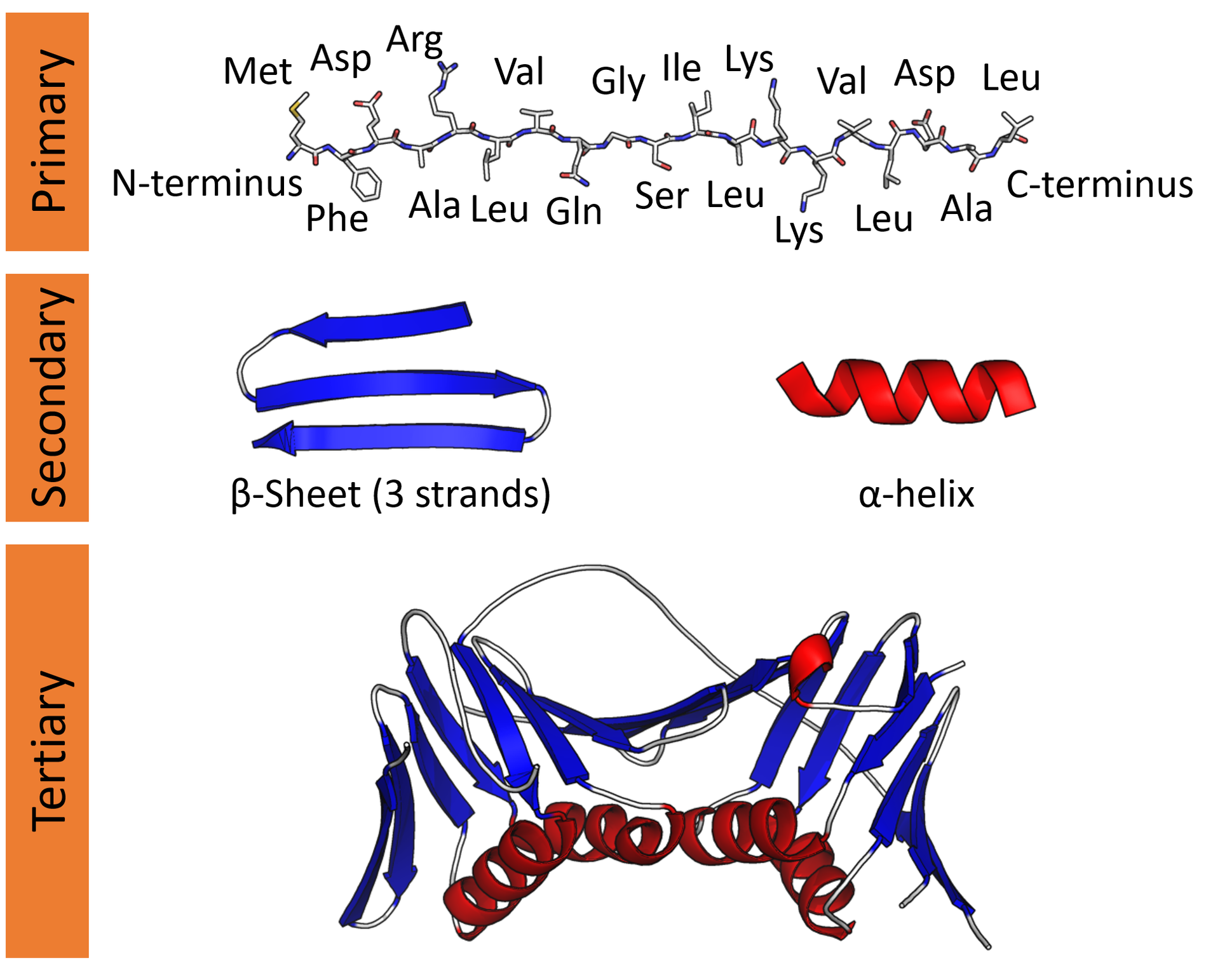
Biochemists often refer to distinct aspects of a protein's structure:
Primary structure: the amino acid sequence. A protein is a polyamide.
Secondary structure: regularly repeating local structures stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The most common examples are the α‑helix, β‑sheet and turns. Because secondary structures are local, many regions of different secondary structure can be present in the same protein molecule.
Tertiary structure: the overall shape of a single protein molecule; the spatial relationship of the secondary structures to one another. Tertiary structure is generally stabilized by nonlocal interactions, most commonly the formation of a hydrophobic core, but also through salt bridges, hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds, and even posttranslational modifications. The tertiary structure is what controls the basic function of the protein.
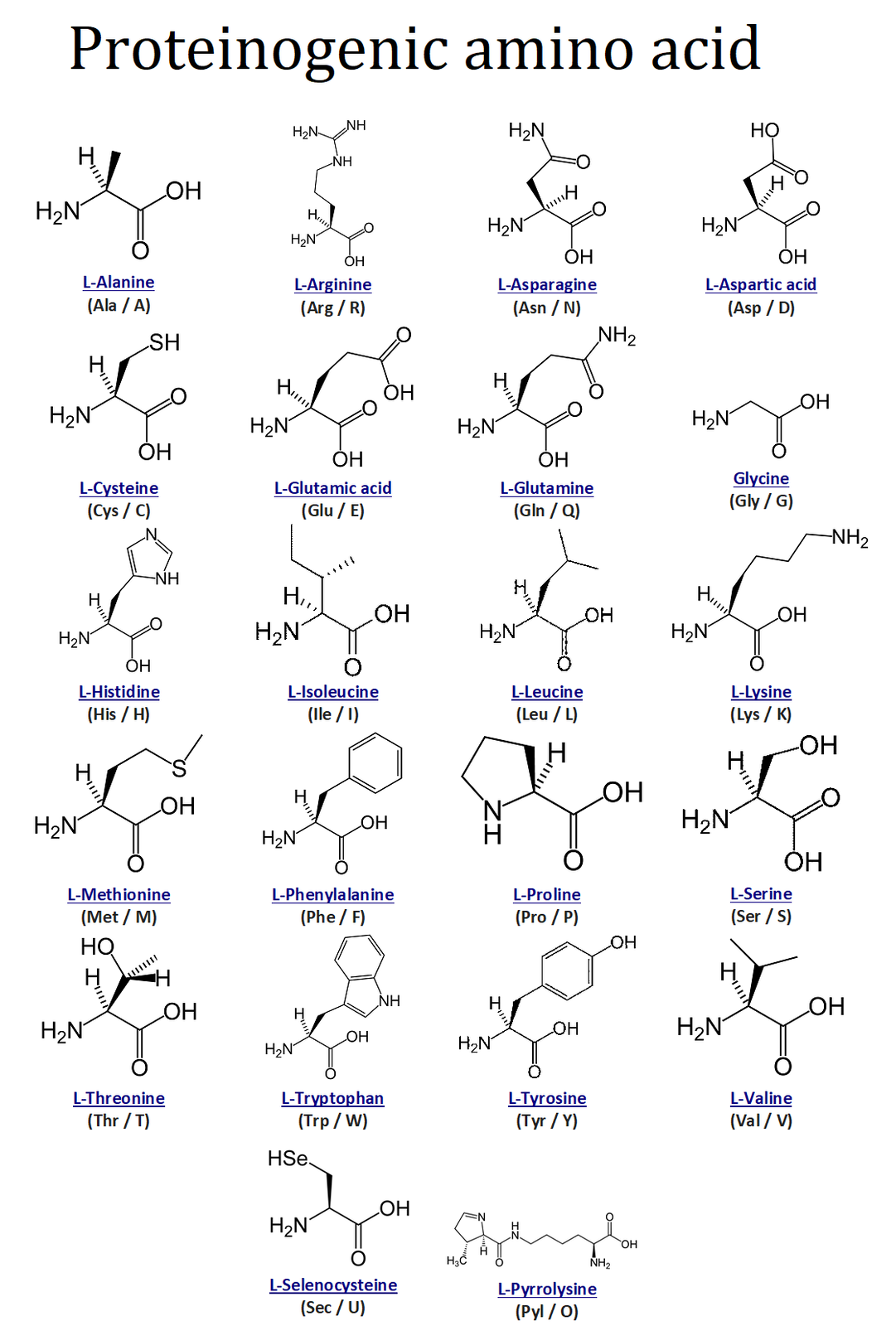
Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation. The word „proteinogenic” means „protein creating”. Throughout known life, there are 22 genetically encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids, 20 in the standard genetic code and an additional 2 that can be incorporated by special translation mechanisms.
Select the statements that are true.
- Linus Pauling described the structure of proteins and received the Nobel Prize
- The element with the atomic number 12 that is part of the protein structure is oxygen
- Polypeptides are protein compounds with chains of less than 100 amino acid residues
- An element that forms a double bond in the peptide bond with carbon is oxygen
- The binding occurring in the protein chain, made of carbon, hydrogen, sodium and oxygen, is a peptide bond
- A protein composed of two molecules of amino acids is a dipeptide
- The amino acid with a molecular weight of 72u is glycine
Create a multiple-choice test based on today's lesson. Then exchange your questions with a friend or classmate.
Question: ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
Summary
The molecules of all proteins are mainly composed of atoms of four elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. Some of the proteins may include sulfur atoms, phosphorus and other elements.
The basic elements building proteins are amino acids.
Proteins are macromolecular chemical compounds, made up of amino acid residues joined by peptide bonds.
Proteins are the main building blocks of organisms. They perform functions: building, transport, regulating and others.
The source of animal protein include eggs, dairy, meat, fish, and vegetable – cereals and legumes, such as beans, soy and lentils.
Keywords
protein, protein structure, elemental composition of proteins
Glossary
białka – wielkocząsteczkowe związki zbudowane z reszt aminokwasowych połączonych wiązaniami peptydowymi; w skład białek wchodzą głównie takie pierwiastki, jak: węgiel, wodór, tlen i azot
wiązanie peptydowe – powstaje w wyniku połączenia się aminokwasów; tworzą je grupy karboksylowa i aminowa łączących się cząsteczek aminokwasów