The Paris Peace Conference and the Treaty of Versailles
to list main decision makers and decisions of the Treaty of Versailles;
to characterize post‑war arrangements for the allies states of the former Triple Alliance states;
to indicate features of the new world order.
The Versailles Peace Conference began on 18 January 1919 in Paris. 27 countries took part. The Versailles Treaty signed on 28 June 1919 had introduced a new world order. By virtue of that Treaty, Germany lost its colonies as well as Alsace, Lorraine, Greater Poland and Pomerania. The Rhineland was demilitarizeddemilitarized and cities of Gdańsk and Klaipėda were converted into free cities. Germany was charged with high war reparations. Separate peace treaties were signed with Austria, Hungary as well as Bulgaria and Turkey. New countries like Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Czechoslovakia, Finland, State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, Ireland, Iceland, Austria and Hungary emerged on the map. The last treaty regulating the contentious and controversial issues was the meeting in Washington. It was devoted primarily to the regulation of navy armaments and Far East issues.
Drag answers into appropriate places.
first, third, fourth, second, fourth, fifth, second, first, third
Politicians arrive to sessions, among them, is Ignacy Paderewski. The Polish Prime Minister exits the car in the ............ minute of the movie.
The Hall of Mirrors, full of politicians, diplomats and observers can be seen for the first time in the ............ minute of the movie.
David Lloyd George, Vittorio Emanuele Orlando, Georges Clemenceau and Thomas Woodrow Wilson join the people gathered in the Versailles' garden. We can see them together from the end of the ............ minute of the movie. This frame has gone down in history.
In the fifth minute, you can see President Woodrow Wilson leaving the Palace of Versailles after the end of the session. He is surrounded by an enthusiastic crowd.
Remember with whom Germany has concluded separatist peace agreements (during the war).
- Serbia
- France
- Romania
- Hungary
- Poland
- Russia
- Ukraine
- Lithuania
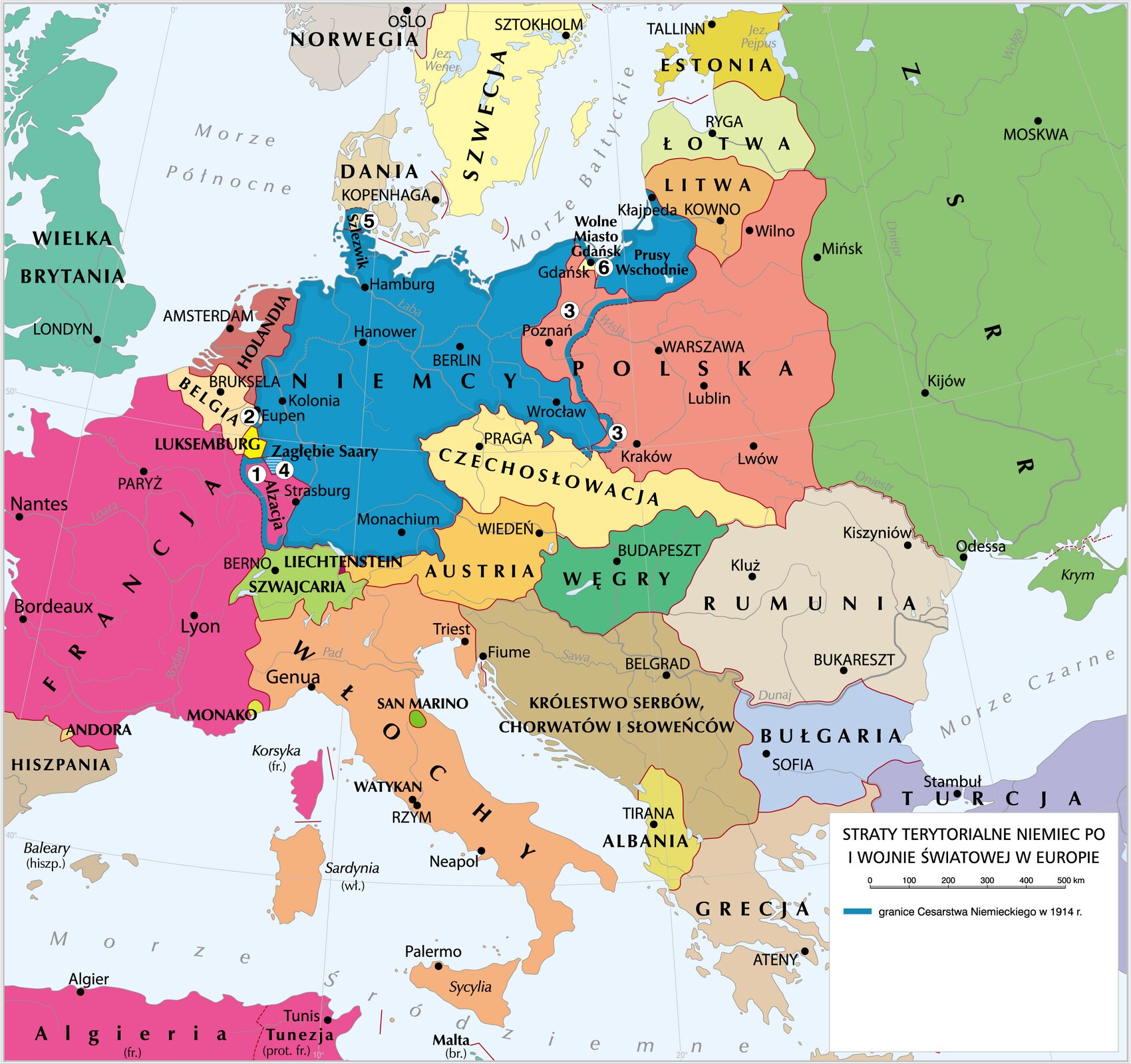
Match the territories to the numbers from the map.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, Free City of Cracow under the protection of the League of Nations, Netherlands, Czechoslovakia
| Number on the map | Territory lost to |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 |

Keywords
dictate, demilitarization, demobilization, reparations, the Versailles Treaty
Glossary
dyktat – narzucony nakaz, rozkaz
demilitaryzacja – zmniejszenie potencjału wojskowego jakiegos państwa na określonym terytorium mocą umowy międzynarodowej
demobilizacja – ogół czynności związany z przejściem danego państwa w stan pokoju
reparacje wojenne – inaczej odszkodowania wojenne, wynik roszczeń wysuwanych przez jedno państwo względem drugiego.
Sala Lustrzana – największa sala pałącu królewskiego w Wersalu; miejsce ważnych ustaleń i deklaracji, m.in. o zjednoczenua Niemiec w 1871 czy podpisania Traktatu wersalskiego w 1919 r. decydent – osoba uprawniona do podejmowania decyzji.
