Natural fibres
what are chemical structures of proteins and complex sugars, e.g. cellulose?
what is the structure of polymers and you can name examples of them?
classify fibres into natural (protein and cellulose), artificial and synthetic, as well as name examples of these;
identify the type of fibres and prepare experiments to identify protein and cellulose, artificial and synthetic fibres;
describe the application of natural, artificial and synthetic fibres, taking into account their advantages and disadvantages.
Natural fibres
Among the natural fibresnatural fibres, there are fibres of vegetable, animal and mineral origin.
Vegetable fibres are obtained from various parts of the plant – seeds (cotton), stems (flax, hemp, jute, ramie), leaves (sisal) or fruit (coconut fibres).
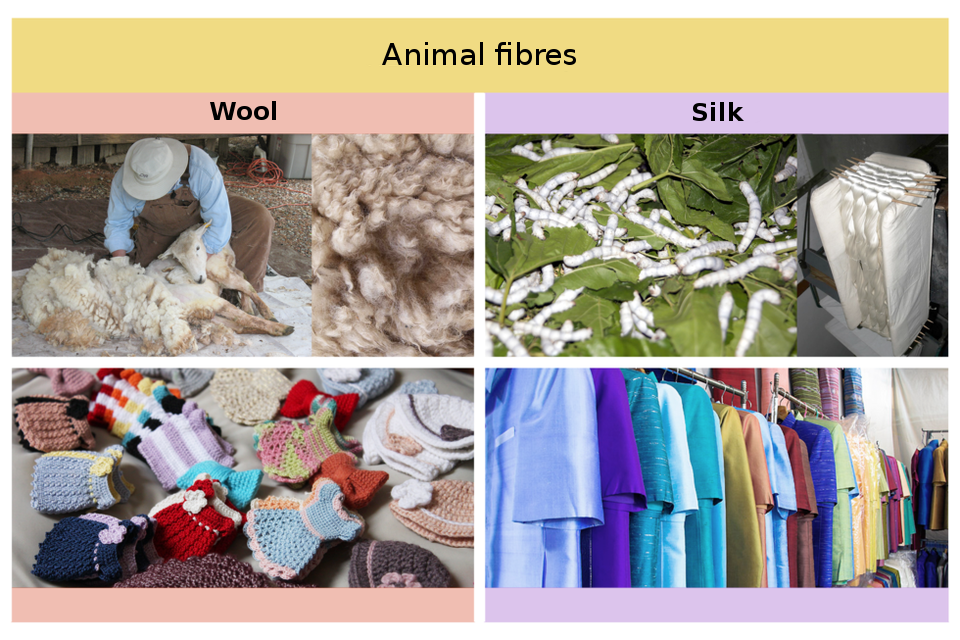
Animal fibres are obtained from, e.g. hair of mammals (wool, bristle), as well as from animal secretions (silk).
Mineral fibres are fibrous inorganic substances (asbestos) or artificial (asbestos substitutes, glass fibres, rockwool or slag wool, ceramic fibres).
Most commonly used – especially for the production of clothing – natural fibres are cotton, wool, linen and silk. Therefore, it is worth to learn more about these fibres.
Consider which organic compounds in plant and animal cells can form fibres. Write down the answer here or in the notebook.
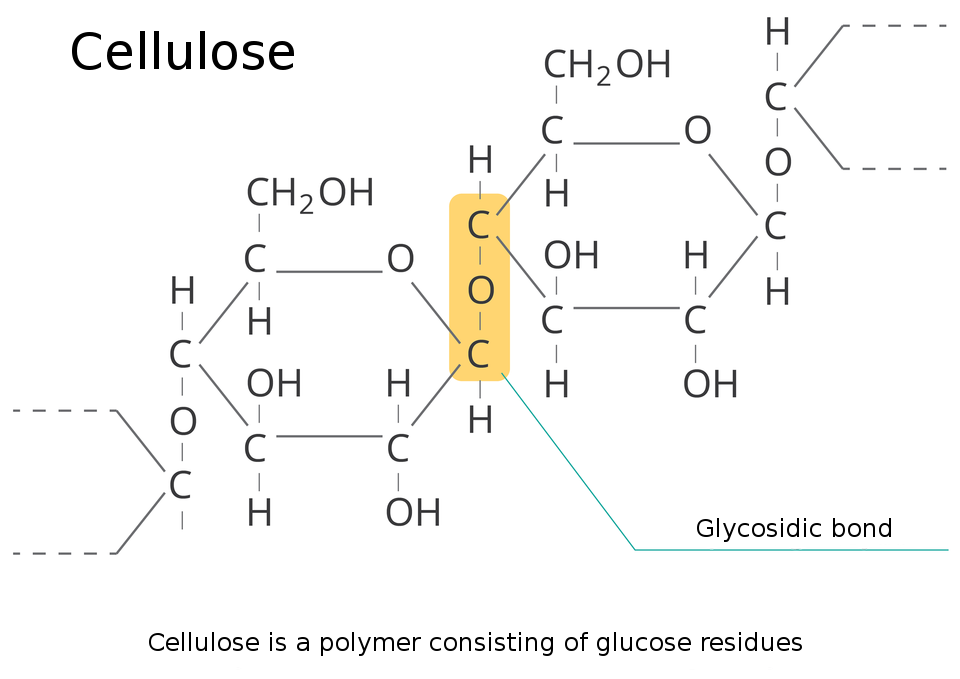
All fibres are made of macromolecules. Natural fibres are made of biopolymers, i.e. cellulose, proteins, and artificial fibresartificial fibres made of natural macromolecules, modified as a result of chemical processes.
Natural fibres occur in nature in a ready‑for‑processing state. These can be supplied by plants, animals and occur in the form of minerals. All vegetable fibres are made of cellulose. In addition to it, vegetable fibres contain small quantities of lignin (a polymer where monomer is alcohol), as well as plant‑based adhesives (pectin).
Among the natural fibres, fibres of vegetable and animal origin can be distinguished. Look at the illustrations presenting both types. Do you recognise them from everyday use? What properties do these have?


Vegetable fibres
Cotton is a fibre obtained from cotton bushes. White fibres surround the plant's seeds, creating numerous white tufts resembling the appearance of cotton wool on the bushes. The mature fibre was once harvested by hand, and today it is harvested mainly by machine.
The properties of cotton fabrics – softness, airy and concurrent durability – create many possibilities for their use. These are easy to care for – can be machine washed, can undergo spinning and be wet pressed at high temperature.
Cotton is used for the production of clothing, bedding fabrics, tablecloths, dressings, fishing nets, and coffee filters.
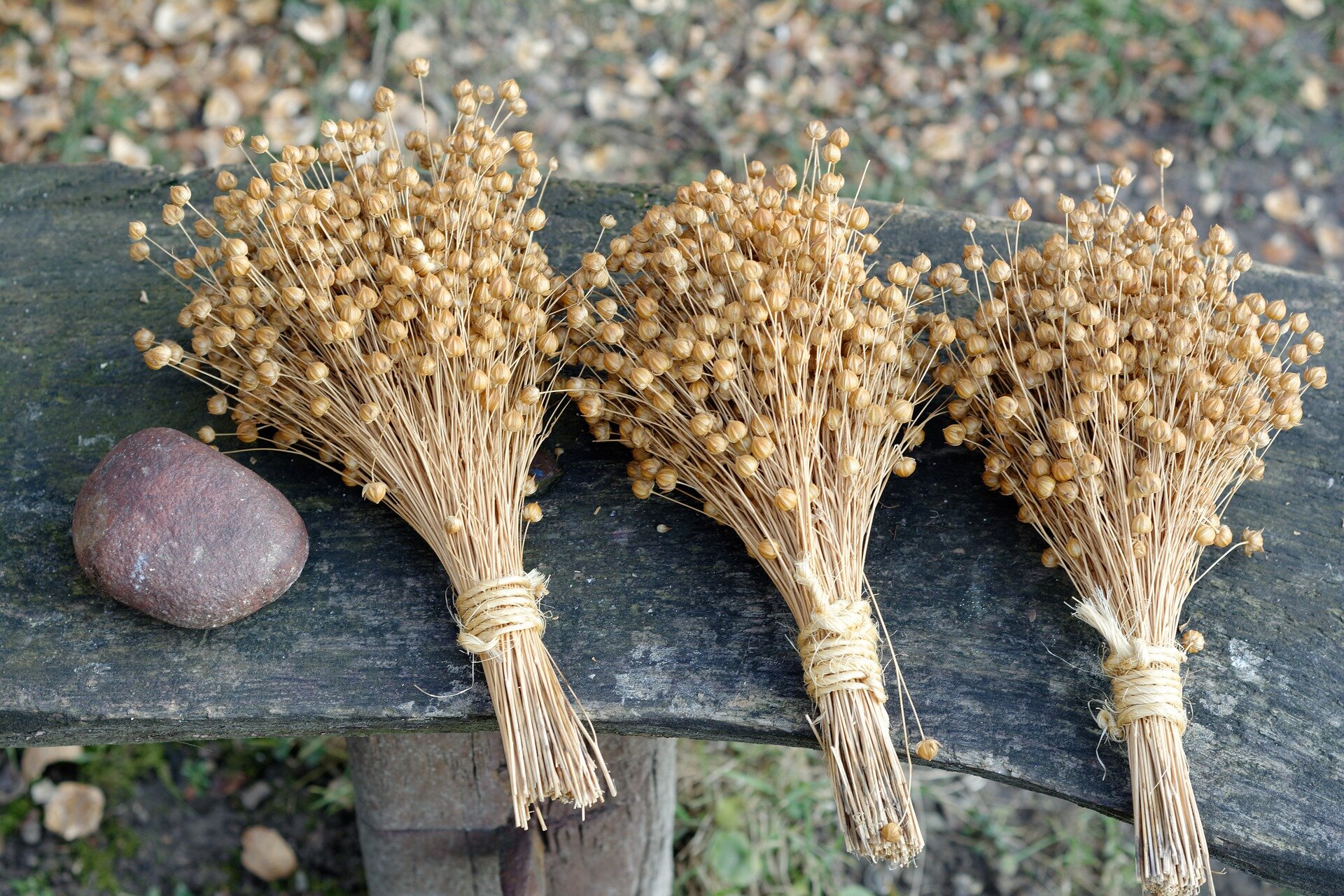
Another plant that provides natural fibres is flax. Flax fibres are obtained from the stems of this plant. It is a long and complicated process, it involves many stages. Flax was the most popular raw material for clothing production until cotton was mechanically processed. Fabrics made of flax are absorbent and „can breathe”. These provide special comfort on hot days. These are also durable and resistant to dirt. Their disadvantage is the susceptibility to creases, which are difficult to iron out (a high ironing temperature is required, marked as level 3. – the highest). Linen clothing and other products made of flax fibre are now treated as exclusive and elegant.
Sisal are hard and very durable fibres obtained from a special grade of agave. These are used to make twines (ropes, cords), mats and sacks.
Animal fibres
Initially, the man used only natural raw materials for making clothes.
In the Stone Age, next to the primitive clothing from the skin, fabrics made of vegetable fibres were also used. The Egyptians wore linen garments, Indians – cotton ones. Nowadays, fibres with various properties and applications are synthesized. However, some features of natural fibres are still very difficult or even impossible to achieve in technological processes.
At first, devices used to spin the thread were very simple, and over time more and more complicated. Over time, manual looms began to be replaced with machines and that's how the modern textile industry raised.

Wool is animal hair. It is obtained mainly from sheep's pelage and from other graminivorous animals – goats, llamas and camels. The most popular is sheep's wool, produced in many types. The highest quality wool is obtained from Merino sheep. It has such advantages appreciated by the users as extremely thin fibres, softness and fluffiness. Excellent thermoregulation properties characterise wool products – woollen clothing provides warmth and quickly absorbs and drains moisture. In addition, the wool is not susceptible to dirt and does not absorb odours. Warmer clothing, carpets, blankets, pillows, quilts are made of wool. Today, wool is mainly used in blends with other fibres and has lost its popularity in favour of synthetic fibres.
Natural silk is a fibre produced by the larva of domestic silk moth. The most popular is Bombyx mori. The caterpillars spin two threads of silk, forming a cocoon in which they pupate. These two fibres are glued together; only the separation and unravelling of the cocoon and the appropriate treatment in hot water allow obtaining strands with a length of even 1 - 3 km. Silk fibres are the most durable among natural fibres. The silk fabric has a characteristic, recognizable from the first touch structure. It is light and airy, it fits perfectly. It is considered the noblest of fabrics. Due to the useful properties and the cost of production, silk is a very expensive fibre. Silk fabrics require gentle treatment – hand washing is recommended at temperatures up to 30°C and ironing at temperatures below 150°C (indicated as level 1).
Mineral fibres
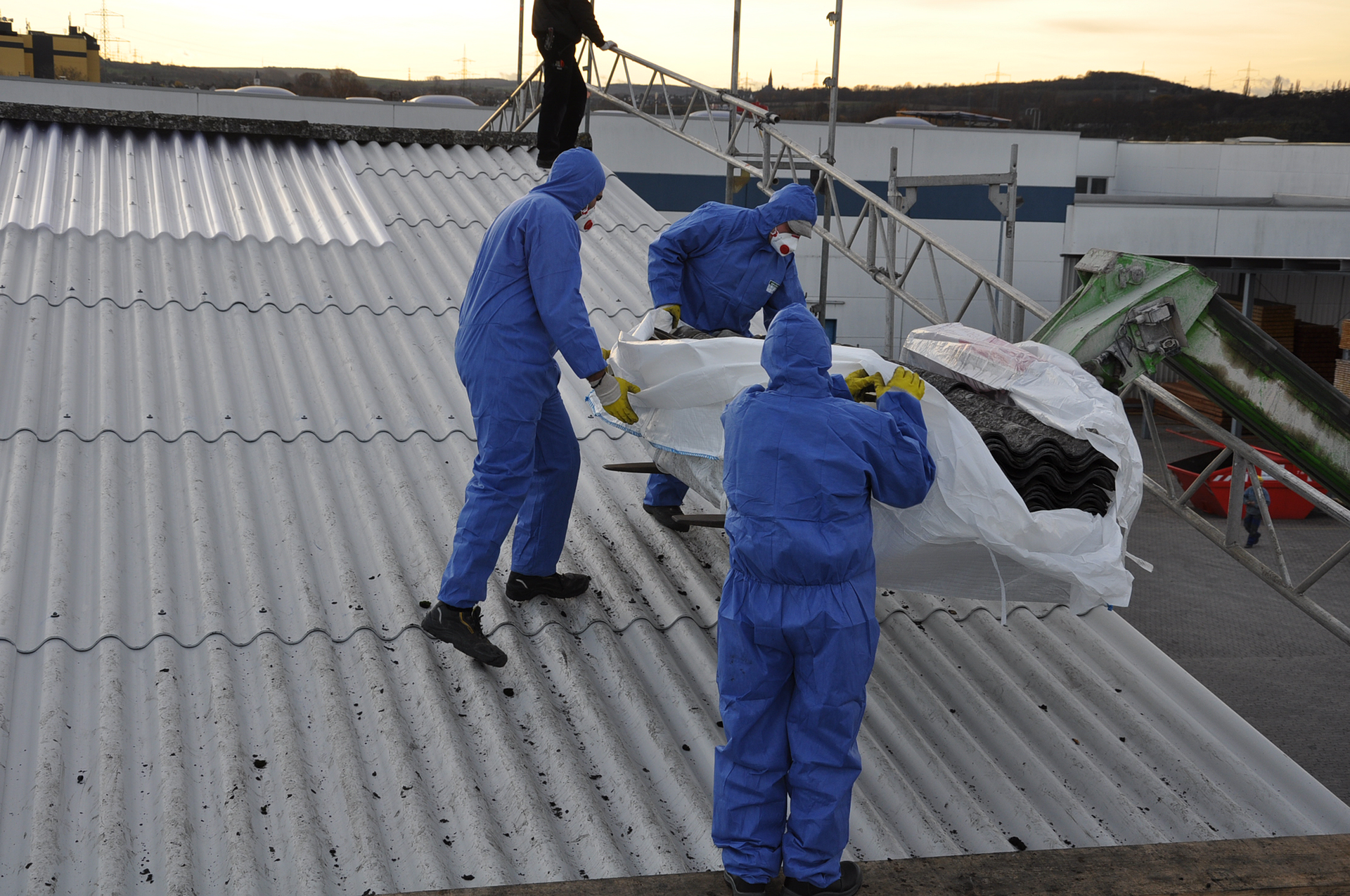
Until recently, asbestos was a commonly used and valued natural mineral fibre, which occurs in several varieties with different chemical composition. Fibrous asbestos is made of thin, soft, shiny fibres of white or grey colour, which are characterised by high‑temperature resistance and poor conductivity of heat and electricity. The asbestos yarn (produced with the addition of cotton) was used in the production of fireproof and acid‑resistant fabrics as well as in the manufacture of cardboard and asbestos tar paper, used for thermal and electrical insulation.

Answer the questions, then reverse the tab by clicking on it and check if the answer is correct.
| What material is made of thin, soft, shiny white or grey fibres characterized by high temperature resistance and poor conductivity of heat and electricity? | Asbestos fibre |
| What fabric is considered the most noble? | Silk |
| Of which material using the natural tendency to creases the most common tablecloths, pillow cases, curtains, kitchen cloths and elegant clothing are made? | Flax |
| What fibre is obtained from agave? | Sisal |
| What kind of wool is the most popular? | Sheep’s wool |
| Which fibre is soft and breathable and easy to care for, e.g. washing in the washing machine and ironing at high temperatures? | Cotton |
Select true statements.
- Silk fibres are obtained from cocoons of bombyx mori.
- Cotton is a protein fibre - it contains keratin.
- Wool fabric combust quickly. Burns after removing from the flame of the burner and forms grey ash.
- Sisal is used to make ropes, mats and sacks.
- Wool turns yellow under the influence of sunlight. It has low resistance to high temperature.
- Asbestos is a mineral fibre used for the production of refractory fabrics and roofing materials called Eternit.
Match the fibres with the products in which these are most commonly applied.
sweaters, fire-resistant fabric, sacks, scarves, kitchen cloths, cotton pads
| cotton | |
| flax | |
| sisal | |
| silk | |
| wool | |
| asbestos |
Summary
Natural fibres can be cellulose fibres (vegetable fibres) or protein fibres (animal fibres). Mineral fibres (asbestos) are also known.
Human‑made fibres are chemically synthesised – made of raw materials of natural origin, e.g. viscose from cellulose – and artificial fibres – made of substances obtained by chemical synthesis.
Today, many types of fibres are produced, which are used to manufacture products that sometimes meet very specialized requirements and serve the safety and comfort of use.
Observation of fibres combustion allows approximate determination of the type of fibre. In addition, protein fibres undergo reactions characteristic for proteins, e.g. xanthoproteic reaction.
Suggest an experiment that will show that wool fabric is made of protein fibres. Prepare the description and scheme of the experiment.
Key words
natural fibres, animal fibres, fibres of vegetable origin, fibres of animal origin, mineral fibres, silk, wool, cotton, sisal, flax
Glossary
włókna naturalne – włókna pochodzenia roślinnego lub zwierzęcego występujące w przyrodzie, które po odpowiedniej obróbce moga być wykorzystane do produkcji tkanin; jedynym naturalnym włóknem mineralnym jest azbest
włókna syntetyczne – włókna wytwarzane w procesach polimeryzacji i polikondensacji związków organicznych (głównie węglowodorów i ich pochodnych), np. poliamid czy poliester
włókna sztuczne – włókna wytwarzane ze związków chemicznych znajdujących się już w przyrodzie, przez formowanie polimerów naturalnych, np. wiskoza powstająca z celulozy, czyli z masy drzewnej