Mixtures vs elements and chemical compounds
what the difference between a simple and a complex substance is;
how to make simple mixtures;
how to define: mixture, homogeneous mixture, and heterogeneous mixture;
how to distinguish between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
how to explain the difference between an element and chemical compound;
how to distinguish a mixture from a chemical compound;
to plan and carry out an empirical test in accordance with the instructions.
Mixtures, elements and chemical compounds – differences
The matter that surrounds us is made of substances or mixtures of substances. Conversion of substances into mixtures or vice versa takes place as a result of physical processes: mixing and separation. Substances are chemical elements and chemical compounds.
There are various substances in our environment. Among them are those that cannot be broken down to the simpler ones. These are chemical elementschemical elements. Of the currently known 118 chemical elements, 90 occur in nature, but only a few are found in the free (native) state.
Mutual transformation of elements and chemical compounds takes place by way of chemical reactions.
Matter types
Look at the diagram presenting the division of matter. Give at least two examples of the type of matter and write them here or in a notebook.
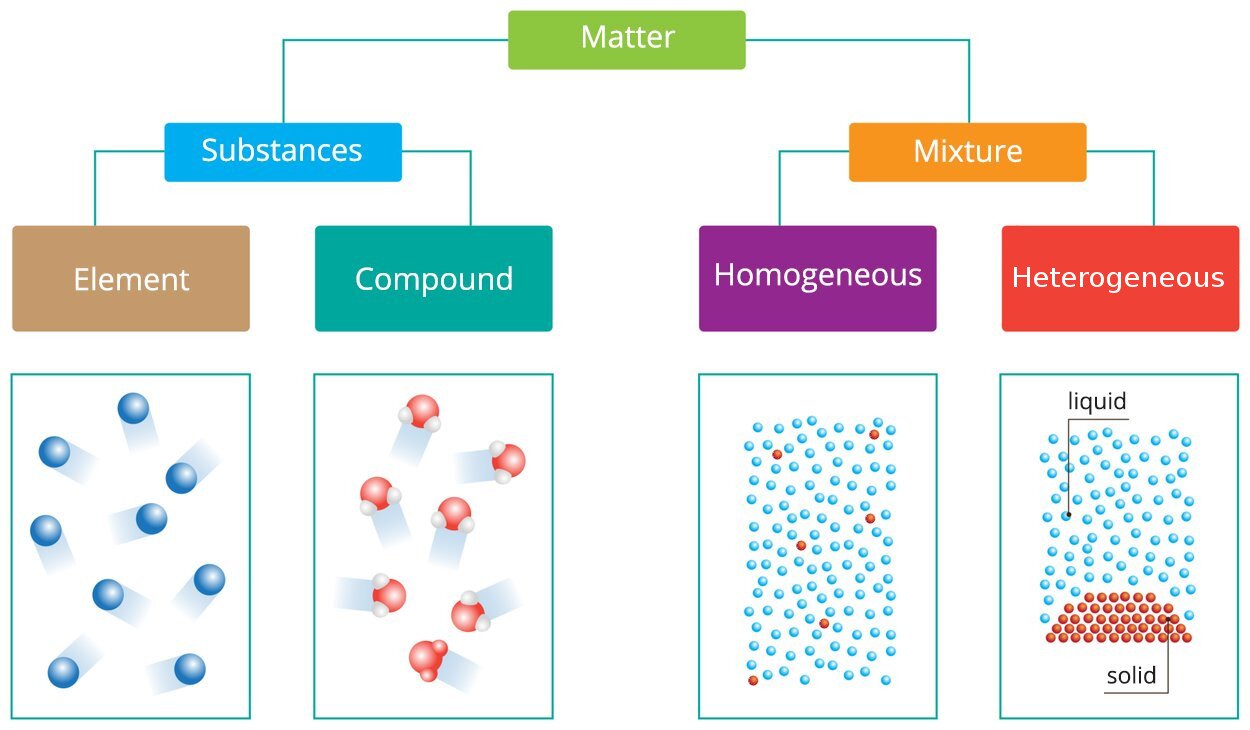
Look at the table presenting the properties of mixtures and chemical compounds. What features of elements can you relate to them?
Mixture | Chemical compound | |
Composition | variable, it is possible to change the quantities of each substance | chemical composition strictly defined (by the law of constant composition) td> |
Connection | substances not connected, mixed | elements connected (by a chemical bond) |
Properties | each substance maintains its properties | properties different from the properties of individual elements |
Separation | it is possible to separate components using physical methods | the possibility of breaking down into elements as a result of chemical reactions |
Examples | air, seawater | water, magnesium oxide |
How do you know what is a mixture and what is a chemical compound?
Look at the diagram that suggests how to distinguish types of matter. Then do the exercises.
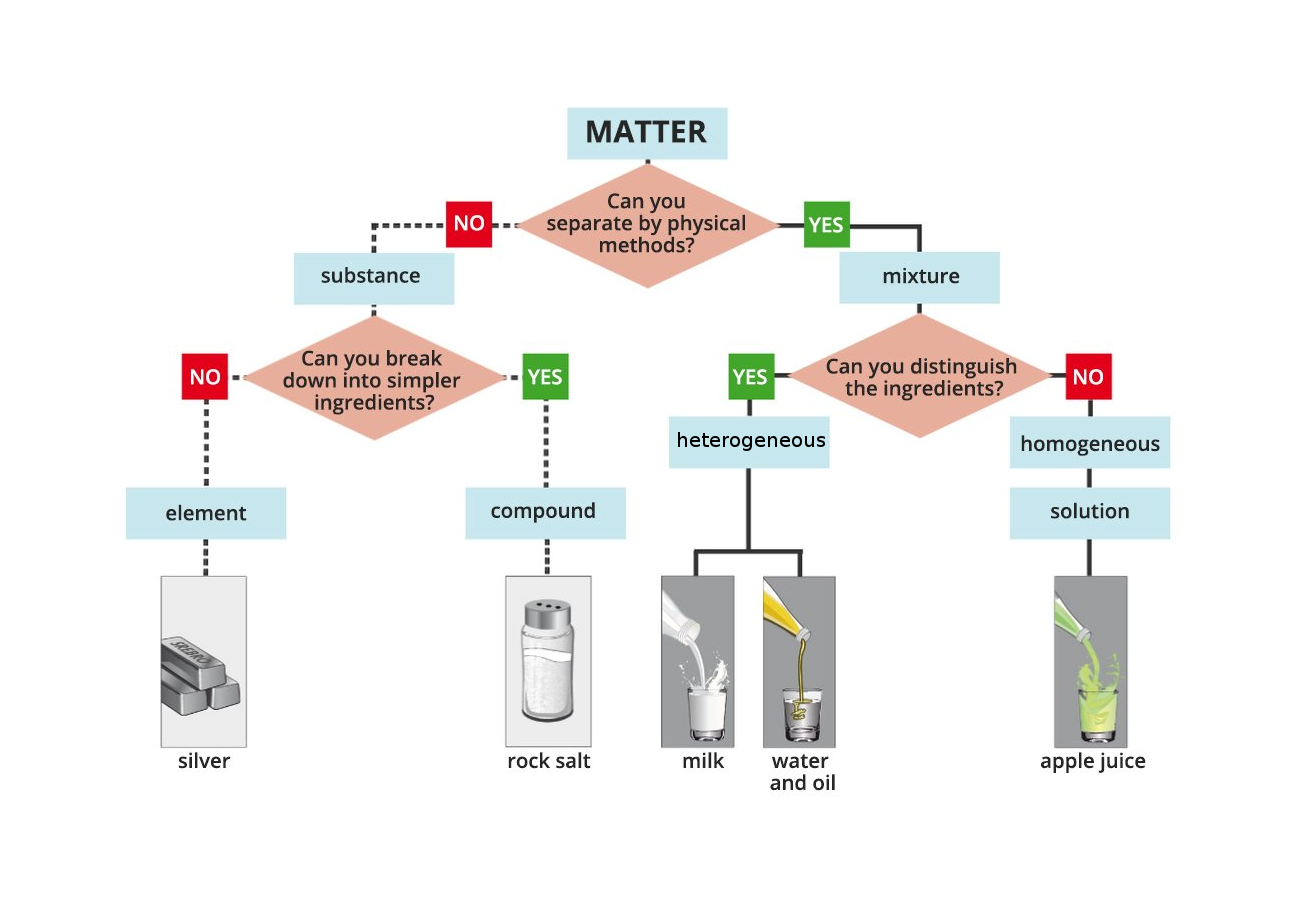
Tasks
A mixture, chemical compound or element? Decide what the description fits, then turn the flashcard over and check the correctness of the answer.
| contains uncombined substances | mixture |
| the substance it consists of cannot be broken down into simpler ones | element |
| contains substances connected by a chemical bond | chemical compound |
| it is air | mixture |
| it is tin | element |
| it is water | chemical compound |
| it is seawater | mixture |
| it is possible to separate its ingredients by physical methods | mixture |
| it is possible to divide it into elements in the result of chemical reactions | chemical compound |
| has a strictly defined chemical composition | chemical compound |
| it has a variable composition | mixture |
Drag sentences into appropriate fields indicating whether the described properties relate to a mixture or to a chemical compound.
It has different properties than the elements it consists of., It results from mixing two or more components., Each component can be easily separated by physical methods., The ingredients can be distinguished by the naked eye.
| MIXTURE | |
|---|---|
| CHEMICAL COMPOUND |
Summary
We encounter different types of mixtures in our surroundings.
All mixtures consist of at least two components mixed with each other in any proportions.
Mixtures, such as water and chalk or smoke, the components of which are visible to the naked eye are called heterogeneous mixtures.
Mixtures, such as sea water, air or metal alloys, the components of which are not visible to the naked eye are called homogeneous mixtures.
Keywords
mixture, homogeneous mixture, heterogeneous mixture, element, chemical compound, substance
Glossary
mieszanina – co najmniej dwie substancje zmieszane ze sobą w dowolnych proporcjach
pierwiastek chemiczny – substancja, której nie można rozłożyć na substancje prostsze