Revising the knowledge about the vibrating motion and waves
Podsumowanie wiadomości o ruchu drgającym i falach
- summarize and revise your knowledge about the vibrating motion and the mechanical wave.
Answer the following questions and test your knowledge.
1. What is the vibrating motion?
Vibrating motion is one of the most common types of movement. The body moves on the same track in both directions and the movement repeats in equal intervals of time.
2. Define the basic quantities describing the vibrating motion.
The time required to perform one full vibration is called the period of motion. The number of vibrations made per the unit of time is the frequency of vibrationsfrequency of vibrations. Frequency is the inverse quantity to the period.
The unit of frequency is 1 Hz (hertz).
The amplitude of vibration is the greatest displacement of the body from the equilibrium position.
3. What is the mathematical pendulumpendulum?
An example of a body performing vibrations is the mathematical pendulumpendulum. It is a very small (punctual) body suspended on a weightless and inextensible thread. The period of oscillation of the pendulum depends on its length. The longer the pendulumpendulum, the greater the period of vibrations (i.e. the lower the frequency).
4. What is natural frequency?
Natural frequency is the frequency with which the body vibrates knocking out the equilibrium position without any resistance.
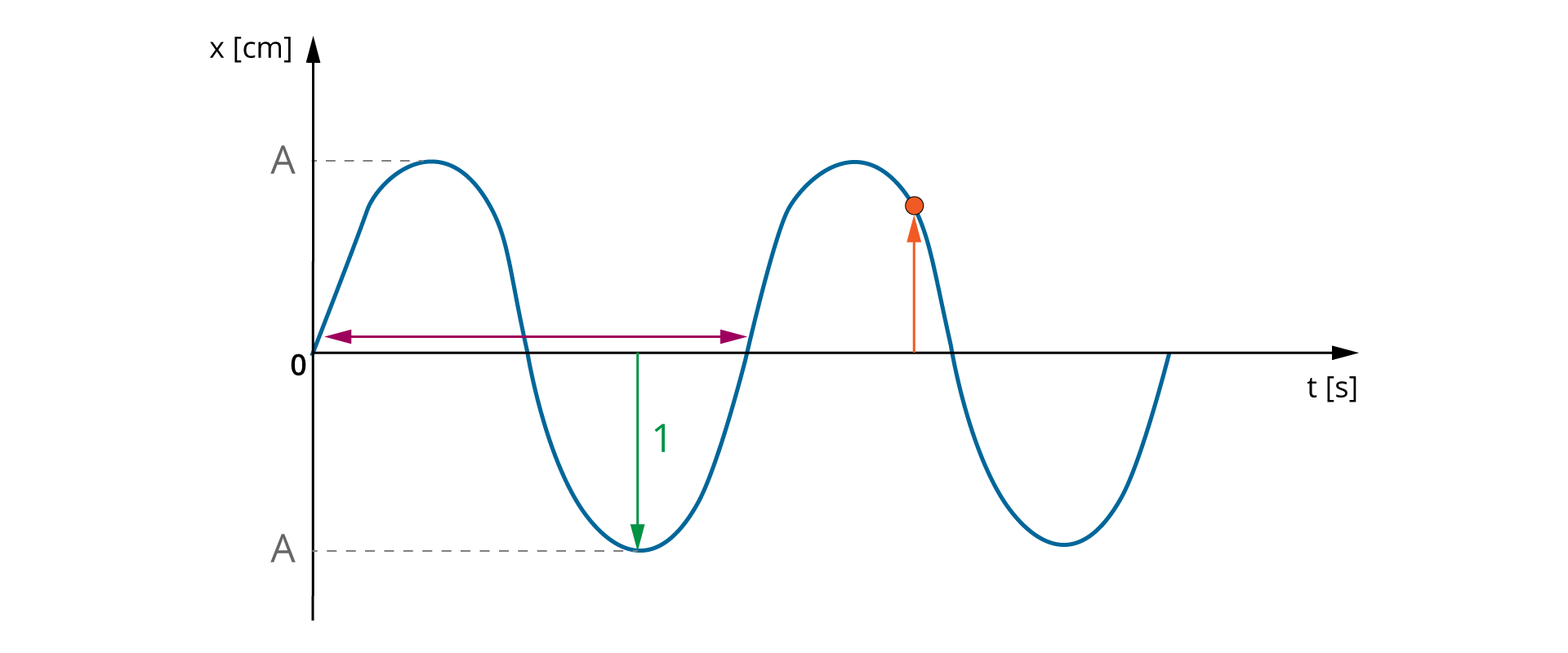
5. Present on the graph the dependence of the displacement on time in the undamped and suppressed harmonic motion.
The dependence of the displacement on time can then be presented on the graph.
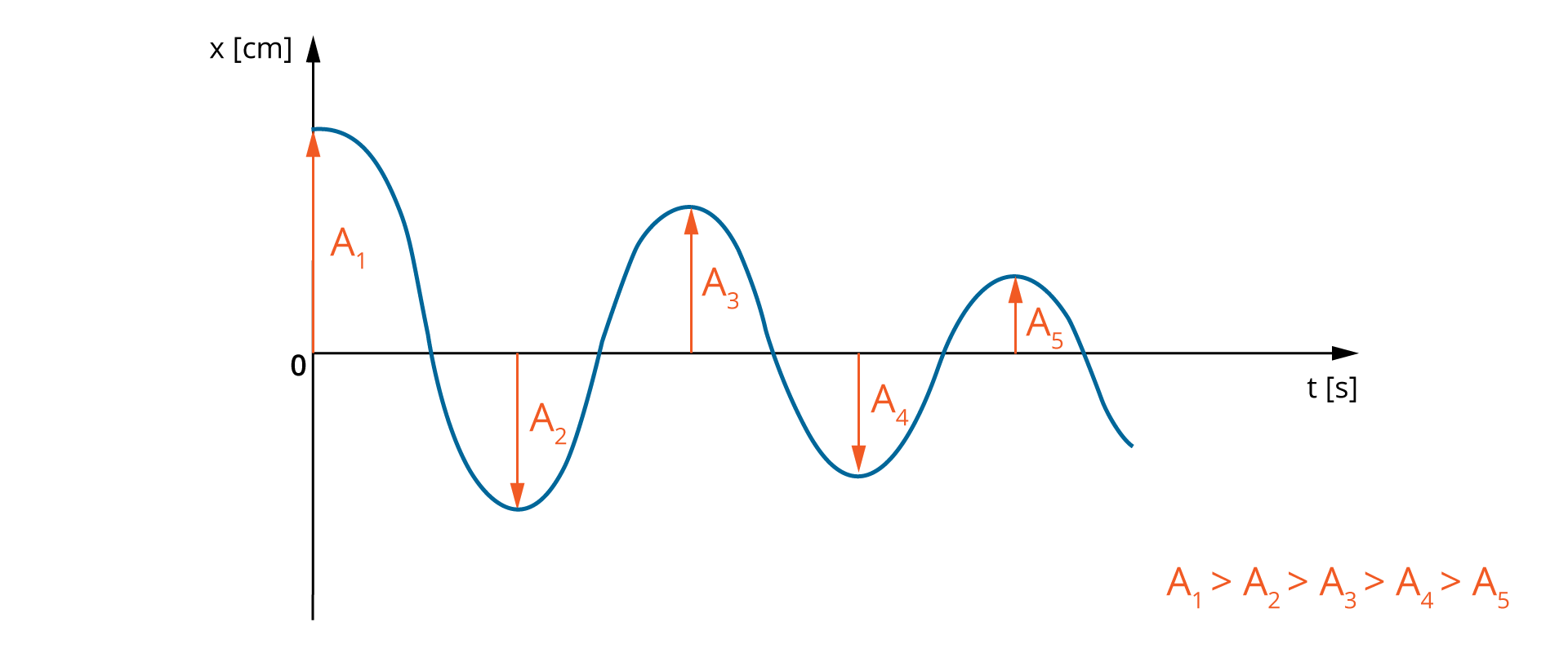
In real conditions, when the resistance of the motion is present, the vibrations are dumped - the amplitude decreases with time.
6. Describe the mechanical energy changes occurring during the harmonic oscillator motion.
The vibrating body has two kinds of energy: kinetic and potential energy of elasticity. During the vibrations there are cyclical mutual transformations of these energies.
The kinetic energy of the oscillating body is the greatest at the moment of the body passing through the equilibrium position (i.e. when it has the highest velocity) and equals zero at the moment of the biggest displacement.
The potential energy of the elasticity of the vibrating body is the greatest at the moment of the maximum displacement and equals zero at the moment when the body is passing through the equilibrium position.
If there were no resistance of the movement, the total mechanical energy (the sum of kinetic energy and the potential energy of elasticity) would be constant. When there is the resistance force, the body loses its mechanical energy and the vibrations are dumped.
7. What is the mechanical wave and what is the propagation of the mechanical wave?
A mechanical wave is called a disturbance that propagates in matter. This disturbance is the vibrations of the particles of the medium. The particles of the medium do not move with the wave; they only vibrate around their balance positions and stimulate further particles to vibrate. Mechanical waves can propagate only in elastic media.
8. Define the basic quantities describing the propagating wave.
The wavelength, marked with the letter , is the distance over which the wave travels at the time when a given medium molecule does one full vibration. The time required for the particle to perform one full vibration is called the wave period.
The wave in a given medium propagates at a constant speed, which can be calculated with the following formula.
Because , we can also write that .
The amplitude of the wave is the maximum displacement from the equilibrium position of the particles of the medium in which the wave propagates.
9. Classify the waves according to the direction of wave propagationwave propagation and the direction of vibrations.
We classify waves into longitudinal and transverse ones.
The transverse wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate in the direction perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation.
The longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate in the same direction as the wave propagationwave propagation.
10. What is a sound?
Sound is an example of a mechanical wave; it is based on propagation of vibrations of the medium particles. It is a spherical wave which spreads in all directions. Like all mechanical waves, it cannot propagate in vacuum. The speed of the sound varies in different media. It is the greatest largest in solids, the smallest in gases.
Bodies vibrating at the frequency of 16 Hz to 20000 Hz are the source of sounds. Strings (guitar, piano), diaphragms (drums) or air columns (flute, organ) can produce vibrations in musical instruments.
11. List and describe the properties of the sound.
Individual sounds differ in timbre, volume and altitude.
The timbre depends on kind of the sound source.
The pitch of the sound depends on its frequency - the higher the frequency, the higher the sound.
The volume depends on the amplitude - the higher the amplitude of the wave, the louder the sound. We measure sound intensity in decibels [dB]. 0 dB is called audibility threshold, 120 dB is called pain threshold.
12. What is echo and reverbreverb?
Echo and reverbreverb are phenomena related to sound propagation and its reflectionreflection. The sound after the reflection from the barrier returns to the source and if the delay between the wave sent and reflected is large enough, we hear an echo; if it is small, we hear reverb.
13. What are ultrasoundsultrasounds and infrasounds?
Waves with frequencies below 16 Hz are called infrasounds and, respectively, those above 20000 Hz are called ultrasoundsultrasounds. Ultrasounds are used in many technologies including medicine, echolocation, defectoscopy, cosmetic procedures, etc. Many animals hear ultrasoundsultrasounds.
Click on the tag and you will get information about the pendulumpendulum clock.
Summary
Vibrating motion is one of the most common types of movement.
The time required to perform one full vibration is called the period of movement. The number of vibrations made per the unit of time is the frequency of vibrationsfrequency of vibrations.
An example of a body performing vibrations is the mathematical pendulumpendulum. It is a very small (punctual) body suspended on a weightless and inextensible thread.
A vibrating body has two kinds of energy: kinetic energy and potential energy of elasticity. During vibrations there are cyclical conversions between these energies.
A mechanical wave is called a disorder that propagates in the medium. The particles of the medium vibrate in this disorder.
The wave in a given medium propagates at a constant speed.
Sound is an example of a mechanical wave; it is based on propagation of vibrations of the medium particles. It is a spherical wave which spreads in all directions. Like all mechanical waves, it cannot propagate in vacuum. The speed of the sound varies in different media.
Individual sounds differ in timbre, volume and altitude.
Exercises
If a person breathes 20 times per minute, the frequency of breathing is
- .
- .
- .
The whistle, i.e. a pipe closed at one end, emits a basic tone of 2750 Hz. The sound speed in the air is 330 .
b) What would be the frequency of the basic tone, if the whistle was shortened by of the length?
Ania was sitting on a swing. The swing had the vibration periodvibration period of 8 seconds. At one moment, Ania was in the lowest position above the Earth. Calculate, from this moment, the shortest time after which Ania was moving at the maximum speed. Justify in English why speed is maximal at this point.
Indicate which pairs of expressions or words are translated correctly.
- drgania harmoniczne - harmonic oscillations
- częstotliwość drgań - frequency of vibrations
- okres drgań - vibration period
- fala harmoniczna - harmonic wave
- infradźwięki - reflection
- pogłos - pendulum
- częstotliwość drgań
- harmonic wave
- propagacja fali
- okres drgań
- vibration period
- drgania harmoniczne
- frequency of vibrations
- wave propagation
- fala harmoniczna
- harmonic oscillations
Glossary
częstotliwość drgań
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: frequency of vibrations
drgania harmoniczne
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: harmonic oscillations
fala harmoniczna
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: harmonic wave
infradźwięki
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: infrasound
wahadło
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: pendulum
odbicie
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: reflection
pogłos
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: reverb
ultradźwięki
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: ultrasounds
okres drgań
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: vibration period
propagacja fali
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: wave propagation
Keywords
frequency of vibrationsfrequency of vibrations
harmonic oscillationsharmonic oscillations
harmonic waveharmonic wave
vibration periodvibration period
wave propagationwave propagation