Genetic diversity
that mutations are the initial source of genetic diversity;
that sexual reproduction ensures genetic diversification of offspring;
species are mutually dependant, there are antagonistic or non‑antagonistic interactions among them;
to describe the meaning of genetic diversity in the adaptation of organisms to local living conditions;
to explain what is the evolutionary arms race and what role plays the genetic diversity in this race;
to explain causes and effects of decrease in genetic diversity.
Genetic diversity (intra‑species) is the diversification of alleles of genes in pools of genespools of genes of the population of a given species.
High genetic diversity makes it possible for species to create various adjustments (adaptationsadaptations), for example to fight with predators and pathogens (viruses, pathogenic microorganisms, parasites).
There is a continuous evolutionary arms race in nature between the hosts and parasites, and between predators and preys, which is a sign of coevolutioncoevolution. By shuffling within pool of genes and appearing of new mutations in genotypes the adaptations appear which enable specific species to achieve superiority over the enemy species, which is reflected in their better adaptation to living conditions in changing environmental conditions.
„Individuals which are more immune produce more offspring and at least some of the individuals from the offspring inherit genes determining increased immunity. As a consequence, the appearance of mutated genes in a given population is more frequent. Analogically, when it comes to pathogens, new mutations increase the efficacy of infecting the hosts, e.g. by breaking their natural defence mechanisms. Pathogens which acquired the ability to infect the host more efficiently multiply more intensively, and therefore they spread in the host’s population more effectively.
The direct cause of decrease in genetic diversity is the decrease in number of individuals in a population. Genes are transferred from one generation to another randomly. The bigger number of individuals has specific allele, the more probable it is that it will be passed onto next generation and it will be strengthened in a population. However, if a specific allele appears in a population occasionally, there is high probability that it will disappear from the pool of genes. Therefore, only properly high population number guarantees passing diversified genetic material onto the next generations. High number of individuals also mean more chances for the appearance of mutations and obtaining new alleles of genes of adaptational importance.
An important cause of the decrease in genetic diversity is extinction of local subspecies or varieties of wild organisms, as well as the appearance of more and more selected, genetically homogeneous varieties of crop plants and breeds of farm animals. With the extinction of wild varieties, all unique alleles, which were in their genotypes and determined the adaptation to local environmental conditions, disappear.
Using different sources of information, indicate examples of 3 species the genetic diversity of which is endangered due to extremely low population number.
One of the method of preserving a feature desired by a human is inbreedinginbreeding, which means crossbreeding of closely related organisms, resulting in the increase in homozygosity in offspring. Individual offspring are very similar to each other in terms of genes, and in the case of crop plants they are sometimes clones. In this way, the pool of genes is depleted gradually in next generations. The use of inbreeding in plants contributes to increase in yields, but it also leads to a situation when new varieties are more susceptible to the attack of various pathogens. In animals, it may lead to increased meatiness of pigs or milkness of cows, but it also reduces the immunity of these animals to diseases.
Thanks to selective breeding people obtained many varieties and breeds of plants and animals. There are thousands of varieties especially for ornamental plants, e.g. roses, which were crossed and selected due to numerous desired characteristics: size of flowers, their colour, scent, ability to climb on supports, production of many thorns or lack of thorns, tree or miniature type, winter hardiness. Due to that they maintained many alleles of genes. Similarly to roses, the species of domestic dog, represented by many breeds, still maintains high genetic diversity.
Match the terms below with their correct definitions.
diversification of genes alleles in pools of genes in the population of a given species, diversity of natural habitats and ecosystems, diversification of species living in specified ecosystems
| Genetic diversity | |
| Species diversity | |
| Ecosystems diversity |
What are negative effects of decreasing genetic diversity? Tick all correct answers.
- loss of ability to adapt to various habitat conditions
- increase in the susceptibility to some diseases
- extinction of some subspecies or varieties
- disappearance of unique alleles from pool of genes
- increase in usability value of farm animals
- increase in yields of crop plants
Summary
Genetic diversity enables the adaptation of a species to environmental changes.
Mutations, by enriching the pool of genes of a population, may give the organisms the advantage reflected by their better accommodation to living conditions in changing environmental conditions.
1. Estimate the probability (high – low) that all the people in the world will die because of an epidemic of a new disease. Justify your prediction.
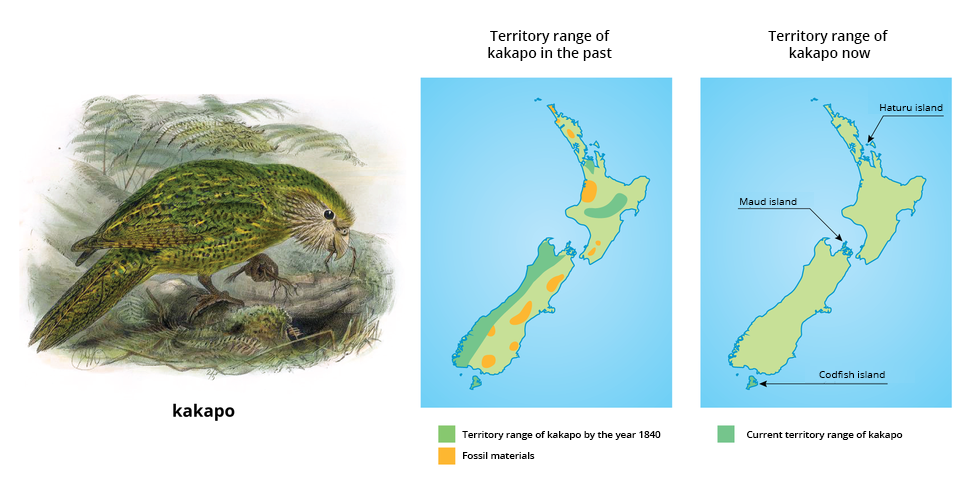
2. Kakapo is a species of a big, flightless parrot (the heaviest parrot in the world) at risk of extinction. As far back as in the mid‑19th century it inhabited almost half of the area of New Zealand. Currently its territory range is limited to few small islands, and its genetic diversity is poor. Explain what was the probable reason for the impoverishment of pool of genes of this species.
Keywords
Pool of genes, adaptation, inbreeding, coevolution
Glossary
adaptacja – przystosowywanie się gatunku do określonych warunków życia poprzez wytworzenie określonych cech (adaptacyjnych), które mogą być dziedziczne lub niedziedziczne
chów wsobny – zwany także kojarzeniem krewniaczym; kojarzenie osobników blisko spokrewnionych ze sobą, którego skutkiem jest wzrost homozygotyczności potomstwa
koewolucja – proces współzależnej ewolucji gatunków pozostających w różnych relacjach międzygatunkowych, np. symbiotycznych lub antagonistycznych, w którym każdy z gatunków wytwarza nowe przystosowania dające mu korzyści, a w przypadku relacji antagonistycznych – przewagę nad drugim gatunkiem
pula genowa – wszystkie allele genów występujących u osobników danej populacji
różnorodność biologiczna – inaczej zwana bioróżnorodnością; zróżnicowanie organizmów na całej kuli ziemskiej na wszystkich poziomach złożoności życia: w obrębie gatunku, pomiędzy gatunkami oraz w obrębie ekosystemów