Mitosis
genetic information is found in the cell nucleus in the form of DNA.
to discuss the importance of mitosis for the functioning of the organism.
Mitosis
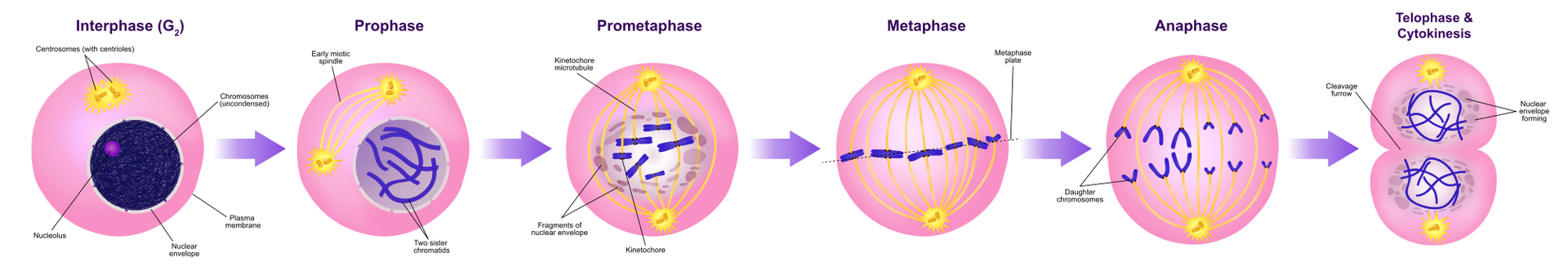
Cell division allows organisms to grow and develop, as well as reproduce, or in other words, increase the numbers. These are the basis for the survival of the species and the evolution of life. The division of eucaryotic cell consists of two stages. The first is the division of the cell nucleus. The second stage is the division of the cytoplasm and cell organelles contained in it.
Nuclear (eukaryotic) organisms are distinguished by two basic types of cell division. One leads to the production of cells with the same number of chromosomeschromosomes and it's called mitosismitosis. The effect of the second, meiosismeiosis, is the formation of cell with reduced by half haploid number in chromosomes.
During mitosis one mother cell produces two daughter genetically identical cells. One could say that the purpose of this division is to multiply the number of the same cells. In the case of unicellular organisms that have a nucleus, the result of mitosis is an increase in the number of individuals. In the case of multicellular organisms, the result of mitosis is their growth, which consists in increasing the number of cells in the body.
The frequency of mitotic divisions can differ at various periods of the organism's life and in various areas of the body. Usually, it is more intense in the early stages of development and is later slowed. Cells of some tissues divide intensively throughout entire life, e.g. human skin cells, meristem cells in plants.
Both diploid cells and haploid cellshaploid cells may undergo mitosis. As a result of the mitotic division of the diploid celldiploid cell two diploid cells will be created, and the haploid cell will become two haploid cells.
Specify how many chromosomes were found in the stem cells from which, as a result of mitosis, there were progeny with the following number of chromosomes in the cell nucleus: 12, 18, 24.
Explain why human blood cells – erythrocytes – do not divide.
Discuss the cell division on the basis of the illustration. Specify the number n and 2n for this cell.
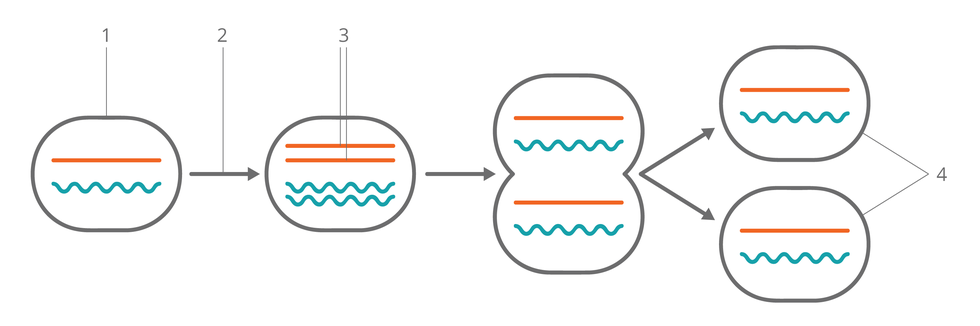
Select all true statements.
- Both haploid and diploid cells may undergo mitotic division.
- Mitosis leads to the creation of two identical genetic cells.
- As a result of mitosis from the diploid cell, a haploid cell is formed.
- Cell organisms can reproduce by mitosis.
Can a haploid cell with a chromosome number of 7 be broken down by mitosis? Indicate the correct answer
- No, because during mitosis, each of the daughter cells would have to get half the chromosomes of the stem cell, and the number 7 is indivisible by 2.
- Yes, because during mitosis the genetic material is copied exactly and each of the daughter cells gets the same copy - in this case 7 chromosomes.
- Yes, but the daughter cells will differ in the number of chromosomes - in one there will be 3 chromosomes and in the other 4.
Summary
Diploid cells contain a double set of chromosomes, and haploid cells contains a single one.
Prior to cell division, there is always a doubling of the amount of DNA in the cell nucleus.
Mitosis is the division of the nucleus, thanks to which two daughter cells with identical genetic information are formed from one stem cell.
Mitosis allows the growth and development of multicellular organisms and the reproduction of unicellular organisms.
Keywords
meiosis, division, haploid cell
Glossary
chromosomy – podziałowa postać DNA; wydłużone, pałeczkowate struktury powstające z nici DNA w jądrze tuż przed podziałem komórki i widoczne w czasie podziału jądra
komórka diploidalna – komórka, która zawiera podwójny zestaw (liczbę) chromosomów (2n)
komórka haploidalna – komórka, która zawiera pojedynczy zestaw (liczbę) chromosomów (1n)
mejoza – proces podziału jądra komórkowego, w wyniku którego z jednej komórki powstają cztery komórki potomne o zredukowanej o połowę (w porównaniu do komórki macierzystej) ilości materiału genetycznego; przebiega dwufazowo – pierwsza faza jest redukcyjna (redukcja liczby chromosomów)
mitoza – proces podziału jądra komórkowego, w wyniku którego z jednej komórki macierzystej powstają dwie komórki potomne o identycznym materiale genetycznym względem siebie i względem komórki macierzystej