Computer resource management
Zarządzanie zasobami komputera
organize files and folders,
copy and move files and folders,
the most commonly used shortcuts Ctrl + C, Ctrl + V, Ctrl + X,
delete and restore files and folders,
create shortcuts to files and folders.
Think about the example of your desk as you organize things on it (e.g. binders, drawers). How can you organize files and folders in your computer resources?
Operations on files and folders
Files and folders allow you to perform various types of operations to organize them on your computer's local disk (as well as in the cloud). These operations can be performed on individual files or folders, as well as on their groups. To perform an operation on a group of objects, first select them.
To select a single file or folder, click on it with the left mouse button - selected object is highlighted.
You can select a group of objects in three ways.
Press and hold the CTRL button and then left‑click on the individual files or folders that you want to select. Clicking again will cancel the selection (the object will stop being highlighted).
Drag the mouse cursor with the left mouse button pressed over the area containing the selected objects.
Point to the first object and then hold down the SHIFT key and click the last object - all objects lying between the first and the last object will be highlighted.
To select all files or folders in the current location, use the key combination CTRL + A (select all).
In macOS, instead of the CTRL key, the Command key is used.
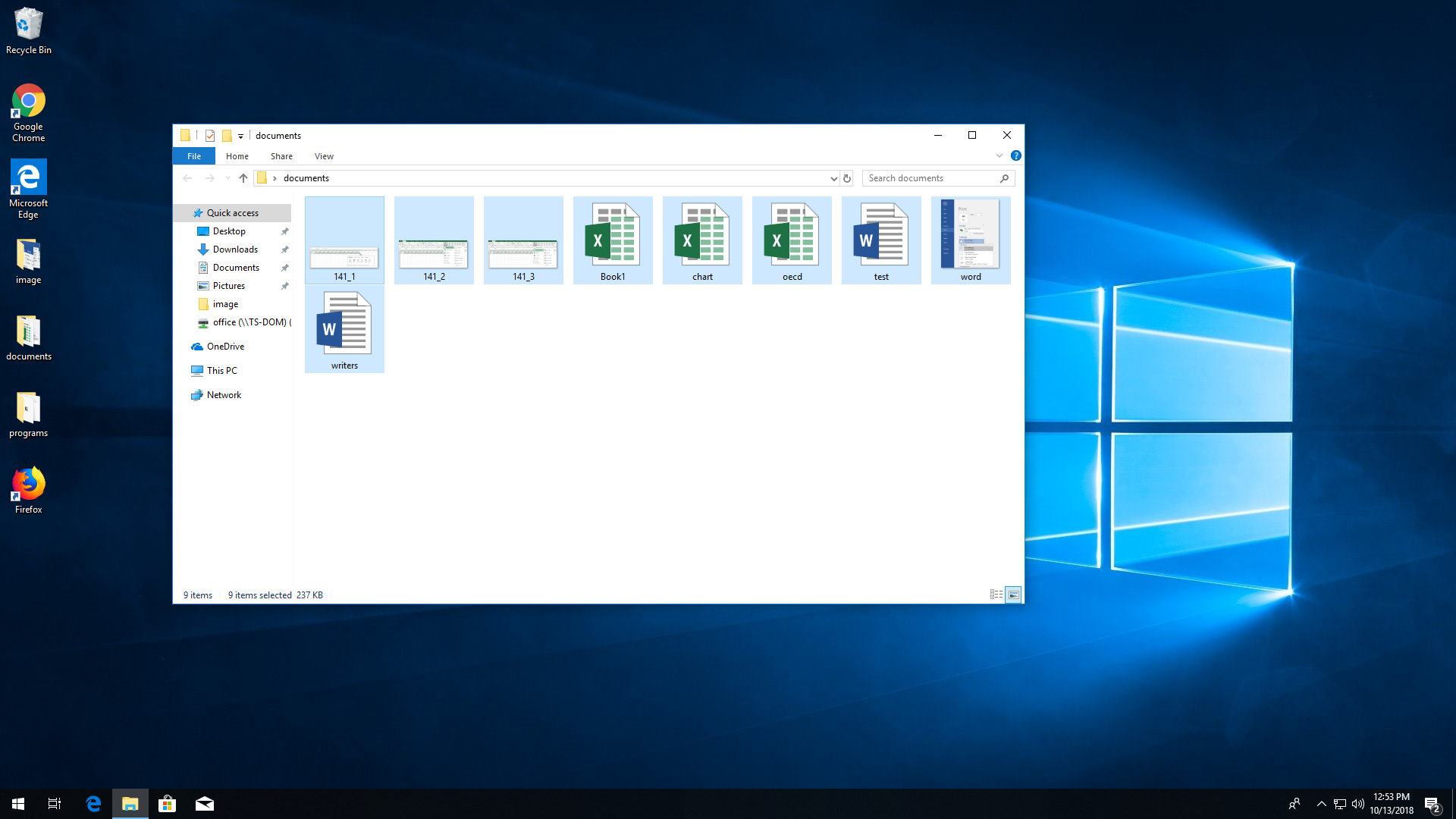
Create a folder called TEST on the Desktop. Then create in it three text files with the names 1, 2, 3. Practice three ways to select an object and a group of objects.
Copying
CopyingCopying is the process of duplicating data stored in electronic form onto a storage medium or other computer memory location.
To copycopy an object or group of objects, select objects, right‑click on the selection and choose Copy from the drop‑down menu. Then right‑click in the desired location and choose PastePaste from the pop‑up menu.
To speed up file copyingcopying you can use keyboard shortcuts: CTRL + C to copy the file and CTRL + V to paste it.
You can also copycopy a file or a folder by clicking on it and holding down the left mouse button, and then dragging its icon with the CTRL key pressed to the destination folder.
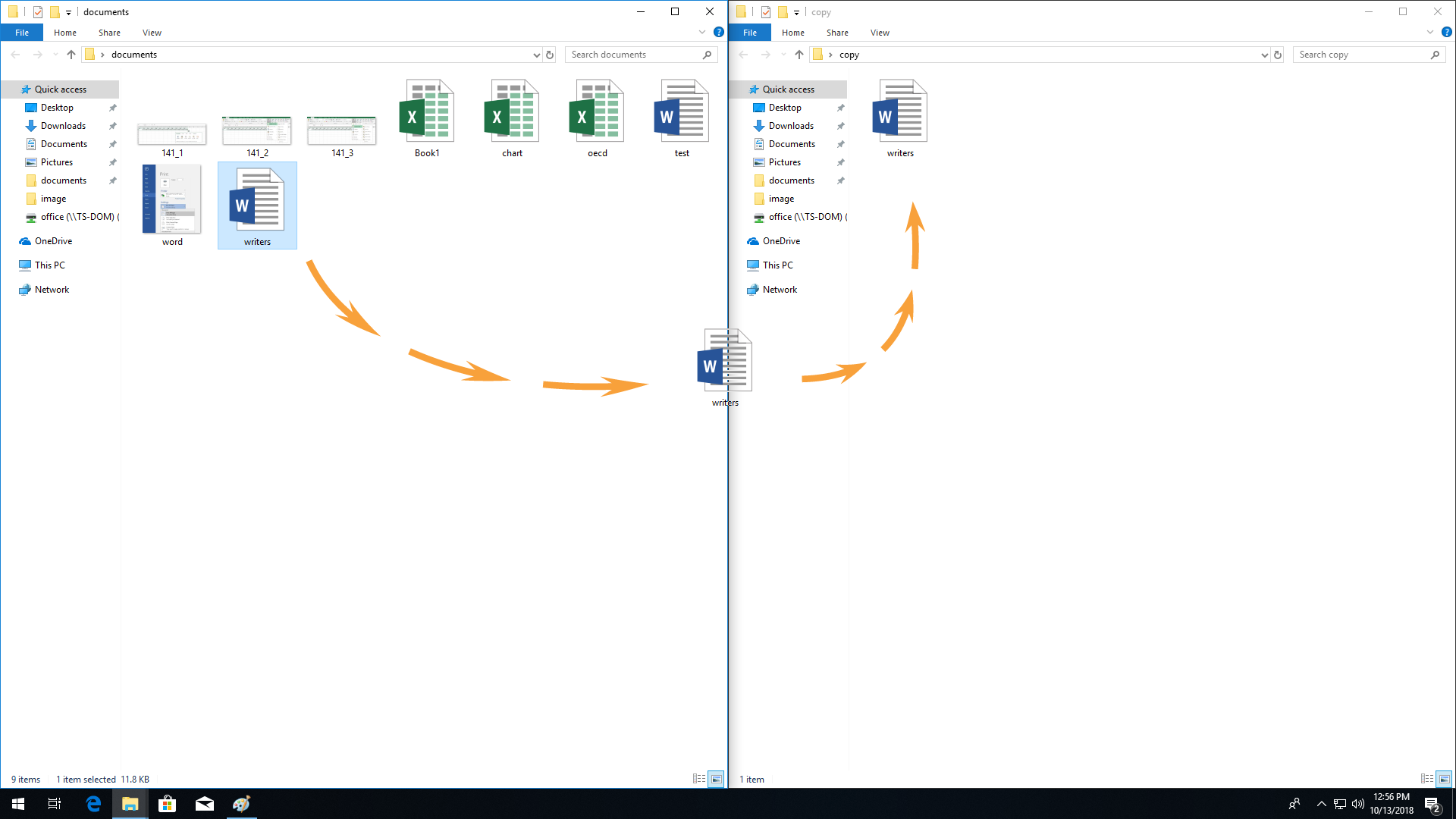
Create a COPY folder in the TEST folder, and then copy files 1, 2, 3 to it using the known copying methods.
Moving
MovingMoving is an operation of transferring an object from one place of computer memory to another.
To move a file, follow the same procedure as copyingcopying - but instead of the CopyCopy command (CTRL + C) use the CutCut command (CTRL + X).
You can also move a file or folder by clicking on it and holding down the left mouse button, and then dragging its icon to the destination folder.
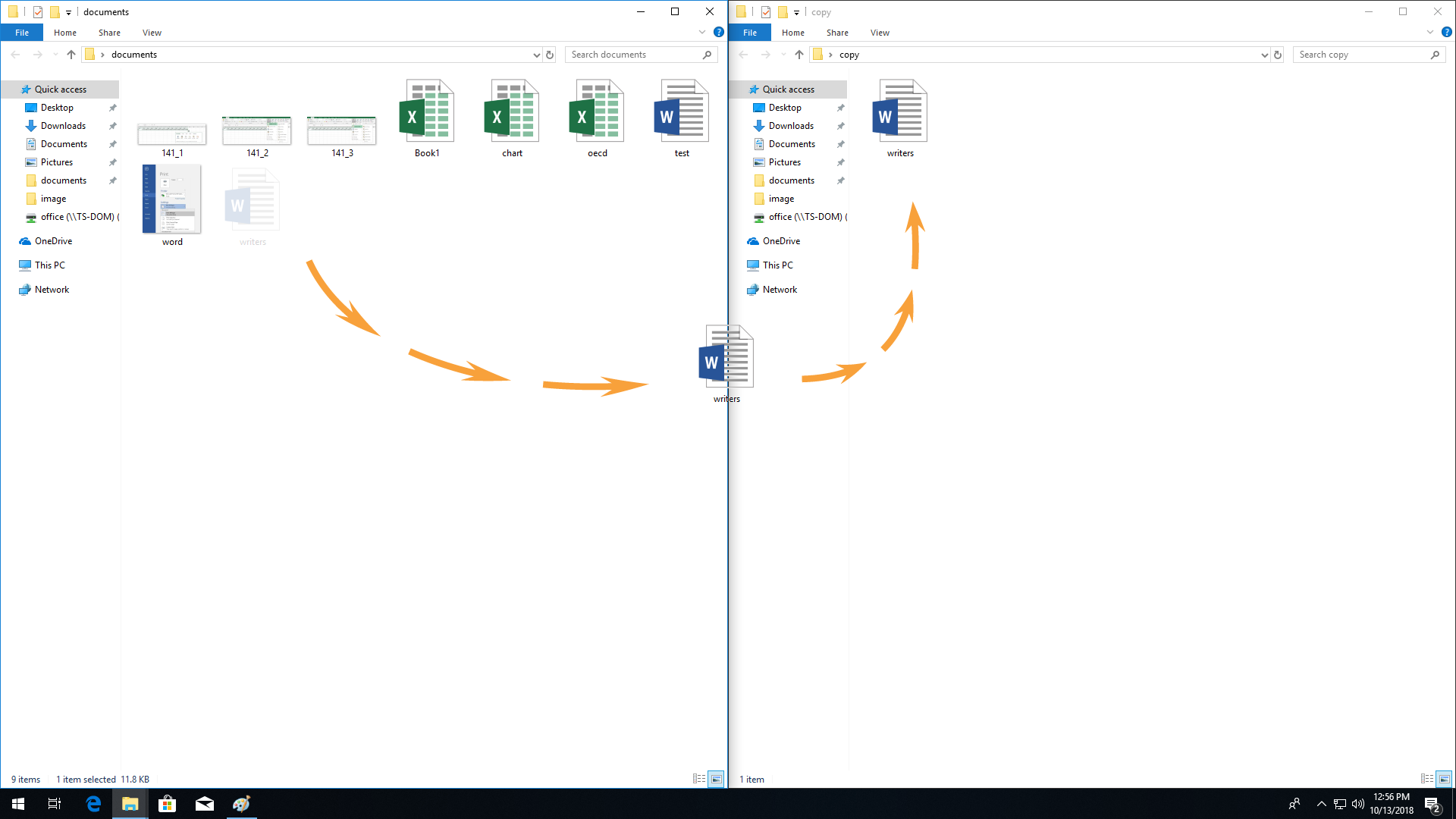
Open the TEST folder, and then move files 1, 2, 3 to the Desktop using the known moving methods.
When copying, in the destination folder window a copy of the file or folder appears. However, when movingmoving, the object disappears from the source folder and appears in the destination folder.
Clipboard
The clipboardclipboard is a specially designated part of the computer's memory reserved by the operating system for saving data indicated by the user. The clipboard is mainly used for transferring and copying data - e.g. a fragment of text, graphics or also files and folders.
To save data in the clipboard's memory, use the Copy command (CTRL + C) or CutCut command (CTRL + X).
You can refer to these data by the use of the PastePaste command (CTRL + V).
Deleting
To free some memory, you can delete objects that are no longer needed. DeletingDeleting files or folders does not immediately remove them physically from the computer's resources, but only moves them to the Recycle BinRecycle Bin.
To delete an object or group of objects, select them, then right‑click on the selection and choose Delete from the drop‑down menu. - - The same effect can be obtained by pressing the Delete button.
After opening the Recycle Bin window, there are several options in the Manage tab:
Empty Recycle Bin - permanently deletes all files placed in the Recycle Bin,
Recycle Bin properties - invokes a dialog box containing information about the location of the Recycle Bin, as well as allows you to set its size and select an option that will cause immediate permanent deletion of the file, without movingmoving to the Recycle Bin,
Restore all items - restores all deleted objects to the locations from which they were removed,
Restore selected items - restores selected objects to the locations from which they were removed.
Recycle BinRecycle Bin - is a separate disk space, where files deleted by the user are temporary stored, as well as protection against irreversible loss of accidentally deleted files. It should be remembered that with a large number of files being deleted, Windows will permanently delete the oldest ones placed in the Recycle Bin, and if the size of the file being removed exceeds the capacity of the Recycle Bin, the system will ask you to confirm deletion of the file, warning that it will be permanently deleted without possibility of restoration.
Delete files 1, 2, 3 using different methods. Then restore them using the Restore selected items option.
File properties
Each object has its own properties, such as location, type, attributes, name, date of creation or size.
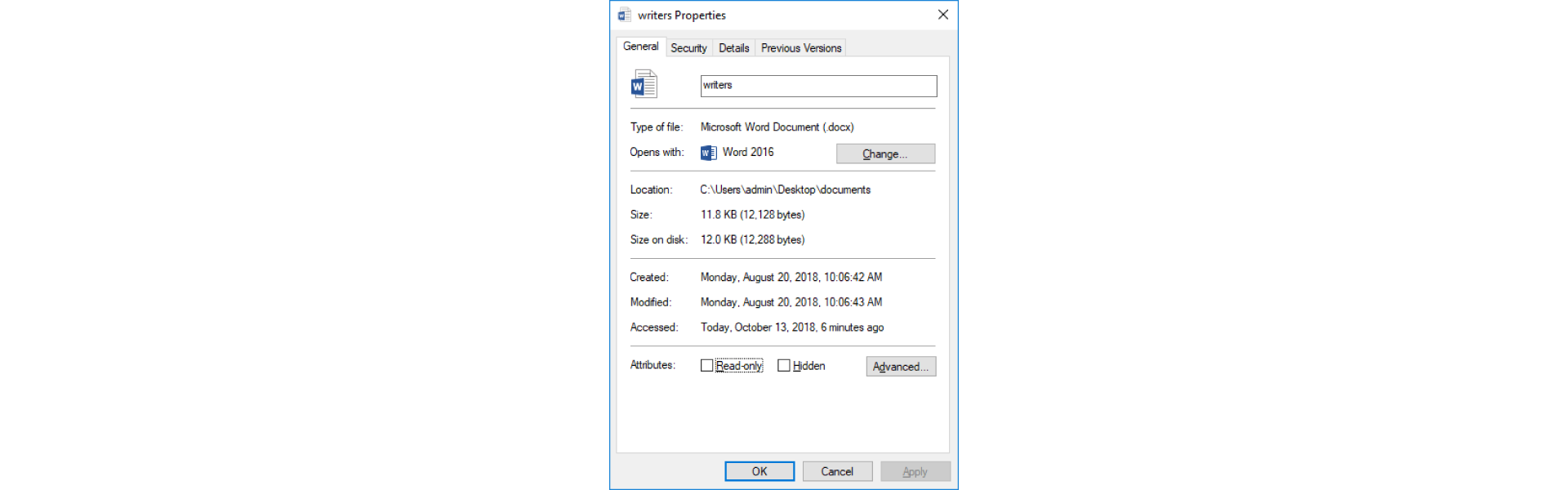
To access the file propertiesfile properties, right‑click on it and select Properties from the drop‑down menu, which opens the dialog with the following tabs - General, Security, Customize, Details and Previous versions.
The General tab - contains information about the type of file, which program opens it, its location, size, when it was created, modified and last used, as well as attributes.
Security tab - you can modify the permissions for a user or groups. Permissions allow you to give full control over the file or to perform individual actions (including modification, reading, writing or special permissions).
The Details tab - contains detailed information about the file - including its description, origin, content.
The Previous versions tab - contains information about previous versions of the file and its modification. Previous versions of the file come from file history or restore points.
Open the properties of the file named 1. Read the information on the tabs.
Shortcut to a file or folder
Considering the number of objects in the computer's memory, it often takes a long time to find this particular one. A shortcut to a file or folder allows you to access it faster - you can create it in a convenient location, for example on your desktop. The shortcut to the program is presented by means of an icon that leads to the program, file or folder, but you can easily recognize it - it has a characteristic arrow symbol in the lower left corner.

To create a shortcut to a file or folder, click on the given location (e.g. on the desktop) with the right mouse button, and then select New and Shortcut from the drop‑down menu. This brings the dialog box where you must select the file location and then the name.
In the TEST folder, create shortcuts for the web browser and the My Documents folder.
The operating system allows you to perform operations on files and folders - you can move, copycopy or delete them. To quickly launch a given program, you can use shortcuts created by the user. Each file and folder has its own properties - you can recognize them using the context menu of the given object.
Exercises
Determine which sentences are true.
- After copying, the file is located in the source folder and destination folder
- After moving, the file is located in the source folder and destination folder
- After copying, the file is only in the destination folder
- After moving, the file is only in the destination folder
Which keyboard shortcuts are used for copying:
- CTRL + C
- CTRL + V
- CTRL + F
- CTRL + A
- CTRL + P
Describe the differences between moving and copying in English.
Indicate which pairs of expressions or words are translated correctly.
- kopiuj - copy
- wklej - paste
- wytnij - cut
- usuwanie - deleting
- zaznaczanie - moving
- przenoszenie - selecting
- właściwości pliku
- selecting
- cut
- kopiuj
- zaznaczanie
- paste
- copy
- wytnij
- wklej
- file properties
Glossary
schowek
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: clipboard
kopiuj
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: copy
kopiowanie
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: copying
wytnij
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: cut
usuwanie
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: deleting
właściwości pliku
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: file properties
przenoszenie
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: moving
wklej
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: paste
kosz
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: recycle bin
zaznaczanie
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: selecting
Keywords
copycopy
cutcut
pastepaste