Asia – the great contrasts. Waterway network
that Asia is the biggest continent in the world;
that thematic maps allow to describe and compare Asian natural environment.
to show on the map the biggest rivers of Asia;
to explain what losing streams and endorheic basins are;
to show rivers in the drainage basinsdrainage basins of four oceans;
to name the biggest lakes both size‑wise and deep‑wise;
The waterway network of Asia is shaped by the terrain and the main features of the Asian climate.
The Asian continent is home to basins of all four oceans. The biggest endorheic basinendorheic basin in the world is located in the central part of the continent. It is cut out from the oceans by mountains. The rivers from that region drain into the Caspian Sea (Lake) and other endorheic lakes, or lose water as they flow downstream, for example, in the sands of the desert.
There is a big difference in the rivers' waterflow in certain regions of Asia due to uneven precipitation and temperature distribution throughout the year. The rivers with basins within the reach of the monsoon climate ceratinly differ from the rivers flowing through other regions. A good example of this is the longest Asian river – the Yangtze (6380 km), the source of which is in the Tibetan Plateau. It flows to the east, towards the Pacific Ocean. The water levels in the Yangtze are high all year, but the highest ones are definitely in spring and summer, when the upper section of the river is supplied with water from melting snow and mountain glaciers. At the same time, the middle and lower section of the river receives heavy rainfall brought by the summer monsoon. A similar phenomenon occurs in many other rivers of Southeast Asia.
The rivers of North Asia are part of the basin of the Arcitc Ocean. The big rivers in that region are: the Lena (4400 km long), the Ob River (3650 km) and the Yenisei (3490 km). Their basins strech towards the cold subpolar and polar continental climate. As a result, they are covered with ice for 6‑7 months a year, and the highest water levels are observed in spring and summer, when the snow and ice in the source are are melting.
The situation is drastically different for the water network in Central Asia, in the endorheic area. Here one can find losing streamslosing streams. Many of them flow into endorheic lakes and swamps or get lost in the sands of the desert.
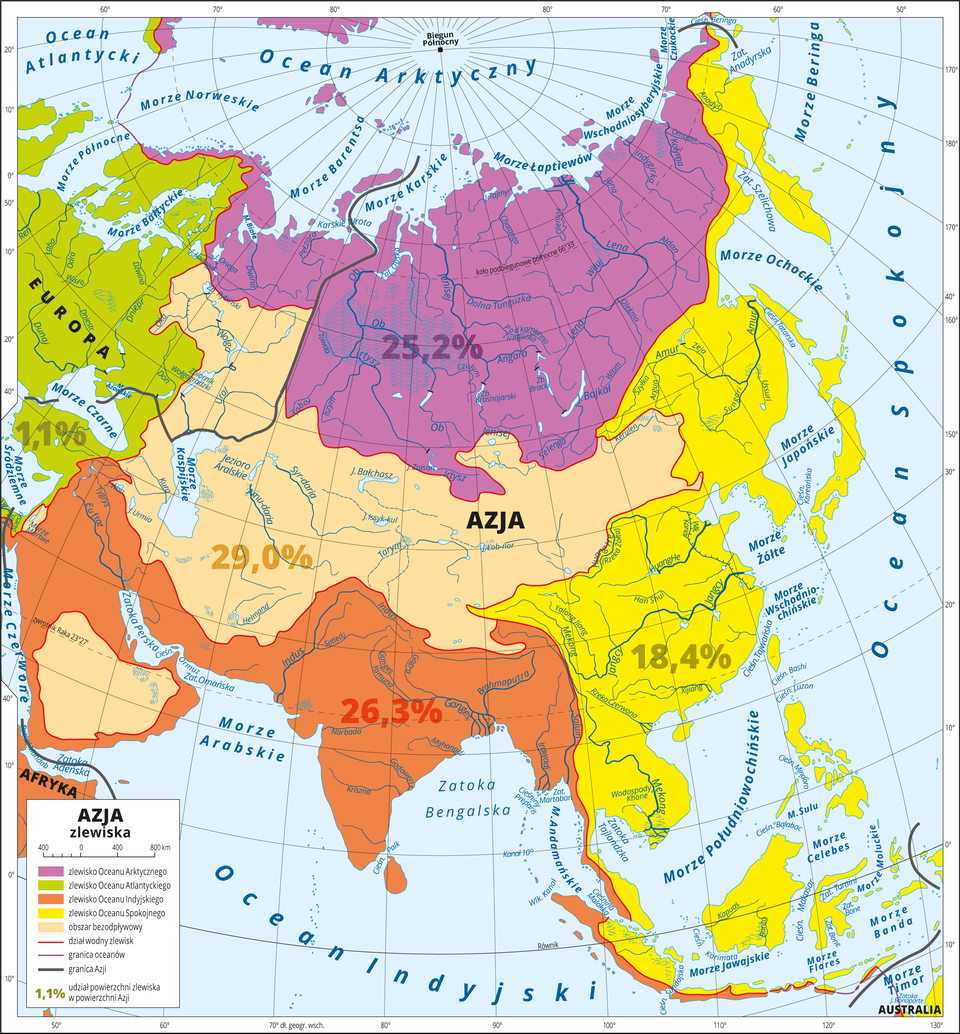
In Asia, there are numerous lakes. The biggest Asian lake is the Caspian Sea, a remnant of an ancient sea. Today, it is an endorheic reservoir with saline water. The bigesst drainage lake in Asia is Lake Baikal, in the basin of Yenisei. It is the deepest lake in the world. Lake Baikal is 1620 m deep. Located in the rift valley, it is the biggest freshwater reservoir in the world.
Lake Baikal is the deepest cryptodepression on the planet. Cryptodepression is a surface below the sea level covered with lake water. Count the depth of Lake Baikal's cryptodepression, knowing that the water surface is situated at 455 m above the sea lever and that the depth of the lake is 1620 m.
The Aral Sea was also a water reservoir once. However, it has been gradually drying out for several decades now due to the dry climate and human activities (people take too much water supplies from the rivers that feed the lake).
Another big and interesting endorheic lake is Lake Balkhash – there is saline water in its eastern part and fresh water in its western part, which is caused by the Ili River that flows into the lake.
Look at the photo below presenting the contrasts in the Asian waterway network.
Do the following exercises based on what you have learned in this class.
Put those Asian rivers in the correct order starting from the longest.
- the Ob River
- the Lena
- the Amur River
- the Yangtze
- the Indus River
- the Amu Darya
- the Ganges
- the Yenisei
Fill in the table based on the given example.
The Yangtze, The Lena, The basin of the Indian Ocean, The basin of the Arctic Ocean, The basin of the Pacific Ocean, The tropical climate area
| The Syr Darya | Endorheic basin | The temperate climate area |
|---|---|---|
| The basin of the Indian Ocean | ||
| The tropical climate area | ||
| The Yangtze | ||
| The Lena | ||
| The basin of the Arctic Ocean | ||
| The basin of the Pacific Ocean |
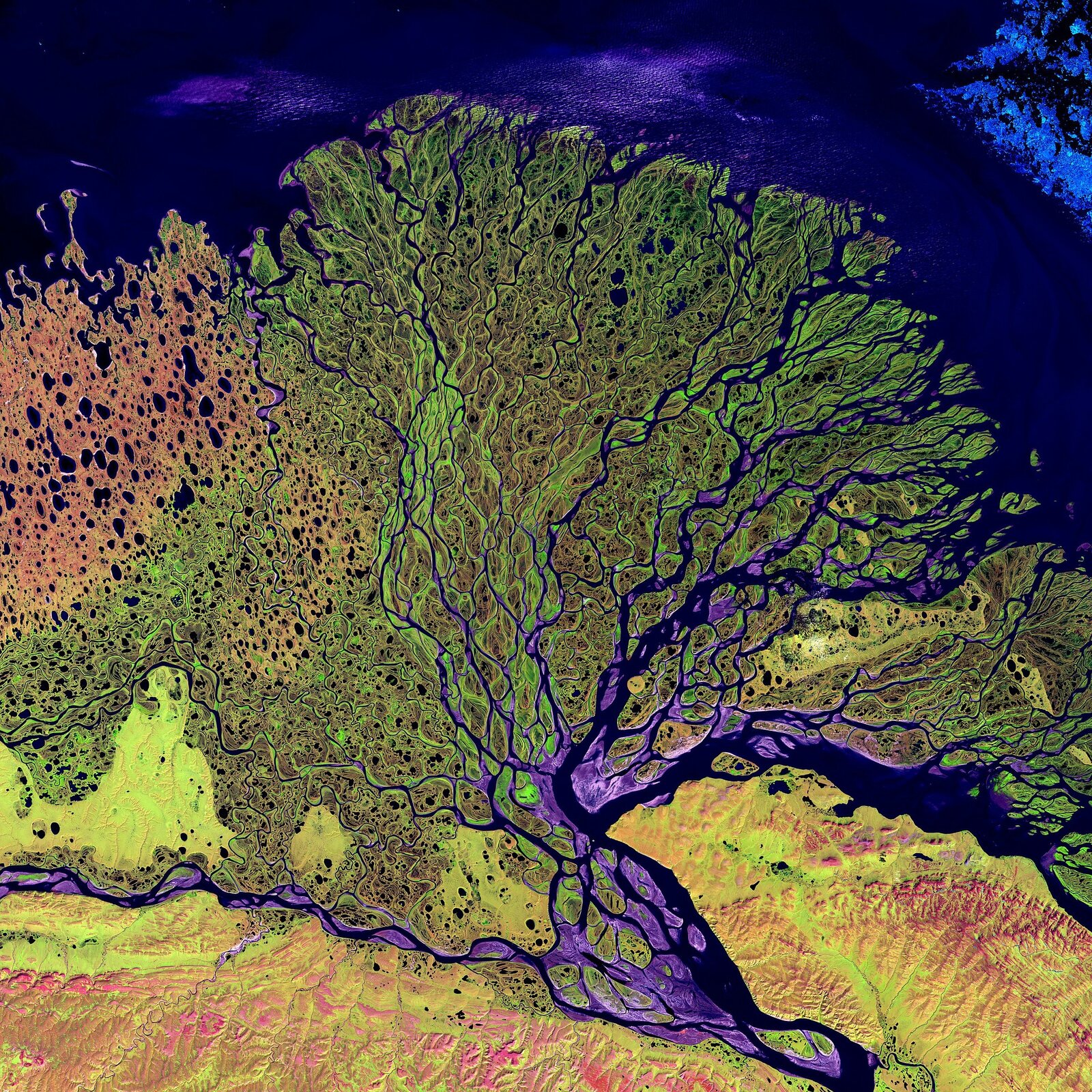

Choose the rivers of Asia that have the same type of outlet of the river that the one from the photo.
- The Ob River
- the Yenisei
- the Lena
- the Indus River
- the Yangtze
- the Ganges
Keywords
Asia, Asian waterways, drainage basin, endorheic basin
Glossary
rzeka okresowa – rzeka płynąca regularnie w okresie opadów, wysychająca zaś w porze suchej.
obszary bezodpływowe – teren, na którym płynące rzeki kończą swój bieg w jeziorach bezodpływowych lub wysychają po drodze. Wody tych rzek nie znajdują odpływu do żadnego z oceanów. Decydującym czynnikiem występowania takich obszarów jest klimat - wyjątkowo suchy, kontynentalny z przeważającym krajobrazem pustynnym i półpustynnym, ale też ukształtowanie powierzchni (kotliny, niecki, depresje).
zlewisko – zbiór dorzeczy, obszar lądowy, z którego wszystkie wody powierzchniowe i podziemne spływają do jednego morza, oceanu bądź też innego zbiornika wodnego.