Blue planet Earth
that in nature there is a water cycle between the atmosphere, land and surface and underground waters;
that life originated in water;
different types of surface waters.
to show the oceans on the map;
to explain what the sea is;
to discuss the phenomenon of low and high tides.
The oceans of the globe
It seems that rivers and lakes contain a lot of water, but it is only a small part of what we will find in the oceans. Fresh water accounts for merely 3.5% of the water on the Earth (glaciers, surface and underground water on land). The rest is salt water contained in seasseas and oceans. All oceansoceans are interconnected, forming a huge body of water called the World Ocean or Global OceanWorld Ocean or Global Ocean.
An ocean is a very vast area covered by saline water, partly separated from other bodies of water. Distinct boundaries of oceans occur only where they border on continents or archipelagoesarchipelagoes or are established arbitrarily (e.g. they are established in places where there are significant differences in temperature and water salinity). Today, we divide the World Ocean into 4 oceans.
The Pacific Ocean, also called the Pacific, is the largest – it accounts for almost a half of the Earth's volume of saline water. It extends from the eastern coastal areas of Asia and Australia to the western coastal areas of both Americas, and in the south it is bounded by Antarctica.
The Atlantic Ocean lies between the western shores of Europe and Africa and the eastern coasts of both Americas.
The Indian Ocean lies between eastern Africa, southern Asia, western Australia and Antarctica.
The Arctic Ocean lies around the North Pole and is almost completely surrounded by the northern shores of Asia, Europe and North America. It has a well‑developed coastline with numerous bays.
Pacific Ocean | Atlantic Ocean | Indian Ocean | Arctic Ocean | |
Surface (million kmIndeks górny 22) | 179 | 92 | 76 | 14 |
Average depth (km) | 4 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
The largest depth (km) | 11 | 9 | 7 | 5 |
Some scholars also distinguish the fifth ocean – Southern Ocean (Antarctic Ocean). It is supposed to encircle Antarctica and reach the 60°S parallel. It differs from the neighbouring oceans because of lower water temperatures. This difference is caused by strong sea currents that prevent the mixing of warm and cold water.
Seas
Some parts of the oceans differ from the neighbouring water bodies in terms of their physical, chemical or biological properties. We call these areas seas. They are at least partially separated by continental shores, clusters of islands (archipelagos), peninsulas or underwater sea‑bottom elevations. A fragment of the sea surrounded by land on three sides is called a baybay.
Poland has access to one sea – the Baltic Sea, which is a part of the Atlantic Ocean. The Baltic Sea is enclosed by land on all sides and only a few straitsstraits connect it with the North Sea. The Baltic Sea is shallower than most other seas and its salinity is much lower.

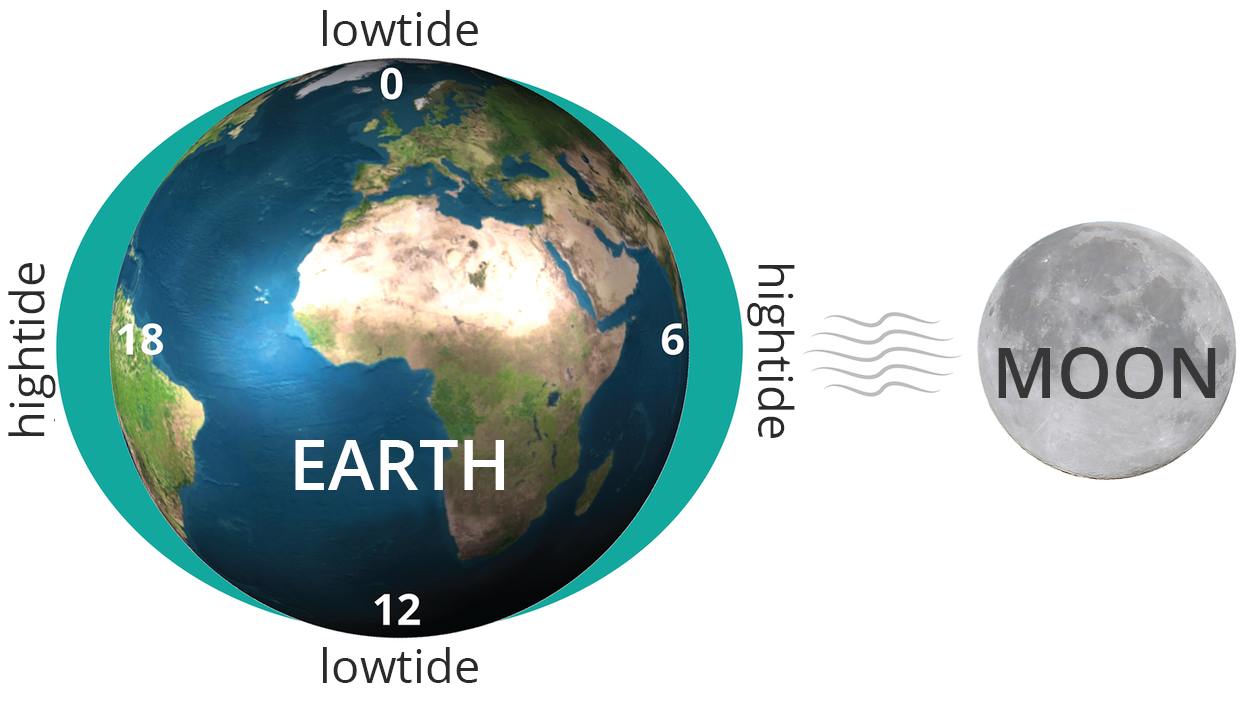
Tides
The water of the World Ocean is in constant motion. TidesTides are the alternate rising (high tide) and falling (low tide) of the water level in the seas and oceans. The tides are mainly caused by the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon. As a result, in sea areas that are closer to the Moon in a given moment, and on the opposite side of the globe, the water level rises, i.e. a high tide occurs, while in other areas the water level falls, that is a low tide is observed. Due to the rotation of the Earth around its own axis, high tide and low tide alternate approximately every 12.5 hours. Therefore, it is possible to calculate the time of high tide and low tide in a given place, which is very important, for example, in port cities.
Before you watch a film entitled “Tides”, write down a research question and a hypothesis. Watching the film, write down your observations and, finally, your conclusions.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film wykonany w technice timelapse, przedstawiający zjawisko pływów morskich.
Complete from the list.
Arctic, Western, Indian, Of Australia, Eastern, Arctic, Of Antarctica, Of South America, Atlantic, southern, Pacific, Antarctic, Europe
The largest ocean is the ................................ Ocean. The smallest of the oceans, the ................................ Ocean, lies in the Northern Hemisphere between the shores of North America, ................................ and Asia. The Indian Ocean lies in the ................................ hemisphere.
Summary
Most of the Earth's surface is covered by the Global Ocean.
At present, we distinguish 4 oceans: Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean and Arctic Ocean.
Some parts of the oceans, separated for example by straits and islands, are called seas.
The alternate rising and falling of the water level in seas and oceans is called tides.
Key words
ocean, sea, the Pacific, high tide, low tide
Match the pairs: English words with Polish definition.
ogół wód pokrywających kulę ziemską (poza wodami śródlądowymi) składający się z oceanów i mórz; oceany i morza wszechoceanu są połączone ze sobą, cykliczne zmiany poziomu wody w morzu lub oceanie; podniesienie poziomu nazywamy przypływem, a obniżenie --- odpływem, część większego obszaru wodnego (oceanu, morza, jeziora) otoczona z trzech stron lądem, część wszechoceanu ograniczona przez sąsiadujące kontynenty, wyspy i ich archipelagi lub wydzielone z powodu róznic w zasoleniu i temperaturze wody, grupa wysp położonych blisko siebie, najczęściej zbudowanych z podobnych skał, zwężenie obszaru wodnego łączące dwa oceany, morza lub jeziora; rozdziela dwa lądy, naturalna część oceanu oddzielona od otaczających ją wód brzegami lądów, wyspami, półwyspami albo w inny sposób powodujący, że wody tego morza różnią się od sąsiednich
| archipelago | |
| strait | |
| sea | |
| ocean | |
| tides | |
| World Ocean | |
| bay |
Glossary
archipelag – grupa wysp położonych blisko siebie, najczęściej zbudowanych z podobnych skał
cieśnina – zwężenie obszaru wodnego łączące dwa oceany, morza lub jeziora; rozdziela dwa lądy
morze – naturalna część oceanu oddzielona od otaczających ją wód brzegami lądów, wyspami, półwyspami albo w inny sposób powodujący, że wody tego morza różnią się od sąsiednich
ocean – część wszechoceanu ograniczona przez sąsiadujące kontynenty, wyspy i ich archipelagi lub wydzielone z powodu róznic w zasoleniu i temperaturze wody
pływy – cykliczne zmiany poziomu wody w morzu lub oceanie; podniesienie poziomu nazywamy przypływem, a obniżenie – odpływem
wszechocean – ogół wód pokrywających kulę ziemską (poza wodami śródlądowymi) składający się z oceanów i mórz; oceany i morza wszechoceanu są połączone ze sobą
zatoka – część większego obszaru wodnego (oceanu, morza, jeziora) otoczona z trzech stron lądem



