Lineage and family tree
genes exist in varieties called alleles that can be dominant or recessive;
the A and B antigens present on the surface of erythrocytes determine the group of human blood;
serological conflict can occur when the mother has a blood group Rh- and the child Rh +.
describe the inheritance of selected traits in humans.
Lineage and family tree
The inheritance of selected traits, e.g. blood groups, can be represented in subsequent generations using a family tree. It is a schematic record of the way inheritance of a given feature within a related group of people. In order to create such a tree, it is necessary to determine who showed the trait we were interested in in particular generations and who inherited it. After saving the tree, we can determine the phenotypesphenotypes and genotypesgenotypes of individual family members and the probability of the appearance of the examined feature in subsequent generations.
Huntington's disease is caused by mutation of a single gene in chromosomechromosome 4. The mutant gene is dominant. It creates a protein with toxic properties that is deposited in nerve cells and causes them to die. The disease consists of progressive dementia and is usually manifested after the age of 35. Usually, the holders of the defective gene already have offspring. Statistically, half of the offspring of a person with a defective alleleallele will inherit this disease.
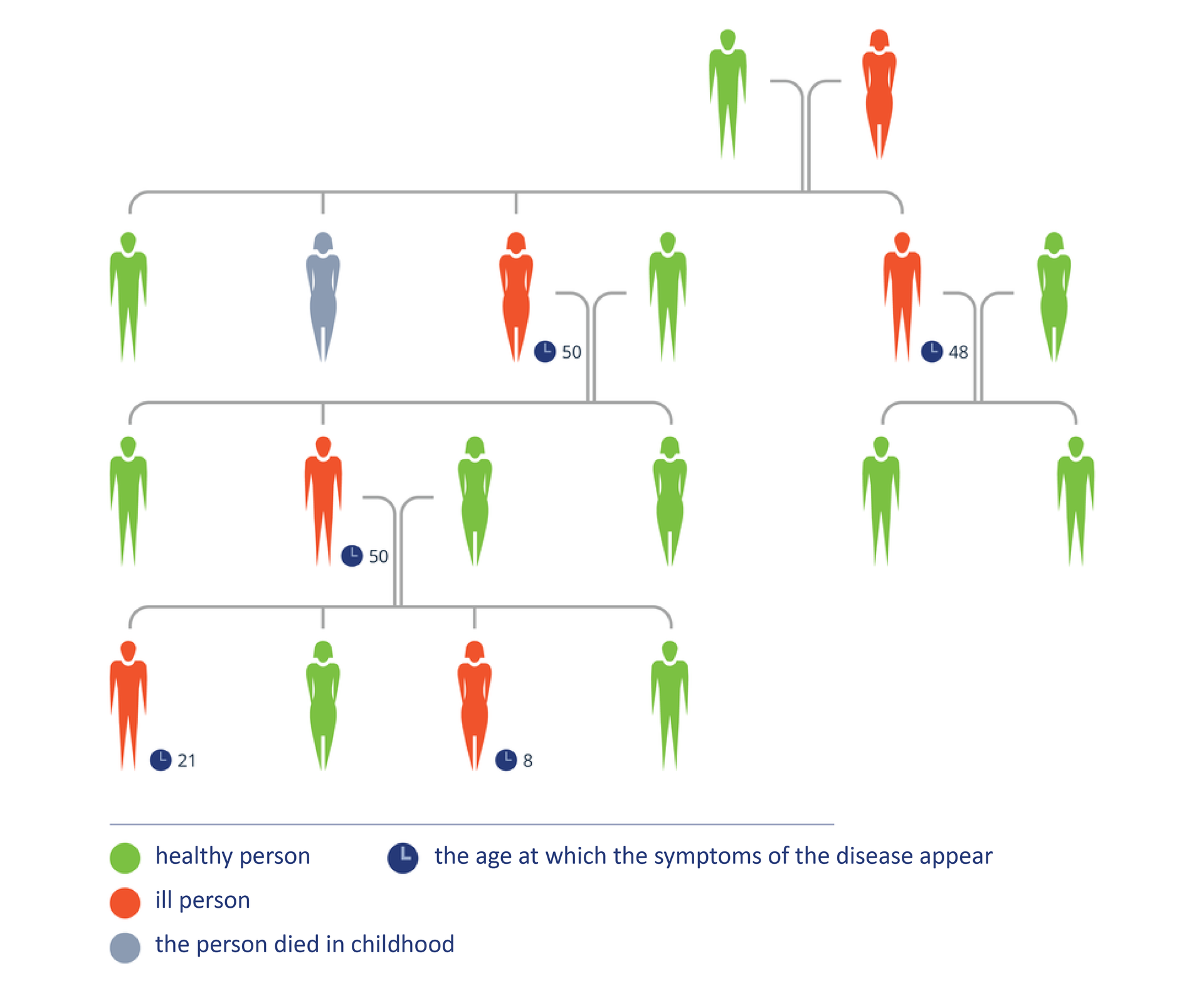
Was the mother of the line shown in Figure 5 homo- or heterozygous for the gene that causes Huntington's disease? Based on what fact can this be determined?
What is a family tree? Indicate the correct answer.
- one of the terms denoting a genetic cross
- a method of a schematic record of the inheritance of a given feature within a family
- the way in which the genotype of future offspring can definitely be determined
- one of the terms denoting a genetically determined disease
Summary
The inheritance of selected traits, e.g. blood groups, can be represented in subsequent generations using a family tree.
Keywords
inherited diseases, lineage, family tree
Glossary
allel – jedna z dwóch lub więcej odmian danego genu, odpowiedzialnego za wytworzenie konkretnej cechy organizmu; allele danego genu są położone w określonym miejscu na chromosomie
chromosomy – podziałowa postać DNA; wydłużone, pałeczkowate struktury powstające z nici DNA w jądrze tuż przed podziałem komórki i widoczne w czasie podziału jądra
fenotyp – zespół wszystkich cech budowy i fizjologii organizmu wyznaczanych przez genotyp i środowisko
genotyp – zespół wszystkich genów danego osobnika warunkujący jego cechy; pojęcie czasem (w krzyżówkach genetycznych) używane w odniesieniu do jednej lub kilku par alleli