Ecosystem diversity
biocenosis and biotope form an ecosystem;
the ecosystem diversity is one of levels of biological diversity;
presence of species in a given ecosystem depends on abiotic and biotic factors;
human actions pose a thread to the biodiversity.
explaining what ecosystem diversity is;
determine and characterize 9 main biomes.
Ecosystem diversity means the diversification of natural habitats and ecosystems functioning within them. The main natural factor being a precondition for global diversity of land ecosystems is climate. It depends, amongst the others, on a distance from oceans and seas, land formation, and elevation above sea level. Individual climate zones have characteristic plant cover which, together with abiotic conditions, influences associations of bacteria, protists, fungi and animals inhabiting them.
Complexes of ecosystems of similar climate conditions, spatial structures and plants and animals are called biomesbiomes. Biomes characteristic for a specific latitude are included in one category, although they may differ in terms of many species inhabiting them (e.g., when continents were isolated from each other for a long time). Examples of such biomes are deciduous forests of the temperate zone in North and South Americas, or deserts in Autstralia and Africa.
Nine main biomes are recognized rainforestsrainforests (tropical), savannahsavannah, desertsdeserts and semideserts, sclerophyllous scrubsclerophyllous scrub, steppessteppes, deciduous and mixed forests, taigataiga, tundratundra, and mountain areas.
The biome of tropical rainforest is characterised by the highest biodiversity of all land ecosystems.
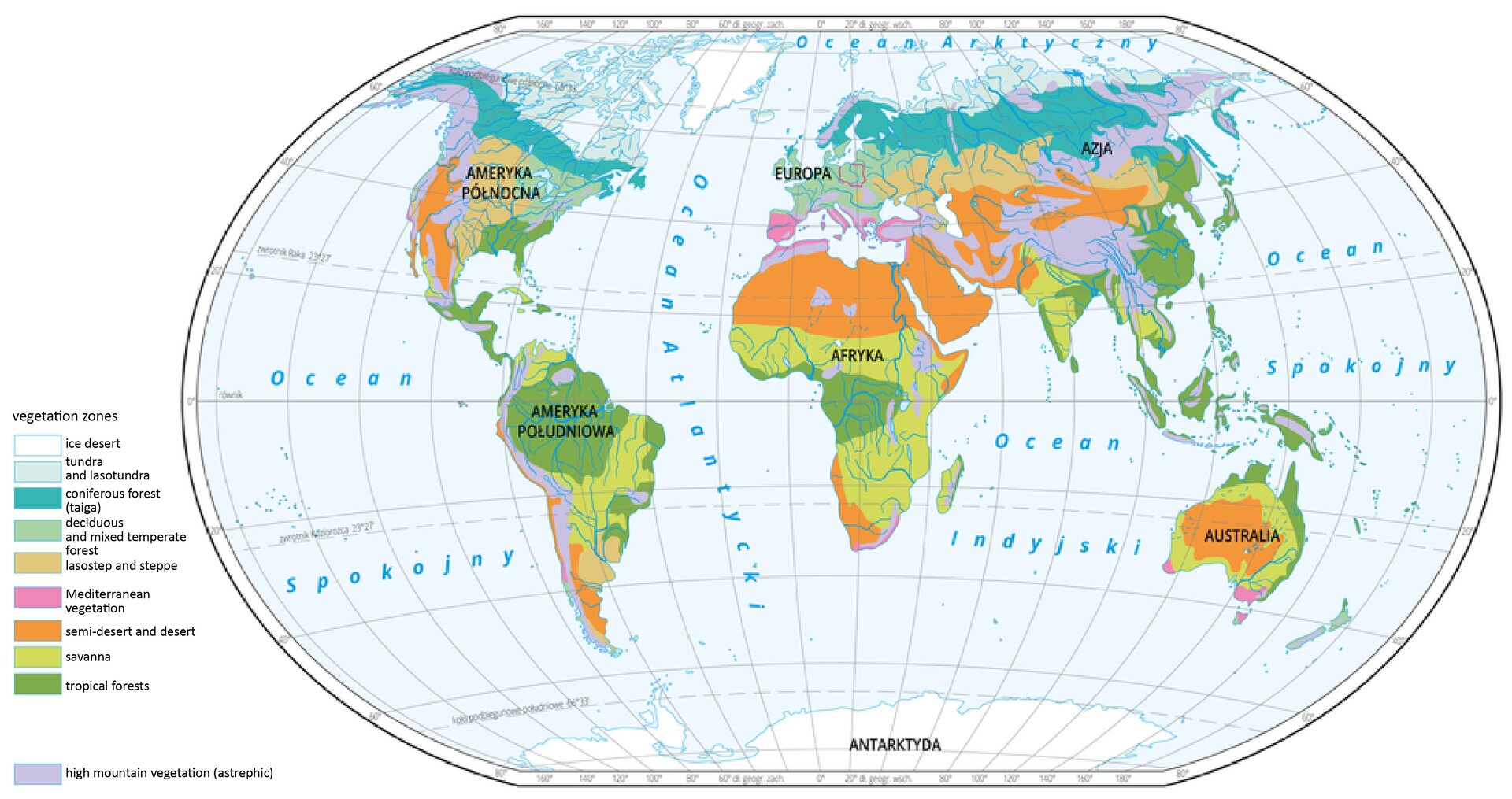
Using your geographical knowledge explain why biomes are arranged latitudinally in Eurasia, and longitudinally in both Americas.
What does the term ecosystem diversity mean? Mark a correct answer.
- diversification of species inhabiting a given ecosystem
- diversification of natural habitats and ecosystems functioning within them
- diversification of a genetic pool in a population of the same species inhabiting different ecosystems
- diversification of ecosystems resulting from the area covered by them
Mark all features characterizing a biome.
- similar climate conditions
- similar spatial structure
- similar plants and animals
- no geographic isolation
Conclusion
The main natural factor being a precondition for ecosystem diversity on a global scale is climate.
Biomes are complexes of ecosystems of similar climate conditions, spatial structures and plants and animals.
1. Which area is characterized by greater diversity of ecosystems: The Himalayas or lands behind a polar circle? Provide grounds for your answer, referring to different factors on which ecosystem diversity depends.
2. Indicate which common pot plants come from the tropical rainforest zone. Describe their features represeting adaptation to the life in that biome.
Keywords
ecosystem, biome, plant zones
Glossary
biom – zespół ekosystemów o zbliżonych warunkach klimatycznych, podobnej strukturze przestrzennej oraz zbliżonej florze i faunie
lasy deszczowe – biom o bardzo wysokiej różnorodności biologicznej, wykształcający się w strefie równikowej na obszarach cechujących się obfitymi, całorocznymi opadami deszczu, wysoką wilgotnością powietrza i temperaturą powietrza utrzymującą się przez cały rok na stałym poziomie (ok. 25°C i wykazującą niewielkie wahania dobowe), gdzie okres wegetacji trwa cały rok; występują w nim głównie szerokolistne, wiecznie zielone drzewa, wysokie byliny, epifity i pnącza; stanowi on miejsce życia dla tysięcy gatunków zwierząt
pustynia – biom formujący się na obszarach zwrotnikowych i podzwrotnikowych, cechujący się suchym lub skrajnie suchym klimatem z małą ilością opadów, nieprzekraczającą 200 mm w ciągu roku, a co za tym idzie – znikomą pokrywą roślinną
sawanna – biom występujący na obszarach podrównikowych w klimacie gorącym z długą porą suchą (średnio 5‑7 miesięcy) oraz stosunkowo krótką porą deszczową (3‑5 miesięcy), o rocznej sumie opadów wahającej się od 200 do 500 mm rocznie; jego roślinność stanowią głównie trawy, wśród których spotkać można pojedyncze krzewy i drzewa
step – biom formujący się w głębi kontynentów w klimacie umiarkowanym ciepłym, cechujący się stosunkowo niską liczbą opadów (250‑400 mm rocznie); charakteryzuje się roślinnością trawiastą z dużą domieszką roślin zielnych, zwykle tworzących zbitą darń
tajga – zwana także borealnym lasem iglastym; biom występujący w klimacie umiarkowanym chłodnym, dla którego charakterystyczne są długie okresy mroźnych zim oraz niska roczna suma opadów (400‑600 mm); typowa dla tego biomu formacja roślinna to las iglasty
tundra – biom wykształcający się w klimacie okołobiegunowym subpolarnym, cechującym się panującą przez zdecydowaną większość roku ujemną temperaturą; gleby tundry pokryte są warstwą wiecznej zmarzliny; występują w niej jedynie mchy i porosty, nieliczne trawy, karłowate drzewa, niewielkie krzewy i krzewinki
zarośla twardolistne – biom występujący na obszarach podzwrotnikowych, gdzie temperatura jest dodatnia przez cały rok, lata są suche i gorące, a zimy ciepłe i wilgotne; występuje w nim głównie roślinność o grubych i skórzastych liściach, których budowa ogranicza utratę wody w wyniku parowania