A paradise for dissenters
what religions predominated during the existence of the Polish‑Lithuanian Commonwealth;
what the Union of BrestUnion of Brest of 1596 was about.
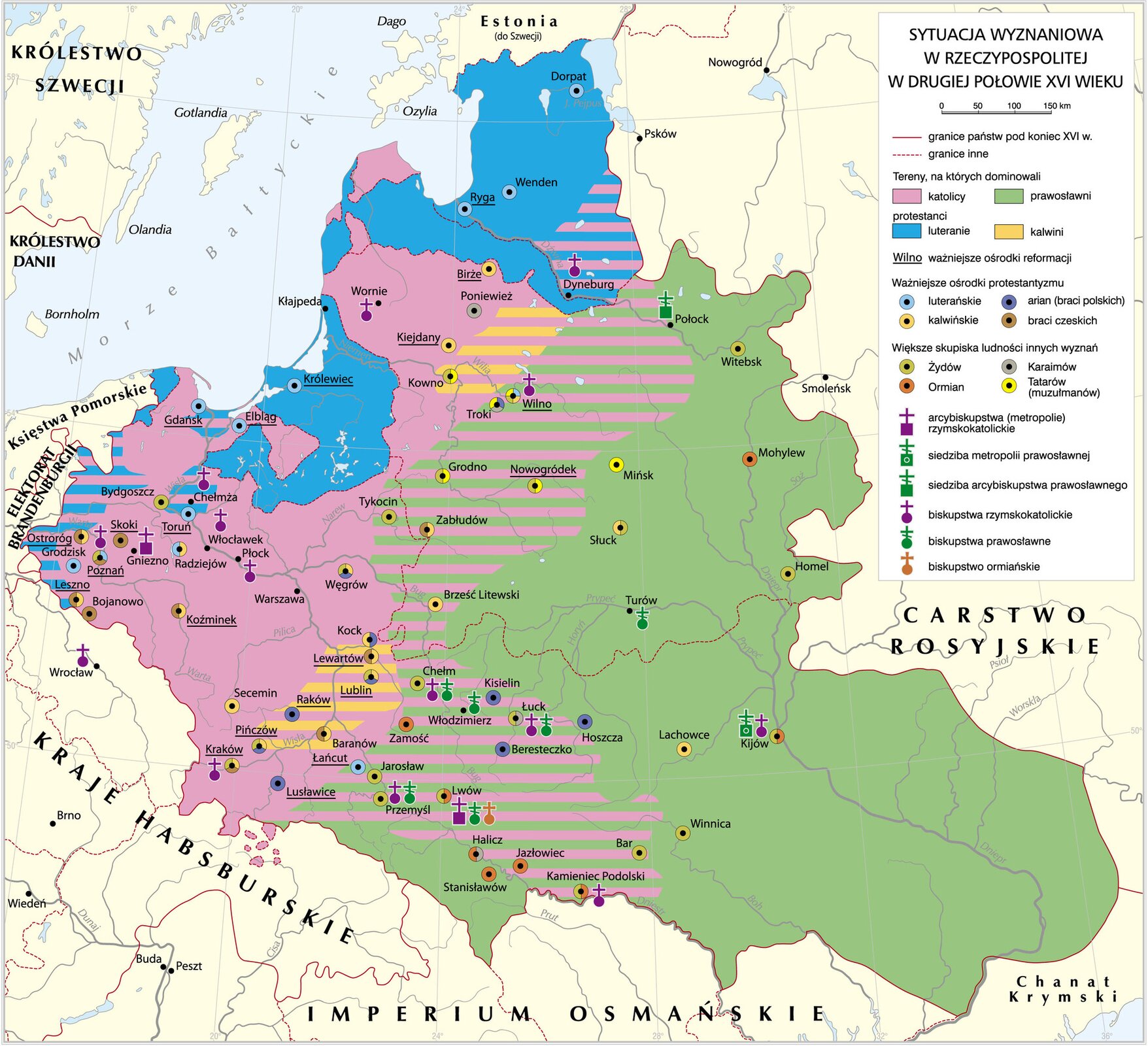
The period of the Polish‑Lithuanian Commonwealth was very diversified in respect of denominations. Earlier, there were two dominating religions. In the area of Greater Poland, Mazovia, Royal Prussia and Lithuania – Western Catholicism, and the Eastern Orthodox ChurchEastern Orthodox Church in the east. In the Catholic church, the hierarchy was linked with the state administration. Large social events were always combined with religious activities (e.g. coronation, election). The second largest denomination after Catholicism was the Eastern Orthodox ChurchEastern Orthodox Church. In 1596, Union was signed in Brest‑on‑the‑BugUnion was signed in Brest‑on‑the‑Bug, in the result of which the Greek Catholic Church in Poland was created. It was a church formed by a part of the OrthodoxOrthodox clergy and believers who recognised the authority of the Pope as the head of the Church and adopted the Western Catholic dogmas.
The beginning of the 15th century was the time of the Protestant ReformationReformation. When the works of Martin Luther arrived to Poland from Germany, where they had been printed, many clerics – following the reformerreformer – abandoned their orders and parishes, and rejected celibacy. Other, who had not abandoned the clerical status, started to preach in the Lutheran spirit. The Lutheran doctrine developed in the Polish land mainly in the areas formerly belonging to the Teutonic Order. Calvinism also found supporters in our country. The social group which found it the most suitable, were medium nobles. This denomination met with the approval of these circles, because it ensured the increase of their power at the expense of the clergy, and subordinated local life to landowners. A large non‑Christian religious group in the Commonwealth were Jews. Jewish religious communities enjoyed broad autonomy in the administrative system of the Commonwealth. The religious diversity had a positive impact on Polish culture. It contributed to the development of literature – especially literary language, education and science.
Get acquainted with the most important to the Church events of the Polish‑Lithuanian Commonwealth era and organize your knowledge. Which of the events were the most important and why?
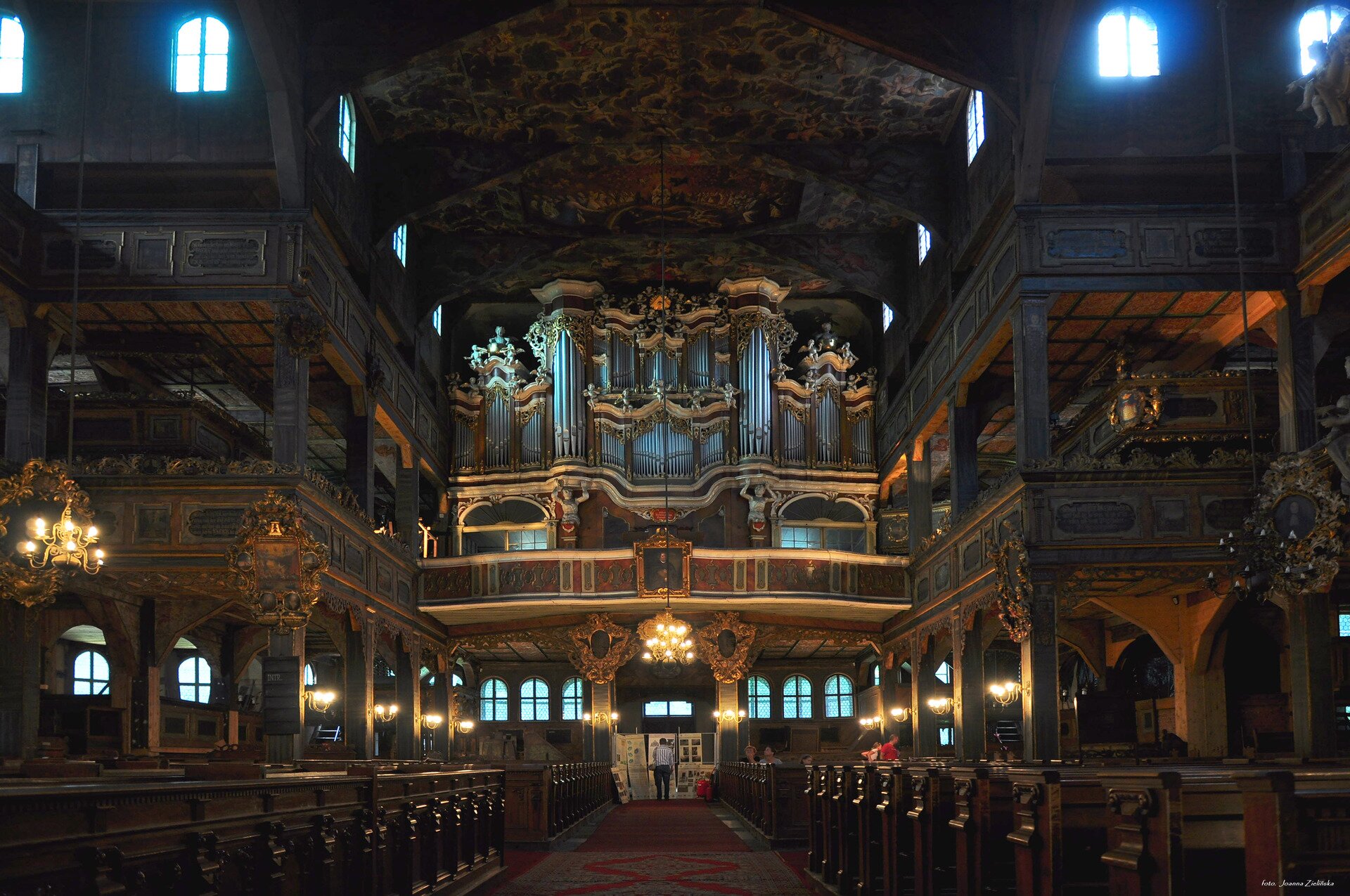
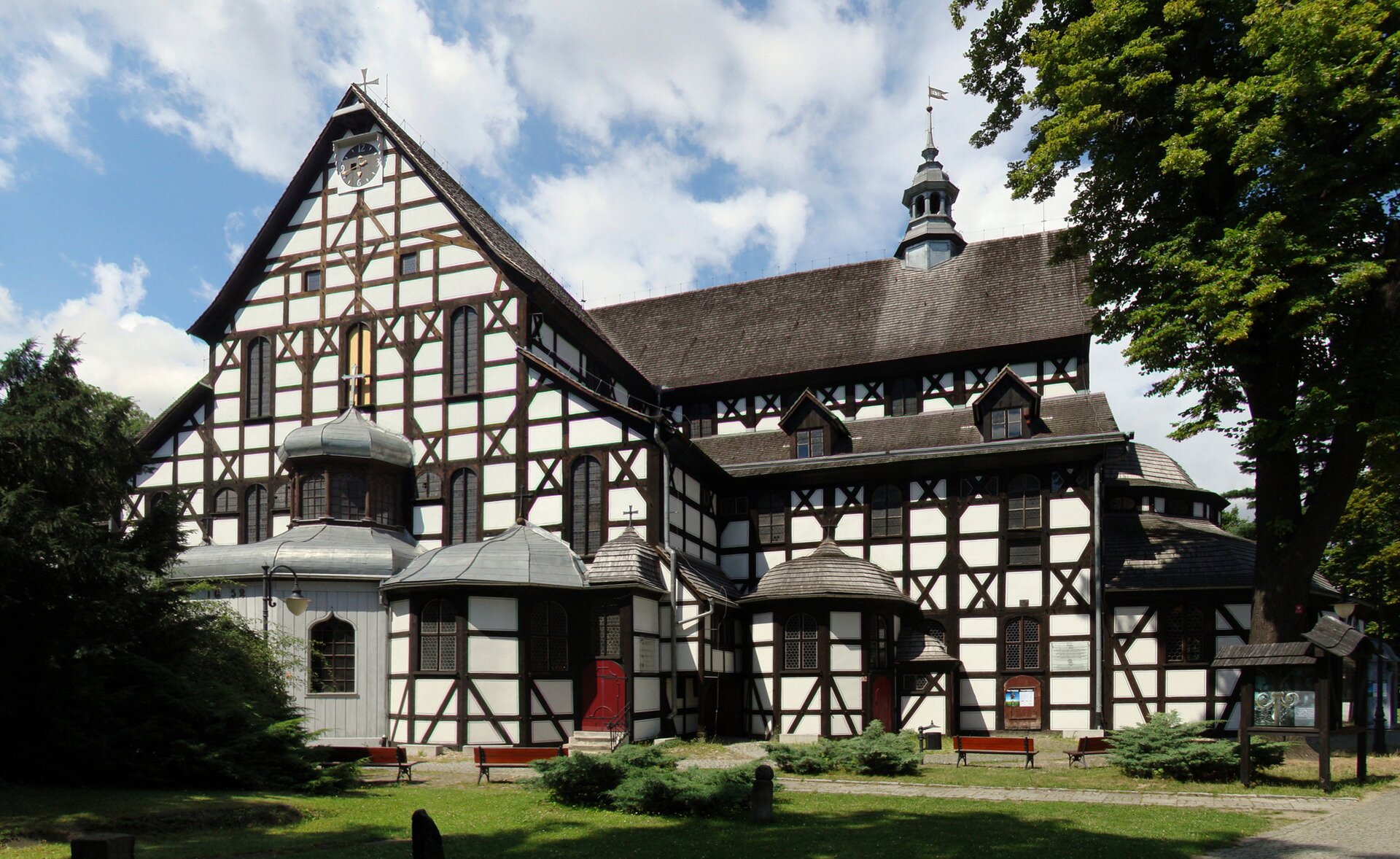
Look for information about the Churches of Peace. Why they were created and what characterized them?
Match terms to definitions.
the union of churches concluded in 1596 in Brest between some of Eastern Orthodox Church bishops of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Western Catholic Church., Jewish religious communities., Eastern ritual Christianity., tolerant approach to the religious beliefs of others.
| Qahals | |
| Eastern Orthodox Church | |
| Union of Brest | |
| Religious tolerance |
Keywords
religion, protestants, Eastern Orthodox, Martin Luther, Calvinism, Teutonic Knights, Reformation
Glossary
Kahały – żydowskie gminy wyznaniowe.
Prawosławie – wyznanie chrześcijańskie obrządku wschodniego.
Unia brzeska – unia kościelna zawarta w 1596 r. między częścią biskupów prawosławnych Rzeczypospolitej Obojga Narodów a Kościołem katolickim w Brześciu.
Tolerancja religijna – postawa tolerancji dla poglądów religijnych innych osób.
Reformacja – ruch religijno‑polityczno‑społeczny zapoczątkowany przez Marcina Lutra, mający na celu odnowę chrześcijaństwa.

