Africa – soil and vegetation zones
that Africa lies symmetrically to the Equator;
the interdependences between climate, vegetation and soil in each area;
what are the climatic factors;
what climate elements are there;
how to read data from a climatic diagram;
what elements of natural environment are there.
the reasons for the symmetrical location of the climate, soil and vegetation zones in Africa;
the examples of interdependencies between climate, soil and vegetation in each African landscape region;
to enumerate characteristic plants and animals in the African landscape regions;
to read dominating soils in each landscape region from the map.
Africa – symmetrical location with respect to the Equator, landscape
Africa is the second biggest continent in the world after Asia. It has an area of 30.3 million km Indeks górny 22. The solid landmass is crossed by the Equator, and the land is positioned towards it almost symmetrically. The prime meridian also goes through Africa.
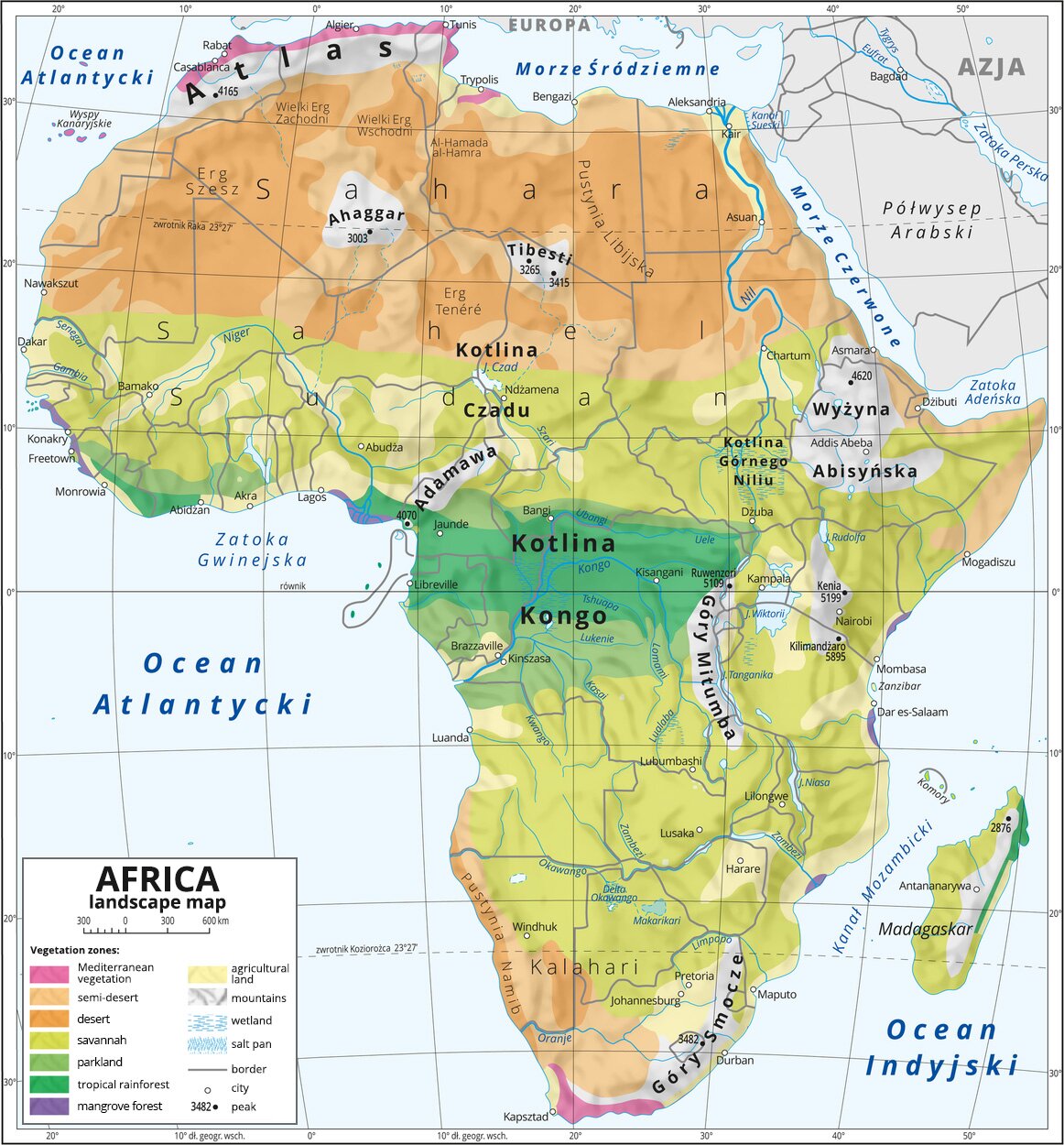
Analyse and describe each of the African zones in terms of vegetation, soil and animals that can be found there. Use various sources of information (geography textbook, geography e‑textbook, Internet resources, geographical atlas). Compare your descriptions with the answers provided by other students.
Using the knowledge acquired in class, do the exercises below.
Match correct information regarding vegetation and soil with the corresponding landscape zones.
|
subequatorial climate
|
xerophytes
|
red and yellow laterite soils
|
|
equatorial climate
|
cacao trees, philodendrons, mahogany trees
|
brown soils
|
|
tropical climate
|
grassy vegetation with individual trees
|
red laterite soils
|
|
subtropical climate
|
sclerophylls with myrtles, laurus and oleanders
|
greyzems and soils in an early stage of development
|
Soils
Africa has a diverse soil cover, which depends on the climate zone, vegetation cover and terrain. The soil cover is symmetrical with respect to the equator, excluding mountainous areas in the east and north of the continent and a large area of the Sahara. Equatorial Africa is dominated by the laterite soils of wet forests as well as red and reddish‑brown soils. Red soils predominate in the savanna zone. Between the savannah zone and the Sahara, there are lixisols, sporadically also black soil occurs. In the Sahara Desert and in South Africa, sandy and gravel soils are the initial soil. Salty soils, solonchak and solonetz, are often found due to salinity. There are characteristic gray desert soils in the Sahara's interior. In the valleys of large rivers there are riverine, alluvial soils. In the Mediterranean zone there are terra rosa, brown soils, brown mountain soils and dry forest soils - these soils are characteristic soils of the Mediterranean coast. In the Great Rift Valley there are podzoluvisols, mountain‑meadow soils and volcanic soils. The reason for the formation of red‑colored soils are iron oxides, which penetrate deep into the soil profile. The soils in the humid zone have a clay‑like consistency, while in the dry zone the soils are made up of loose particles.
Vegetation
African vegetation is diverse. It shows a significant relationship with climatic zones, especially with rainfall. Only in Madagascar, vegetation belts have a shape similar to the meridian, however, this is largely associated with unusual climatic conditions on the island. Regardless of the flora, vegetation of Africa exhibits a certain symmetry with respect to the equator. On the northern and southern extremities, there is a strip of damp vegetation, then stripes or patches of desert, semi‑desert, savanna and equatorial vegetation are located towards the equator.
In which climatic zones do the animals in the pictures live? If you don’t know, reverse the flashcard.
| {image#Elephant} | Elephant – Equatorial zone |
| {image# Fennec fox } | Fennec fox- Tropical dry climate |
| {image# Gorilla } | Gorilla – Tropical rainforest zone |
| {image# Lion} | Lion - Equatorial zone |
| {image#Camel} | Camel - Tropical dry climate |
| {image# Mouflon } | Mouflon – Subtropical zone |
Match the pairs: English words with Polish definition.
rośliny sucholubne, które mogą przetrwać długotrwałą suszę, ponieważ mają silnie rozwinięty system korzeniowy lub posiadają sztywne, przekształcone w ciernie liście, utrudniające parowanie wody. Do kserofitów zaliczamy na przykład rozmaryn, aloes., roślina rosnąca na innej roślinie, ale zwykle nie prowadząca pasożytniczego trybu życia. Korzysta z innego gatunku jako podpory, a odżywia się najczęściej samodzielnie
| epiphyte | |
| xerophyte |
Keywords
savannah, Africa, equatorial forests
Glossary
epifit - roślina rosnąca na innej roślinie, ale zwykle nie prowadząca pasożytniczego trybu życia. Korzysta z innego gatunku jako podpory, a odżywia się najczęściej samodzielnie
kserofit - rośliny sucholubne, które mogą przetrwać długotrwałą suszę, ponieważ mają silnie rozwinięty system korzeniowy lub posiadają sztywne, przekształcone w ciernie liście, utrudniające parowanie wody. Do kserofitów zaliczamy na przykład rozmaryn, aloes.