At the lake
what the living conditions are in water;
the features of specific parts of a river;
how plants and animals have adapted to living in rivers.
to differentiate between the littoral, pelagic and benthic zones;
to describe the conditions in the different zones of a lake;
to evaluate the living conditions in each lake zone;
to recognise selected plants and animals which live in a lake.
Living conditions in lakes
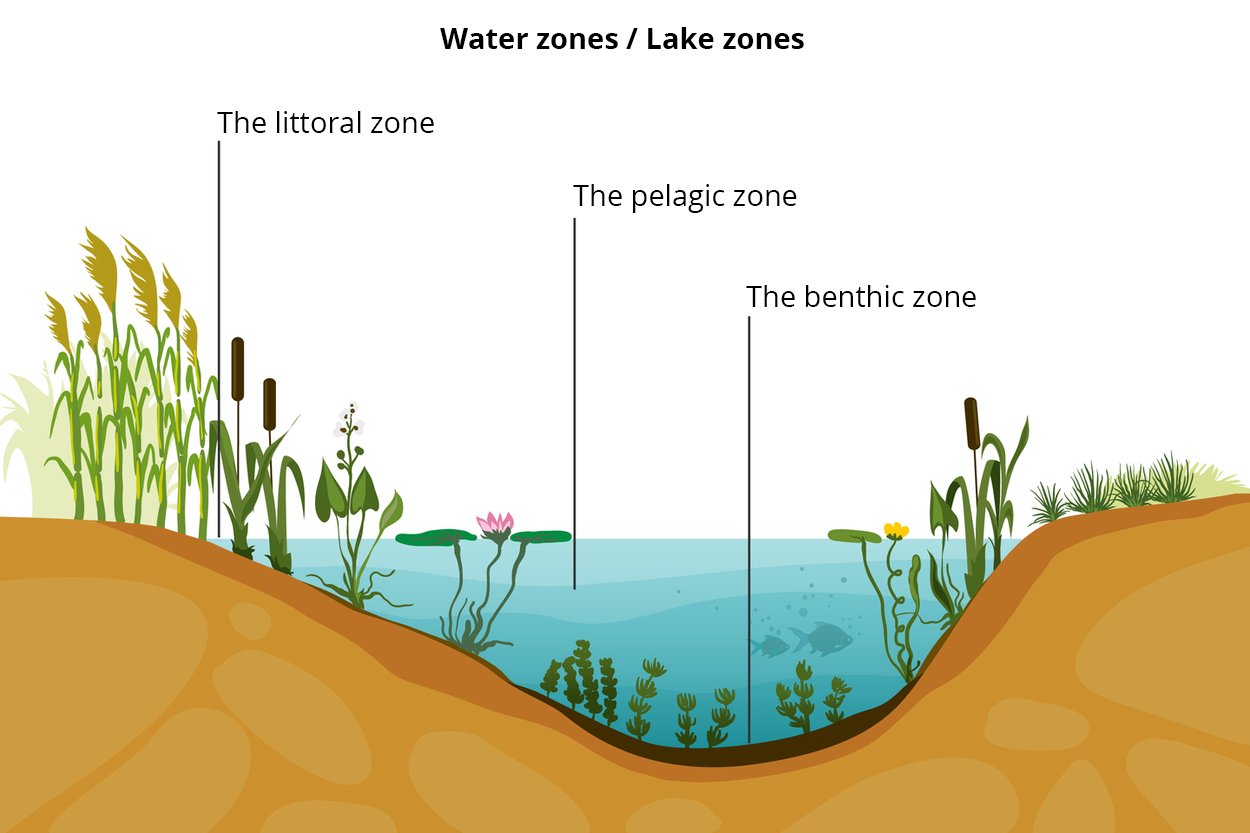
A lake is an inland body of water, which is formed in a natural depression filled with surface or underground water. It is inhabited in almost its entirety by organisms. The waters of a lake can be divided into three main zones: littoral, pelagic and benthic.
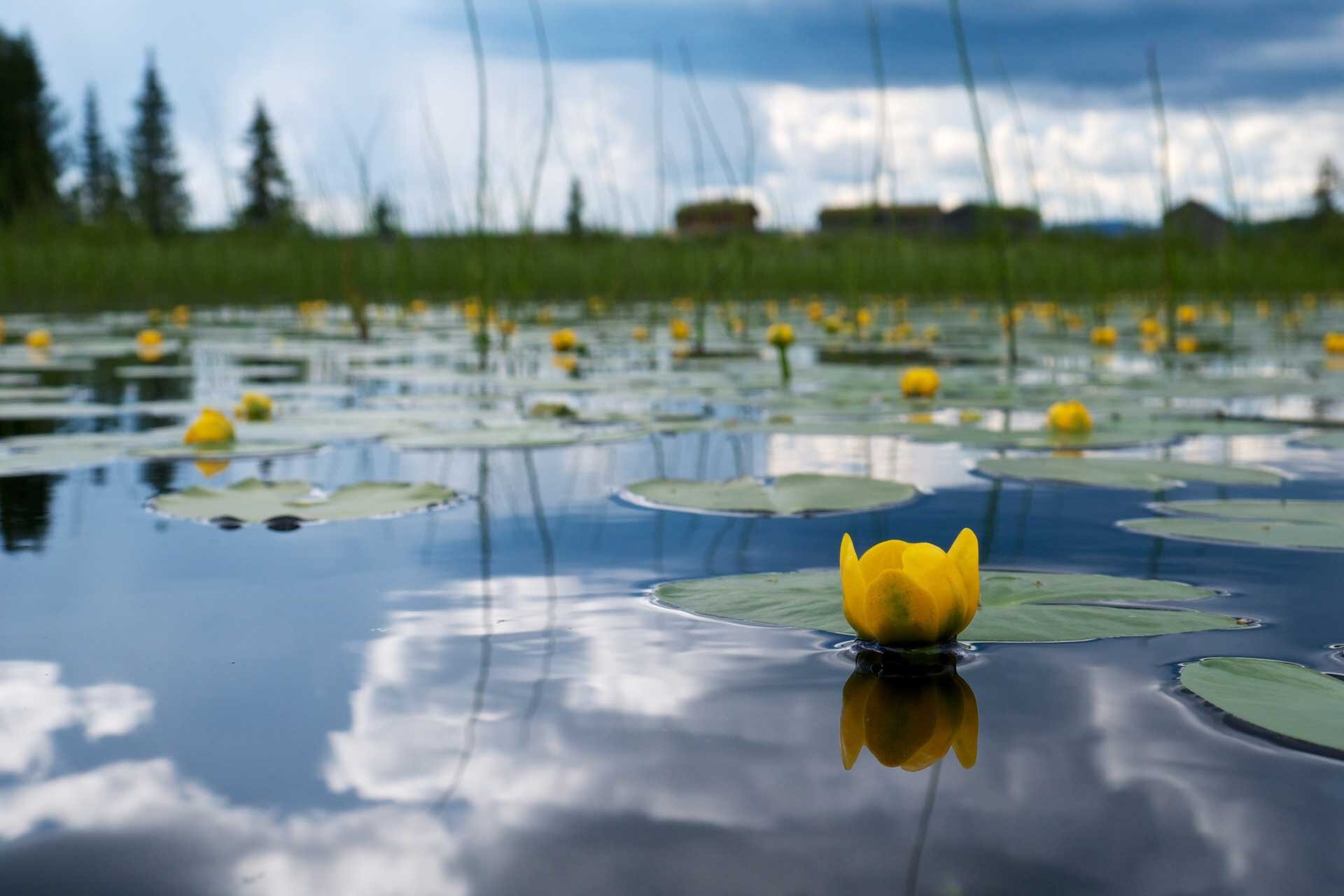
The littoral zoneThe littoral zone is so shallow that sunlight reaches the bottom. Due to this, plants can grow there. The water is well oxygenated and permanently supplied with minerals, which drift down with rain water. In this zone, however, fluctuations in the lake's water levels can be most strongly felt, along with rippling and pollution reaching the lake from land. Large temperature changes occur here throughout the day and over the course of the year.
The pelagic zoneThe pelagic zone denotes the open expanse of water away from the banks, which does not have contact with the bottom. It reaches such a depth that the Sun's rays still penetrate it, and so its depth is dependent on the water's transparency. Living conditions for organisms quickly worsen as the depth increases in this zone, as the amount of light and the oxygen content of the water decrease, and the water temperature falls.
The benthic zoneThe benthic zone denotes the area at the bottom of the lake, where sunlight does not reach, in addition to the water directly neighbouring the bottom, to which sunlight also does not reach. In deep lakes, the water at the bottom has a temperature of +4⁰C all year round. Here, there is very little oxygen dissolved in the water, and periodically, there may be none at all.
The thick vegetation growing around the littoral zone may poze a threat to people trying to swim in its waters. It is easy to get tangled up in these plants, and the muddy bottom provides legs with no support. This is why you should only swim in designated bathing areas.
Lake plants and animals
A lot of plants and animals live in lakes. Their distribution, however, is very uneven. The vast majority live in the littoral zone, significantly less in the pelagic zone and the least in the benthic zone.
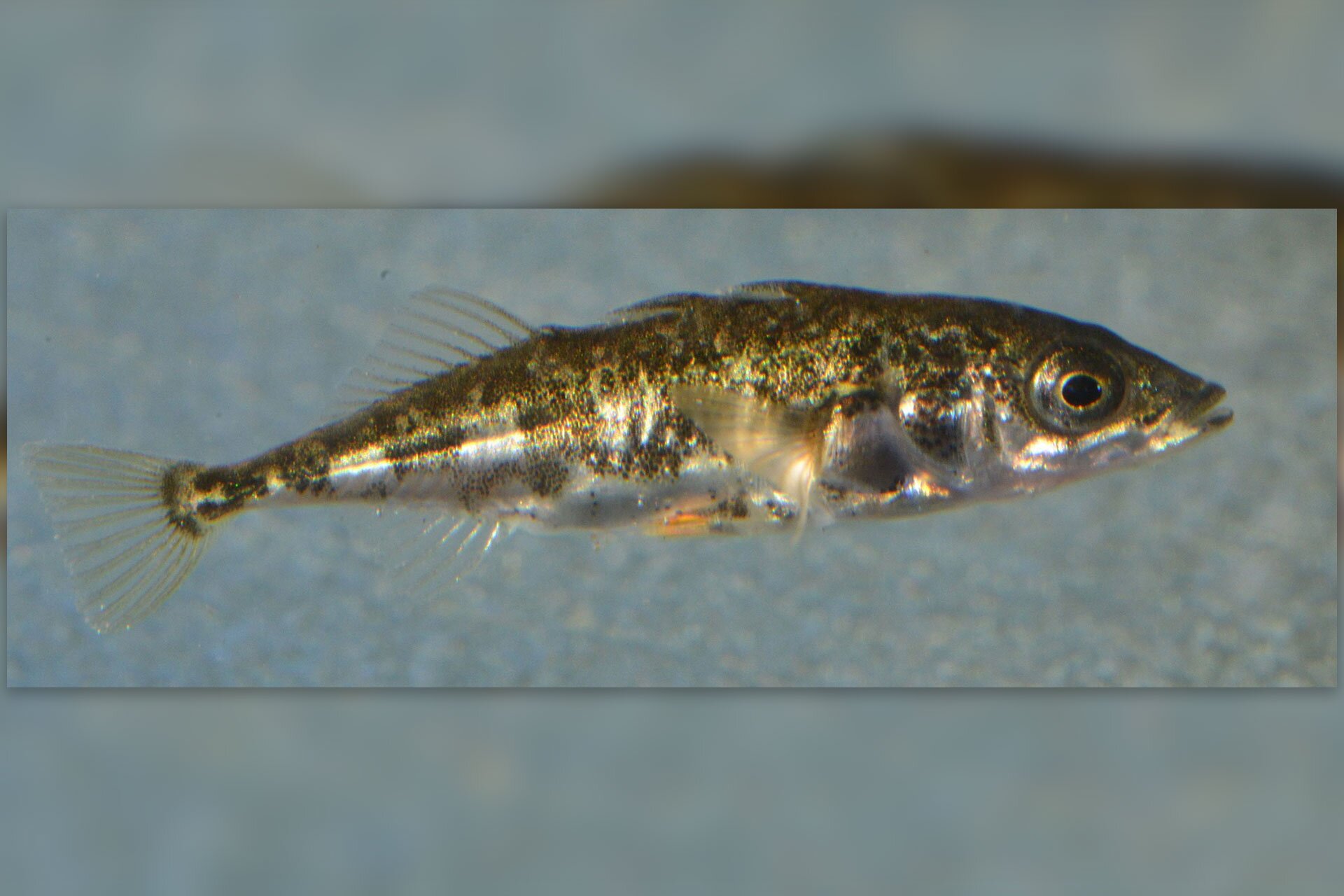
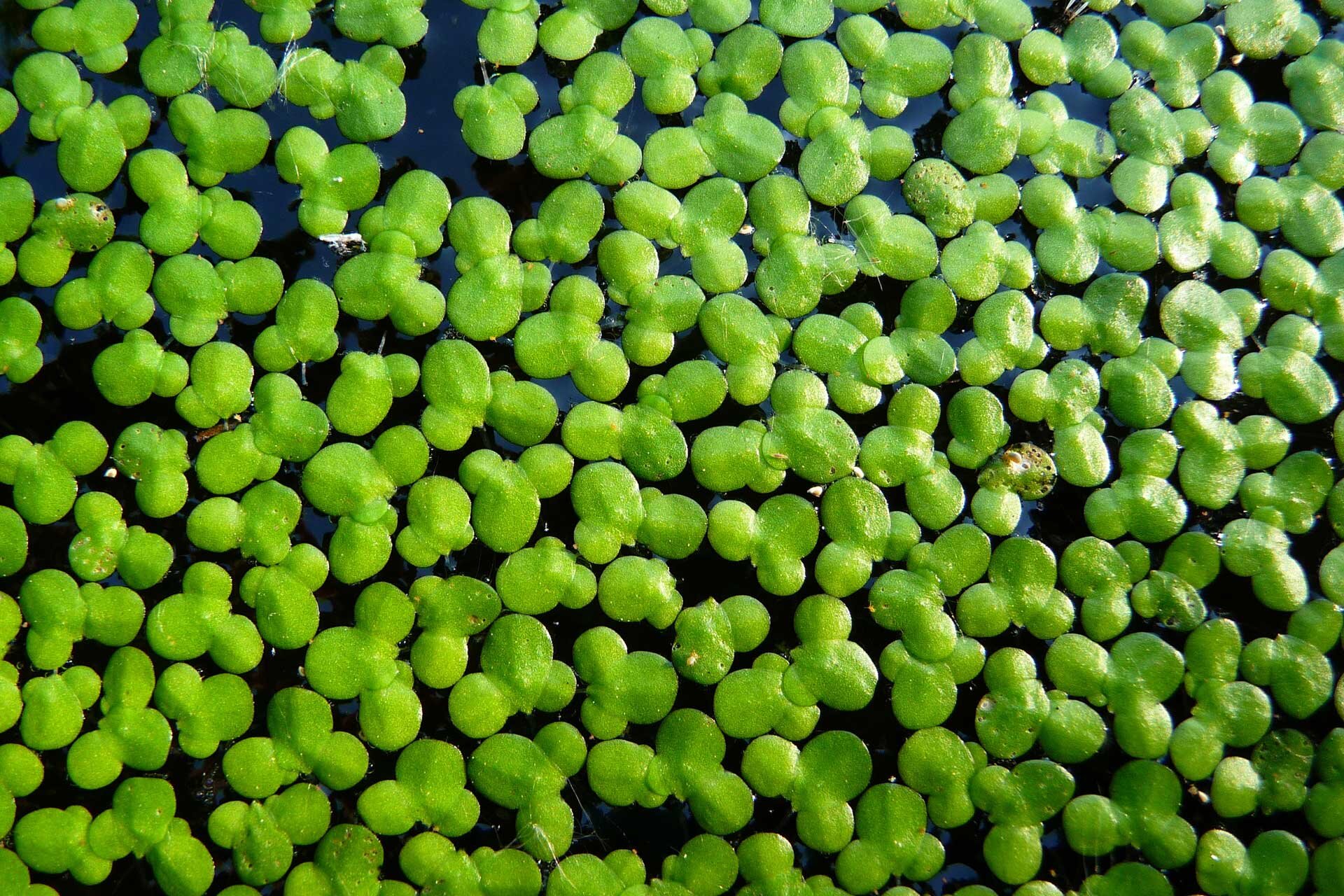
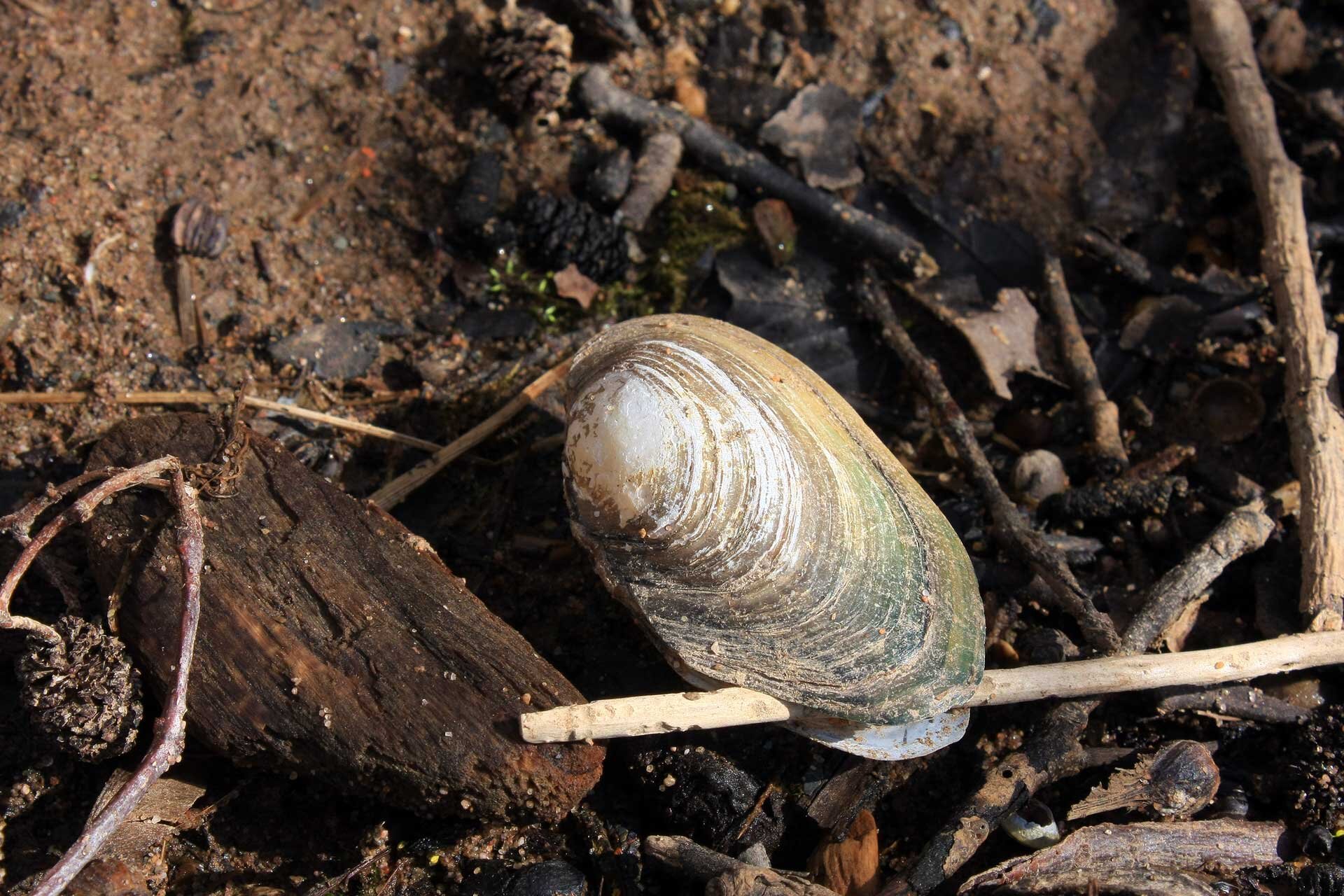
Plants growing in the littoral zone grow out of the shallow water, and sometimes grow on the land right next to the bank in places which are flooded by waves. These are often reeds, bulrushes and calamus. Numerous animals live here, which are strongly linked to both the water and the land, such as frogs and other amphibians, marsh turtles, grass snakes and waterfowl and wading birds (for example ducks and geese, grebes, herons, storks, cormorants and many more). Plants with floating leaves grow a little further from the banks, for example the yellow water‑lily and the white nenuphar, and even further hornworts and waterweeds, as well as common duckweed, which floats on the water. Insect larvae live among the plants (for example the larvae of dragonflies and mosquitos), snails, leeches, crabs, clams and fish (for example sticklebacks, roaches, tench, perch and pike).
In the pelagic zone, plants are almost exclusively represented by plant plankton. Animals which occur include zooplankton and a few types of fish, for example bleak and zander.
Plants cannot live in the benthic zone because of the lack of light, and the animals feed on organic remains which fall from above, or smaller animals. Small annelids live here, the larvae of certain insects, clams and fish looking for food in the mud at the bottom (catfish, lavaret and carp).
The water in lakes is not replaced for a very long time. Even a small amount of pollution will stay in the water for many years.
Summary
We divide a lake into three zones in relation to the conditions found there: littoral, pelagic and benthic.
In the littoral zone, the water is the warmest, there is the most oxygen, and sunlight reaches the very bottom; the most plants and animals occur here.
In the pelagic zone, light reaches the water, but there are few plants and little organic material; plankton and a few animals occur here.
In the depths near the bottom, it is dark, cool and there is little oxygen; there are almost no plants here, and animals feed on remains falling from other zones, organic material or other animals.
Keywords
lake, the benthic zone, the littoral zone, the pelagic zone
Match the pairs: English words with Polish definition.
część przestrzeni jeziora, która nie ma kontaktu ani z brzegami ani z dnem, a wraz z głębokością obniżają się w niej temperatura i zawartość tlenu oraz zmniejsza ilość światła słonecznego, przestrzeń jeziora, do której nie dociera światło słoneczne; jest ciemno, chłodno i mało tlenu, strefa jeziora przylegająca do brzegu, w której światło słoneczne dociera do samego dna, następują tu duże zmiany temperatury wody w ciągu dnia i roku
| the benthic zone | |
| the littoral zone | |
| the pelagic zone |
Glossary
strefa denna – przestrzeń jeziora, do której nie dociera światło słoneczne; jest ciemno, chłodno i mało tlenu
strefa przybrzeżna – strefa jeziora przylegająca do brzegu, w której światło słoneczne dociera do samego dna, następują tu duże zmiany temperatury wody w ciągu dnia i roku
strefa toni wodnej – część przestrzeni jeziora, która nie ma kontaktu ani z brzegami ani z dnem, a wraz z głębokością obniżają się w niej temperatura i zawartość tlenu oraz zmniejsza ilość światła słonecznego





