Atom and its structure
that matter is not continuous and it consists of particles;
that elements have particular names and symbols.
name individual elements of the atom;
determine the space in which electrons, protons and neutrons are located;
use the term: nucleonsnucleons, mass numbermass number, atomic numberatomic number;
determine the number of protons, neutrons, electrons based on atomic and mass numbers;
perform calculations using the atomic mass unit.
What the atom is?
The basic elements constructing the matter are atomsatoms. The substances that create the material world are made up of different atoms. Atoms have mass, volume and shape. Each element consists of atoms of only one kind: iron – from atoms of iron, and gold - from atoms of gold. Individual atoms of iron and gold are made up of the same particles and only their amount is different. Therefore, these differences are sufficient and these create elements with different properties.
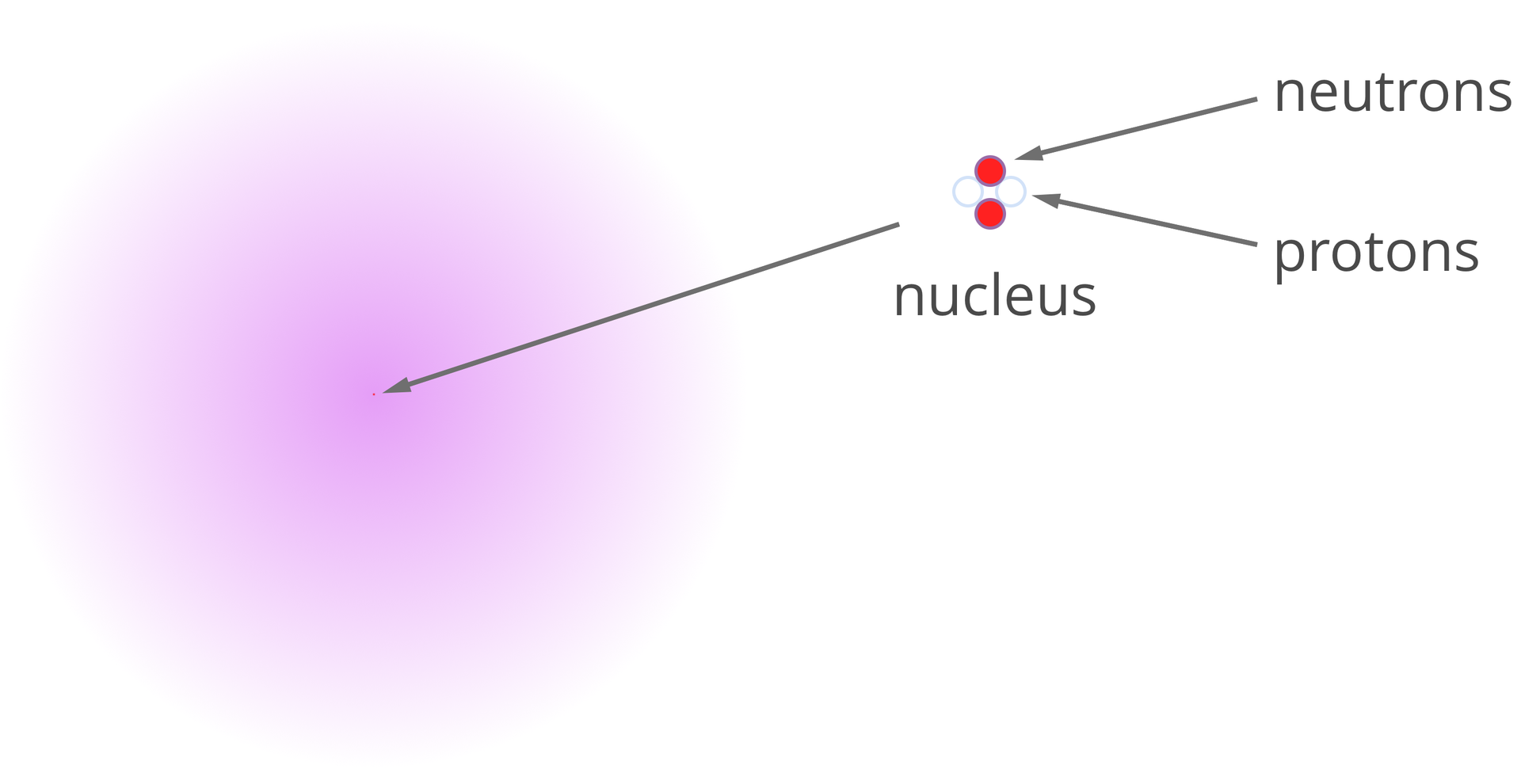
Watch the animation „Atom structure and its charge”. Pay attention to what the atom consists of. Which particles are charged and what charges are? Write down the answer.
Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie filmowe przedstawia strukturę atomu i jego ładunek elektryczny, the structure of the atom and its charge. Atom składa się z jądra i chmury elektronowej. Jądro zbudowanie jest z naładowanych dodatnio protonów, protons i obojętnych elektrycznie neutronów, neutrons. Chmura elektronową tworzą naładowane ujemnie elektrony, eletrons. Elektrony poruszają się wokół jądra atomu. Skala wielkości jądra atomu została porównana do monety jednego gorsza rzuconego na boisko stadionu narodowego.
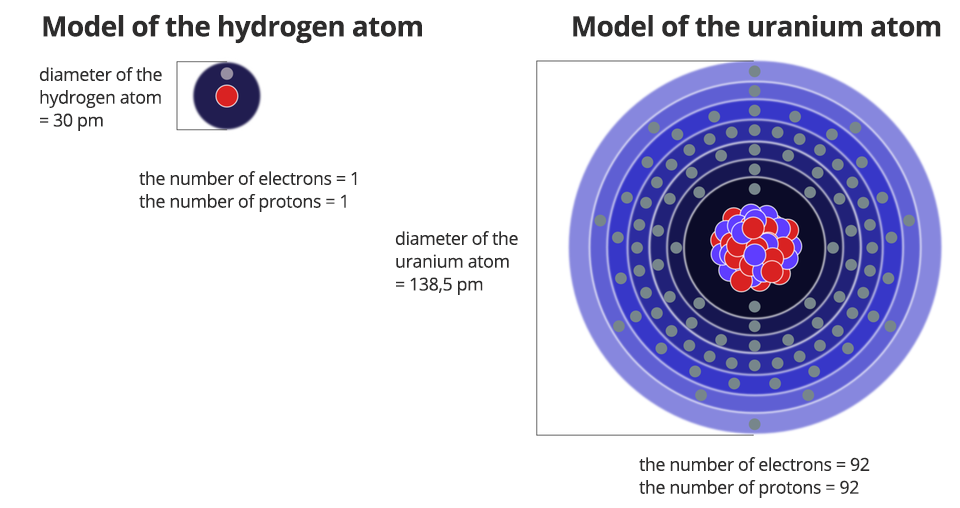
Each atom is an electrically neutral particle (it is not charged). In its interior, negative and positive charges are balanced. It means that the number of protons and electrons in each atom is the same.

The number of neutrons does not affect the atom's affiliation to a given element.
Name | Symbol | Charge | Location in the atom |
electron | e (eIndeks górny ––) | -1 | space outside the nucleus |
proton | p (pIndeks górny ++) | 1 | nucleus |
neutron | n (n) | nucleus |
The negative charge of the electron and the positive charge of the proton have the same absolute value (these differ only in characters). It was found out that the negative charge of the electron is an elementary negative charge. Thus, the proton has an elementary positive charge.
Atom description
To describe an atom, give the number of protons (or electrons) and neutrons included in it.
Try to present the carbon atom, which contains two electrons, two protons and two neutrons in the atomic nucleus in different ways. You can create a spatial model of the atom, describe it with words or draw it, using the following sketchbook, and print the drawing. The presentation technique is optional. Which of these methods will be the most readable in your opinion?
Atoms can be described with two numbers: atomic and mass. Atomic number ()Atomic number () is the number of protons in the nucleus, whereas mass number ()mass number () is the number of nucleons (the sum of protons and neutrons). These numbers are ordered and located next to the symbol of the element. On the left side of the symbol in the upper index, the mass number is located, and in the lower index - atomic number .

Name of particle | Symbol of element | Number of protons in nucleus | Number of neutrons in nucleus | Number of electrons | Mass number | Atomic number | Notation |
hydrogen | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
oxygen | 8 | 8 | 8 | 16 | 8 | ||
calcium | 20 | 20 | 20 | 40 | 20 | ||
argentum | 47 | 60 | 47 | 107 | 47 |
Atomic mass of elements
In the description of the mass of atoms, a value called atomic mass unitatomic mass unit or unit which is marked with the symbol u is used. Its value is 0.00000000000000000000000166 g (1.66 · 10Indeks górny -24-24 g)
The mass of the element's atom, which is expressed by this unit, is called the atomic mass.
The atomic mass of hydrogen is about 1 u, which means that the actual mass of the hydrogen atom is equal to one unit, i.e. 0.00000000000000000000000166 g (1.66 · 10Indeks górny -24-24 g).
The mass of subatomic particles can also be expressed in atomic mass units. It turns out that the masses of the proton and neutron are equal to about 1 u. The mass of the electron is much smaller than the mass of the proton and neutron.
Name | Symbol | Charge | Mass [u] |
electron | e (eIndeks górny --) | -1 | |
proton | p (pIndeks górny ++) | 1 | 1 |
neutron | n (n) | 1 |
Summary
The basic element of matter is the atom.
The atom is made of a nucleus and electrons moving around it (negatively charged particles).
The atomic nucleus is located in the centre of the atom and consists of nucleons, which are protons (particles with a positive charge) and neutrons (uncharged particles).
Nearly the entire mass of the atom is concentrated in the atomic nucleus.
The number of electrons and protons in the atom is the same.
Atoms are described by mass number () and atomic number () – .
The atomic number is the number of protons in the atomic nucleus.
The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in the nucleus of the atom.
Unit of atomic mass is unit [u], and its value is 1.66 · 10Indeks górny -24-24 g.
Keywords
atom, atom structure, atomic nucleus, proton, neutron, electron, nucleon
Glossary
pierwiastek – zbiór atomów o jednakowej liczbie protonów w jądrze
atom – najmniejsza część pierwiastka chemicznego, zachowująca jego właściwości
elektron – trwała cząstka elementarna o ładunku ujemnym (elementarnym ładunku ujemnym); składnik atomu, zajmuje obszar w przestrzeń wokół jądra
jednostka masy atomowej – atomowa jednostka masy, unit [u] – jednostka masy wykorzystywana do określania względnych mas atomów (tzw. mas atomowych), liczbowo równa 1,66 · 10 Indeks górny -24-24 g
jądro atomowe – centralna część atomu, zbudowana z jednego lub więcej protonów i neutronów (nie wszystkie jądra atomowe zawierają neutrony); stanowi niewielką część objętości całego atomu; w jądrze skupiona jest prawie cała masa atomu
liczba atomowa – liczba protonów w jądrze atomowym (równa liczbie elektronów)
liczba masowa – liczba nukleonów, równa sumie liczby protonów i liczby neutronów
neutron – cząstka bez ładunku elektrycznego, składnik jądra atomowego
nukleony – składniki jądra atomowego; zaliczają się do nich protony i neutrony
proton – cząstka o elementarnym ładunku dodatnim, składnik jądra atomowego