Byzantine Empire - Greek empire of the Romans
how Constantinople became the second Rome;
how the Roman Empire was restored during the reign of Emperor Justinian I;
what reforms and changes were introduced by the Emperor Justinian I;
why Byzantine EmpireByzantine Empire is called the continuation of Rome.
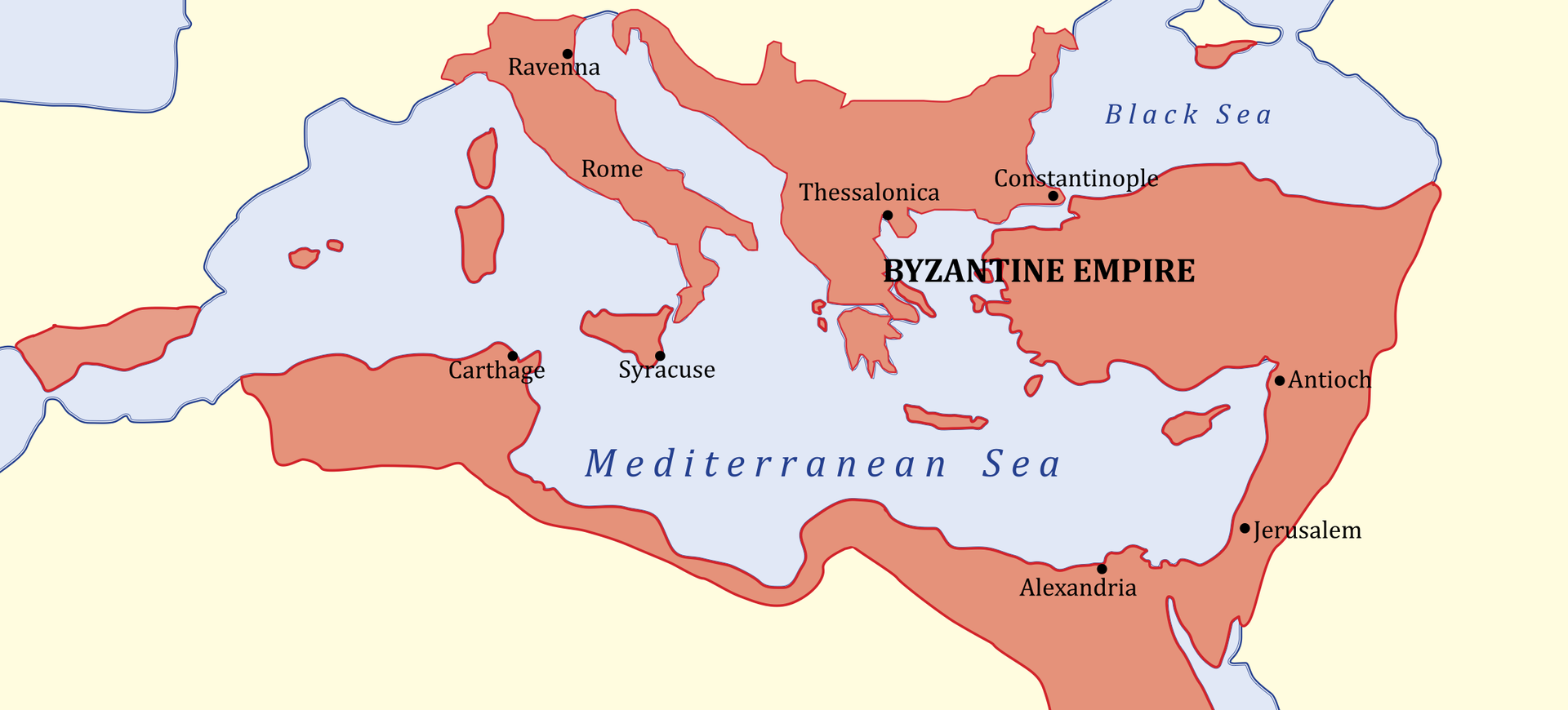
After the fall of the Roman Empire in 476, the role of the descendant and continuer of the Roman tradition was taken over by the Byzantine Empire with the capital city in Constantinople. The inhabitants of the Eastern Empire, called ‘Greek’ by many because of the popularity of Greek language and culture, emphasized their Roman roots and ancestry. The capital city of the Empire was a great city. During its prosperity it had 500,000 inhabitants. Three elements decided about its strength – the imperial power, the army and the administrationadministration, as well as a dynamic economy. This allowed to keep a wealthy treasury, and thanks to this, a permanent army. It was also possible to pay tributes to barbaric rulers who threatened the empire.
The most important citizen of Byzantine Empire was the Emperor. He was unlike others, though. He considered himself the ruler of all the Romans, he was supposed to realize the mission of christianisation of the world given to him by the God and he was also the representative of the God on earth. Formally, he was chosen by the highest ranking officials that created the Senate, however, no one contested the rule of inheriting the power and the rule being transferred from generation to generation. The imperial rule, which ruled over all subjects and church officials, was based on an efficient administrative apparatus, which main goal was to ensure high income to the treasury and the safety and peace of the subjects. All of it was regulated by rules and acts of law.
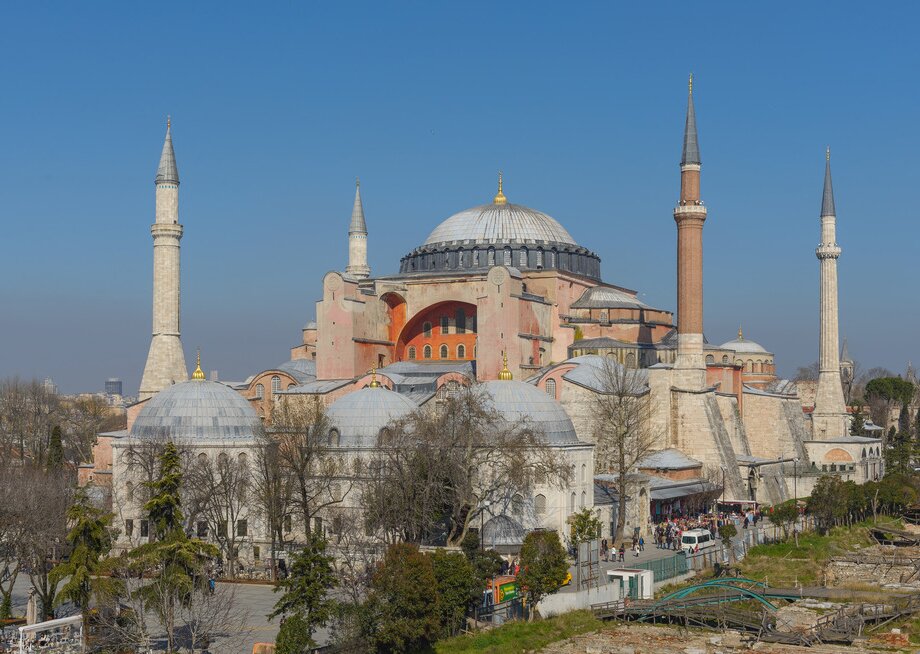
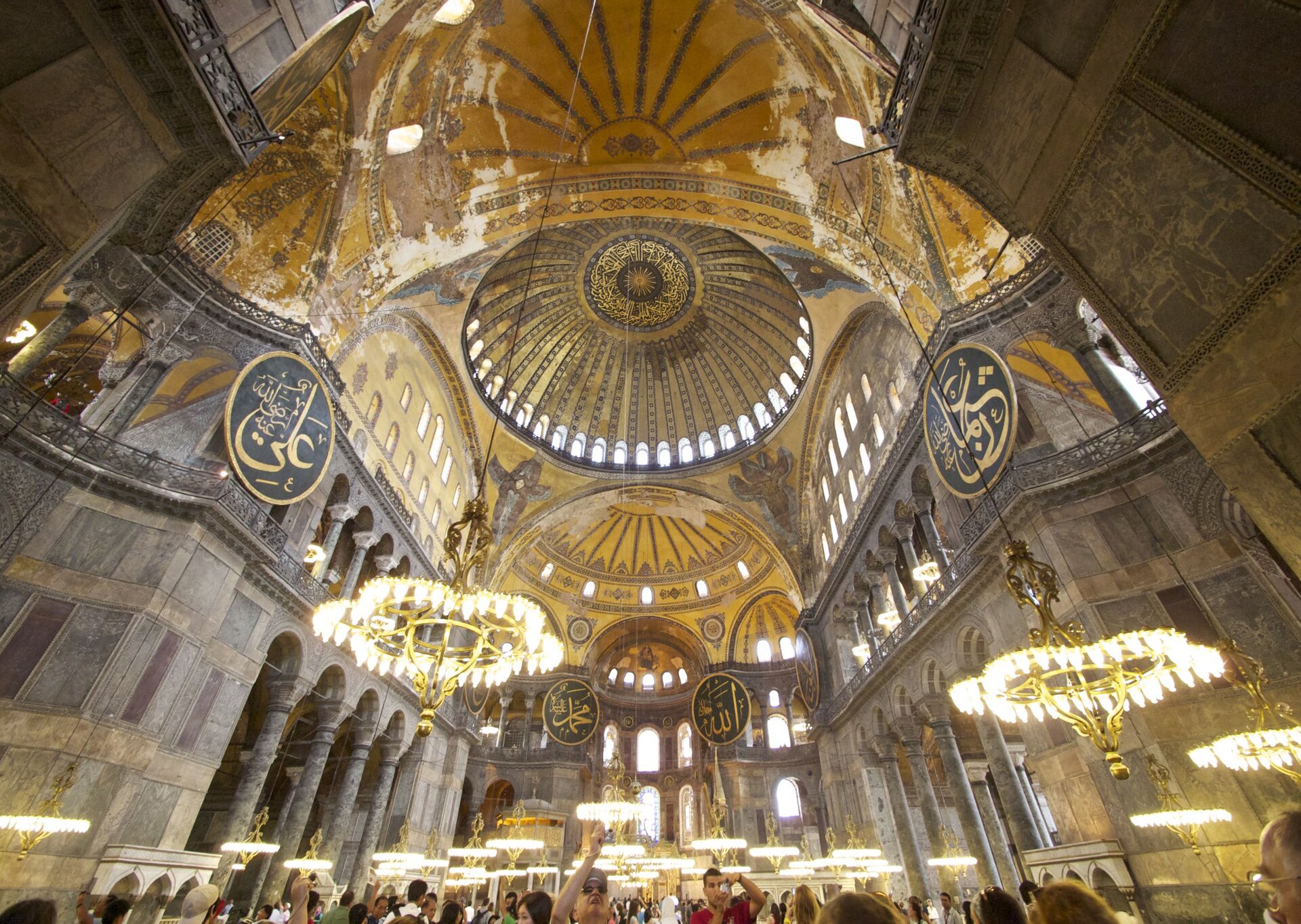
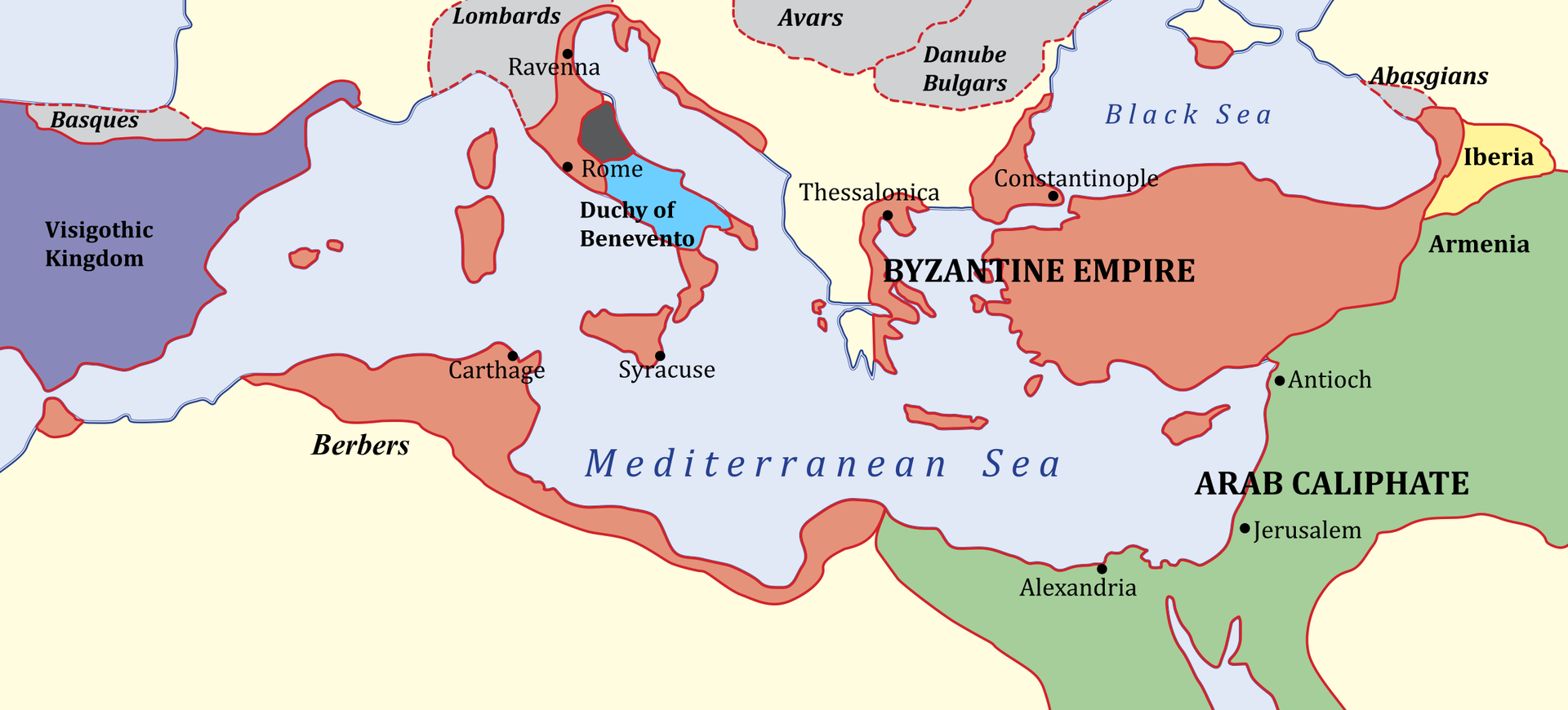
The most prominent Emperor of the early Middle Ages was Justinian I, called the Great. He ruled between 527 and 565 and left his mark on nearly all aspects of life in the Empire. He revolutionized the state apparatus, basing his rule not only on the aristocracy, but also on talented “new people” who came from lower classes. Thanks to his protection, they became fully dependant on the emperor, but also fulfilled his will unconditionally. Among them were not only great leaders like Belisarius, but also agile administrators and lawyers introducing the reforms of the Emperor. Justinian I dreamt of rebuilding the great Empire and thanks to an efficient army led by extraordinary leaders he practically managed to achieve that in the middle of the 6th century. He was also the author of the great legal reform – he organized the rules into the Justinian CodeCode, as well as built the most important building of Constantinople – the Church of God’s Wisdom. The restoration of the Roman Empire did not last long. Numerous attacks of enemy armies – Persians from the east and Awars from the north; Bulgarians and Slavs in the Balkans, as well as the Muslims from the Arab Peninsula, ended the age of Byzantine Empire’s dominance, depriving it of its political power in the Mediterranean basin already in the 7th century.
Select in the text the most important reason for the fall of the Eternal City as seen by Procopius.
most important causes
Simultaneously with Emperor Zeno the Isaurian in Byzantine Empire, the Western Roman Empire was ruled by Emperor August, called Romulus Augustulus [...]. Very recently, the Romans invited as their allies the tribes of the Scirii, the Alans and other Goth tribes [...] The stronger the influences of the Barbarians were becoming the weaker the significance of Roman soldiers was and the Romans suffered from attacks from the invaders who were tormenting them [...]. They [...] demanded to be allowed to participate in the division of the farmlands in Italia. [...] Among them was one warlord called Odoacer [...]. He promised them he will fulfill their demands if they make him the ruler. Obtaining thus the rule, he did not harm the Emperor [...]. Though he granted the Barbarians with third part of the farmland [in Italia].
(J. Garbacik, K. Pieradzka, Teksty źródłowe do historii powszechnej wieków średnich, Kraków 1978, s. 17).
Look at the timeline of the most important events in the history of the Byzantine Empire.
True or False? Arrange the information in the correct order
The Imperial rule in Byzantine Empire was ruled by succession., Ordering of laws and rules was conducted by the Emperor Justinian I, which resulted in publishing the Justinian Code in 534., Hagia Sophia, the church of Holy Wisdom, was constructed by Constantine the Great., Constantinople in 6th century had around 500 thousand inhabitants and was the biggest city in Europe., The capital city of the Byzantine Empire was Constantinople., The first invasion of the Arabs on the Byzantine Empire took place in 6th century., Germanic tribes served in the army of the Byzantine Empire., Byzantine Empire was founded on three pillars: the Imperial rule, the army and the administration., Belisarius was an exceptional official of the Empire, a great reformer., The name Byzantine Empire was used already in Antiquity.
| True | |
|---|---|
| False |
Keywords
Byzantine Empire, Empire, Emperor
Glossary
Bizancjum – w starożytności miasto leżące nad cieśniną Bosfor, od którego swoją nazwę wzięło cesarstwo wschodniorzymskie. Po objęciu władzy przez Konstantyna Wielkiego zmieniono jego nazwę na Konstantynopol.
Hipodrom – tor wyścigowy dla koni i rydwanów w starożytności w kształcie prostokąta zakończonego z krótszych stron półokręgami.
danina składana przez jednego władcę innemu w dowód uznania jego przywództwa, zwierzchności lub w zamian za zagwarantowanie pokoju.
rozejm – inaczej zawieszenie broni, oznacza czasowe wstrzymanie działań zbrojnych między walczącymi stronami.
Administracja – nazywana również aparatem urzędniczym to zbiór instytucji państwowych powiązanych i współpracujących ze sobą przy zarządzaniu państwa.
Kodeks – zbiór przepisów i aktów prawnych.
Pragmatyzm – postawa oznaczająca podejmowanie tylko takich działań, które przynoszą konkretne korzyści.