Carboxylic acids – structure
what the structure of saturated hydrocarbons is;
how to draw a structural formula of given hydrocarbon;
how to create names of hydrocarbons;
what the valence number of carbon in organic compounds is;
that the functional group in a hydrocarbon molecule substitutes hydrogen atom.
to construct models of carboxylic acid molecules;
to write molecular and structural formulae of simple carboxylic acids;
to name carboxylic acids.
Ethanoic acid
When wine goes bad, ethyl alcohol is converted into ethanoic acid. This reaction takes place in presence of oxygen and enzymes produced by acetic bacteria. This process is called acetic fermentationacetic fermentation.
Chemical equation – denoted with words:
Chemical equation – molecular equation:
The following can be concluded from the chemical equation:
In presence of oxygen and enzymes ethyl alcohol undergoes a chemical reaction the products of which are ethanoic acid and water.
Ethanoic acid consists of the same number of carbon atoms as ethane. This substance is classified as ethane derivative as their composition is similar. That is why its systematic name is ethanoic acid.
In the ethanoic acid molecule carbon atoms are linked together with a single bond. One oxygen atom forms a double bond with a carbon atom. The second oxygen atom forms one bond with a hydrogen atom and the other one with a carbon atom. The remaining hydrogen atoms are fixed with carbon with a single bonds.
Molecular formula of ethanoic acid allows us to name the types and number of individual atoms. But we will not be able to find out how are these atoms bonded in the molecule. It is the structural formula that gives information about the number of bonds between individual atoms.
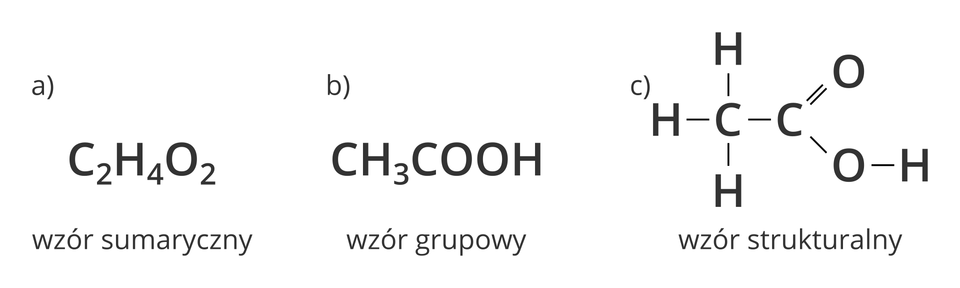
1. molecular formula
2. group formula
3. structural formula
Methanoic acid
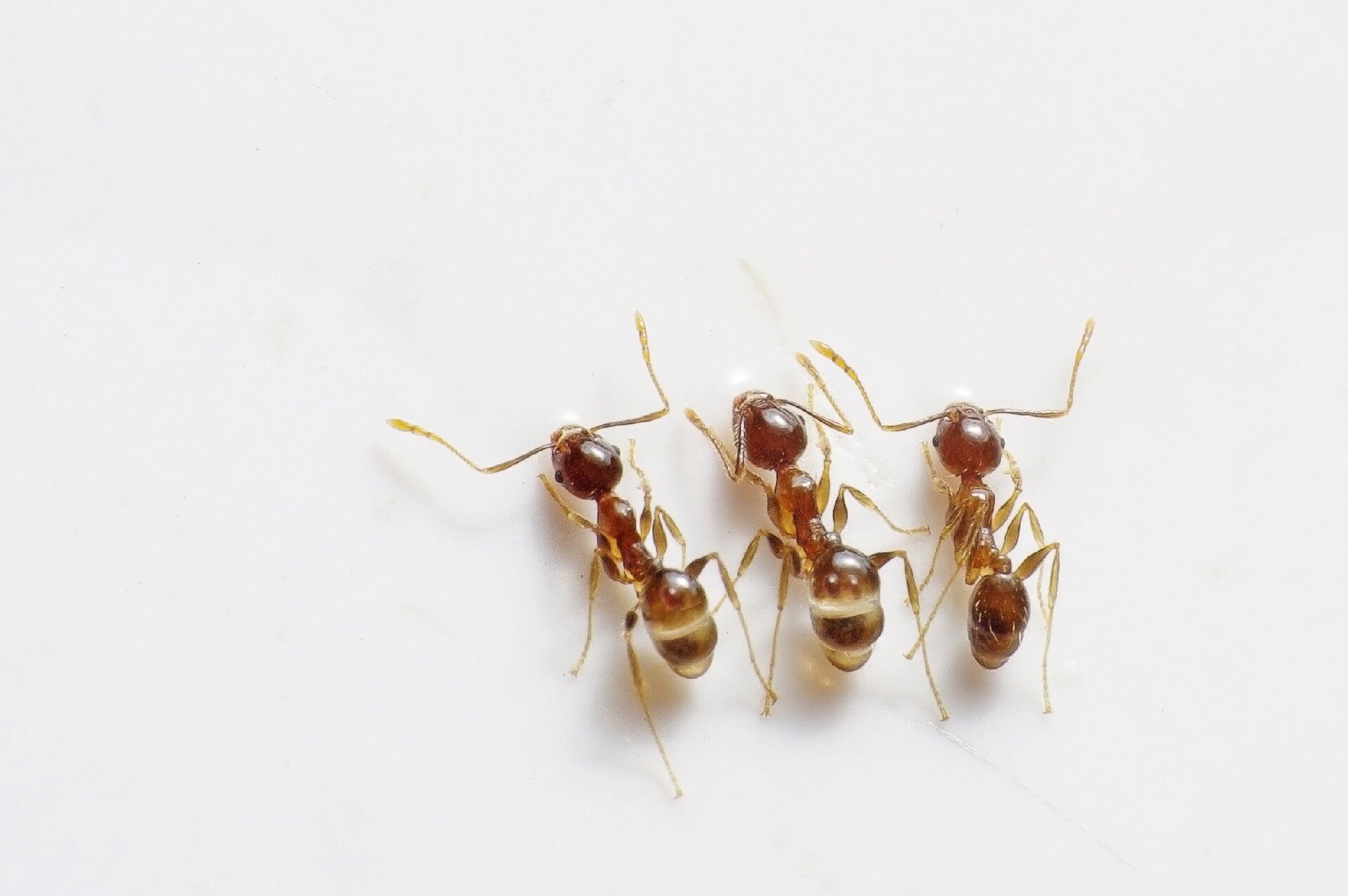
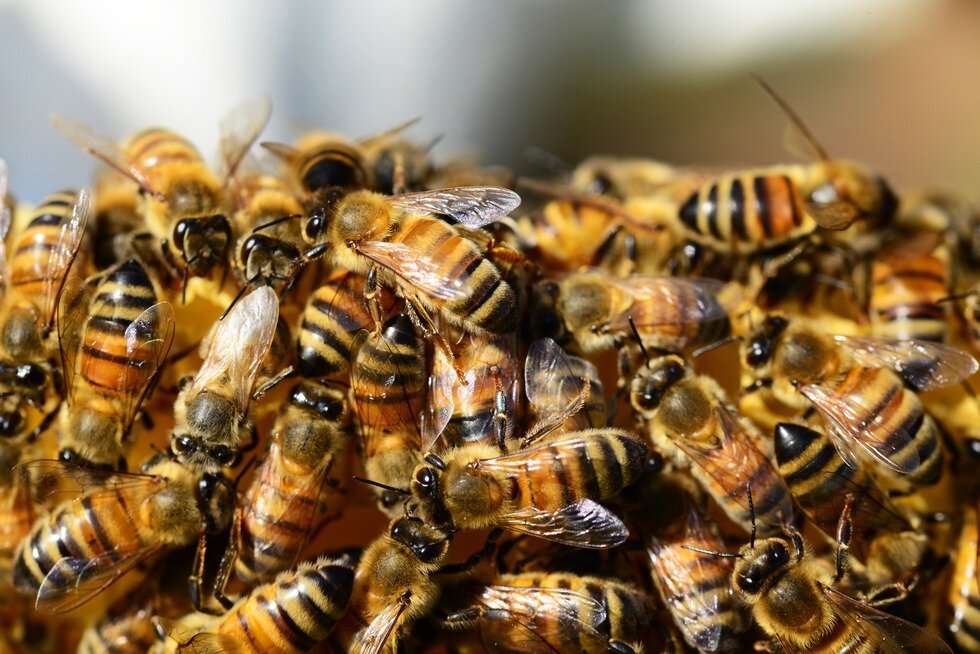
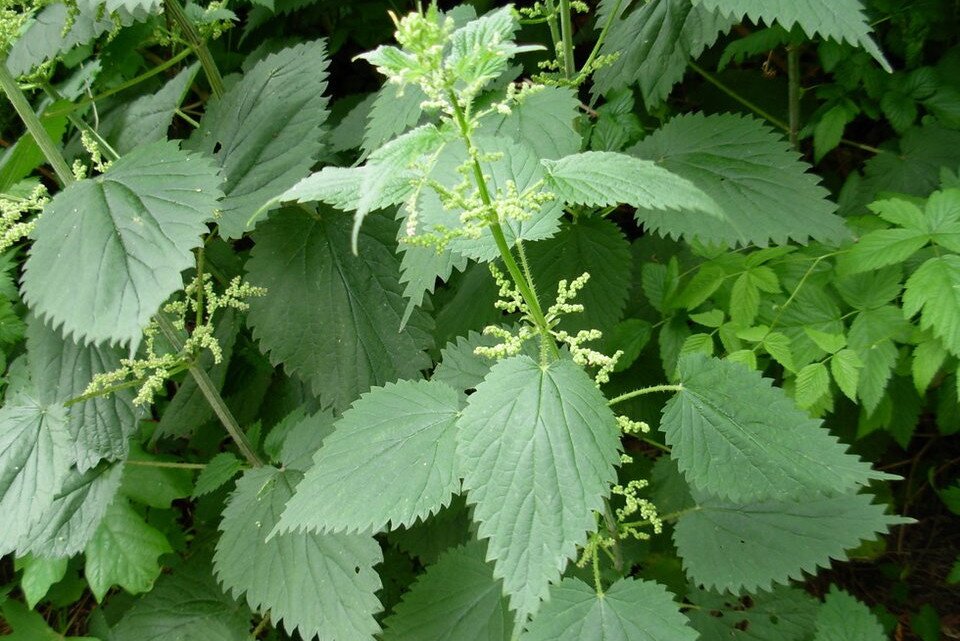
View the photo gallery and think where methanoic acid can be found.
Design a model of a methanoic acid molecule that consists of one carbon atom, two hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms.
Methanoic acid is present in venom of ants which use it to destroy parasites. The same acid is produced for example by bees and nettle – a well known plant that stings. When we touch a nettle we will immediately feel burning and pricking and, develop itchy blisters on our skin. This is because on the leaves there are present small plant hairs (trichomes) which inject the irritant formic acid under the skin.
Methanoic acid is believed to be a derivative of methane. It contains one carbon atom in a molecule.
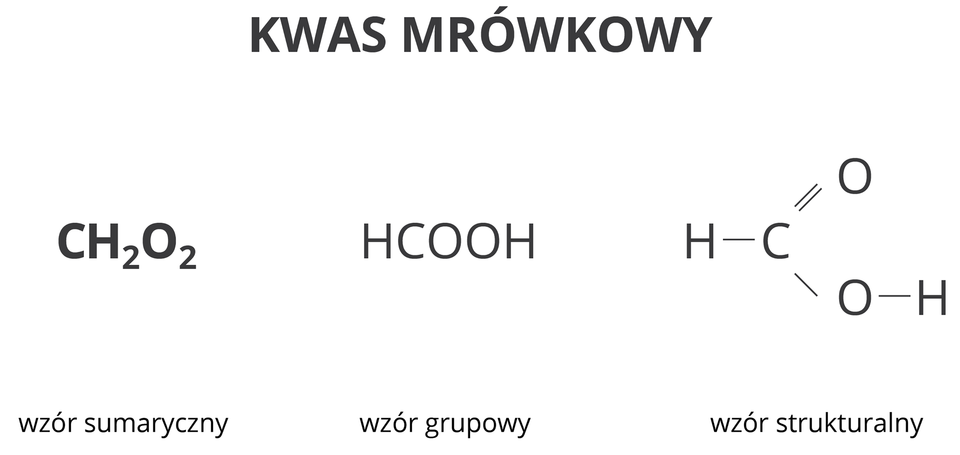
1. molecular formula
2. group formula
3. structural formula
4. Formic acid
Organic acids – hydrocarbon derivatives
Carboxylic acidsCarboxylic acids are hydrocarbon derivatives in which hydrogen atom (or atoms) is (are) substituted with a functional carboxyl groupfunctional carboxyl group . Carboxylic acids are classified according to the number of carbon atoms into lower ones – with smaller number of carbon atoms, and higher ones – with several carbon atoms in a molecule. Methanoic and ethanoic acids are lower acids.
– a group typical of carboxylic acids is bonded with a hydrocarbon group. A group of atoms bonded with a hydrocarbon chain will be called a functional group.
Thus group is a functional group of organic acids.
Organic acids with a carboxyl group are called carboxylic acids.
Like hydrocarbons, organic acids with one carboxyl group in a molecule form a homologous series. The systematic names of carboxylic acids consist of two parts. In order to create the systematic name, the name of alkane with the same number of carbon atoms in a molecule to the word „acid”, adding the ending -oic; for example methanoic acid, ethanoic acid. It should be noted that common names are usually used in practice. Common names are associated with the occurrence of acids. Formic (methanoic) acid is found in ant venom, butyric (butanoic) acid – in rancid butter, and lactic acid – in some dairy products.
Table 1. shows acids listed according to the number of carbon atoms in a molecule. Each subsequent molecule differs from the previous one in group. This series is called a homologous series of carboxylic acidshomologous series of carboxylic acids.
Table 1. Names and formulas of selected carboxylic acids.
Systematic name of carboxylic acid | Common name of carboxylic acid | Molecular formula of carboxylic acid | Semi‑structural formula of carboxylic acid |
methanoic acid | formic acid | ||
ethanoic acid | acetic acid | ||
propanoic acid | propionic acid | ||
butanoic acid | butyric acid | ||
If the carboxylic acid is an alkane derivative and contains one carboxyl, its generalized formula is as follows:
The general formula of monocarboxylic acids derived from alkanes.
Organic acids make contain several carboxyl groups in their molecules (for example oxalic acidoxalic acid) and other functional groups such as a hydroxyl group (for example lactic acidlactic acid).
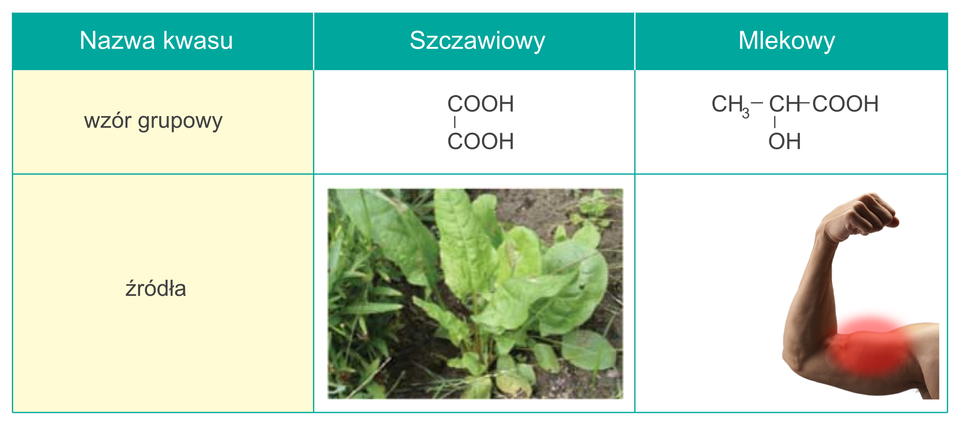
1. acid name
2. Oxalic acid
3. Lactic acid
4. group formula
5. source
Select the systematic name of the compound with a formula CH3COOH.
- ethanoic acid
- butyric acid
- methanoic acid
- propanoic acid
- formic acid
- acetic acid
Arrange the acid names so that they would become a part of homogeneous series of carboxylic acids.
- etanoic acid
- methanoic acid
- propanoic acid
- butanoic acid
Summary
Ethanoic acid is one of the products of acetic fermentation. Diluted alcoholic beverages undergo this process.
Carboxyl group is a functional group of carboxylic acids.
Carbxylic acids are hydrocarbon derivatives which contain at least one carboxyl group.
Methanoic and ethanoic acids classified as lower carboxylic acids.
Provide a generalized formula of carboxylic acids derived from alkanes. Mark hydrocarbon part and the functional group.
Keywords
carboxylic acids, methanoic acid, ethanoic acid, carboxyl group
Glossary
fermentacja octowa – proces chemiczny, któremu ulega alkohol etylowy pod wpływem enzymów wytwarzanych przez bakterie octowe; jego produktami są kwas octowy i woda
grupa karboksylowa – grupa funkcyjna o wzorze , nadająca kwasom karboksylowym charakterystyczne właściwości
kwasy karboksylowe – pochodne węglowodorów, zawierające w cząsteczkach jedną lub więcej grup karboksylowych
kwas mlekowy – kwas karboksylowy, będący pochodną propanu; jego cząsteczka zawiera dwa rodzaje grup funkcyjnych – karboksylową i hydroksylową; powstaje m.in. w mięśniach podczas intensywnego wysiłku fizycznego
kwas szczawiowy – kwas dikarboksylowy zawiera dwie grupy karboksylowe w cząsteczce; jest pochodną etanu; występuje w roślinach, np. w szczawiu i rabarbarze
szereg homologiczny kwasów – szereg związków chemicznych – kwasów karboksylowych uporządkowanych według wzrastającej liczby atomów węgla w cząsteczce, w którym dwa kolejne związki różnią się od siebie o grupę atomów


