Colonies
who and when started the colonial conquests;
about the greatest colonial powers and the lands in their possession;
why it was extremely profitable to have colonies;
why there was a rivalry between colonial powers;
which country became the largest colonial empire in history.
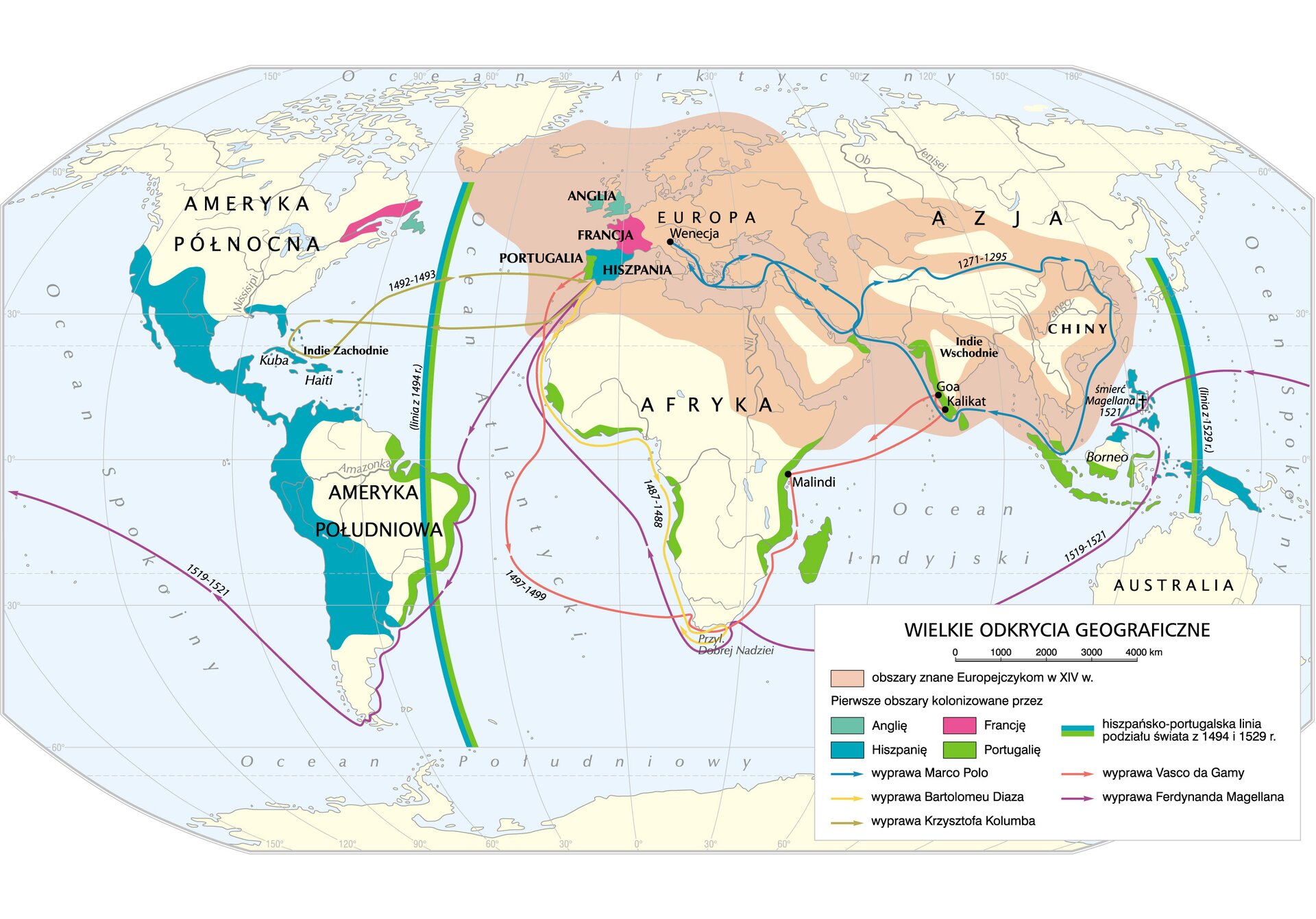
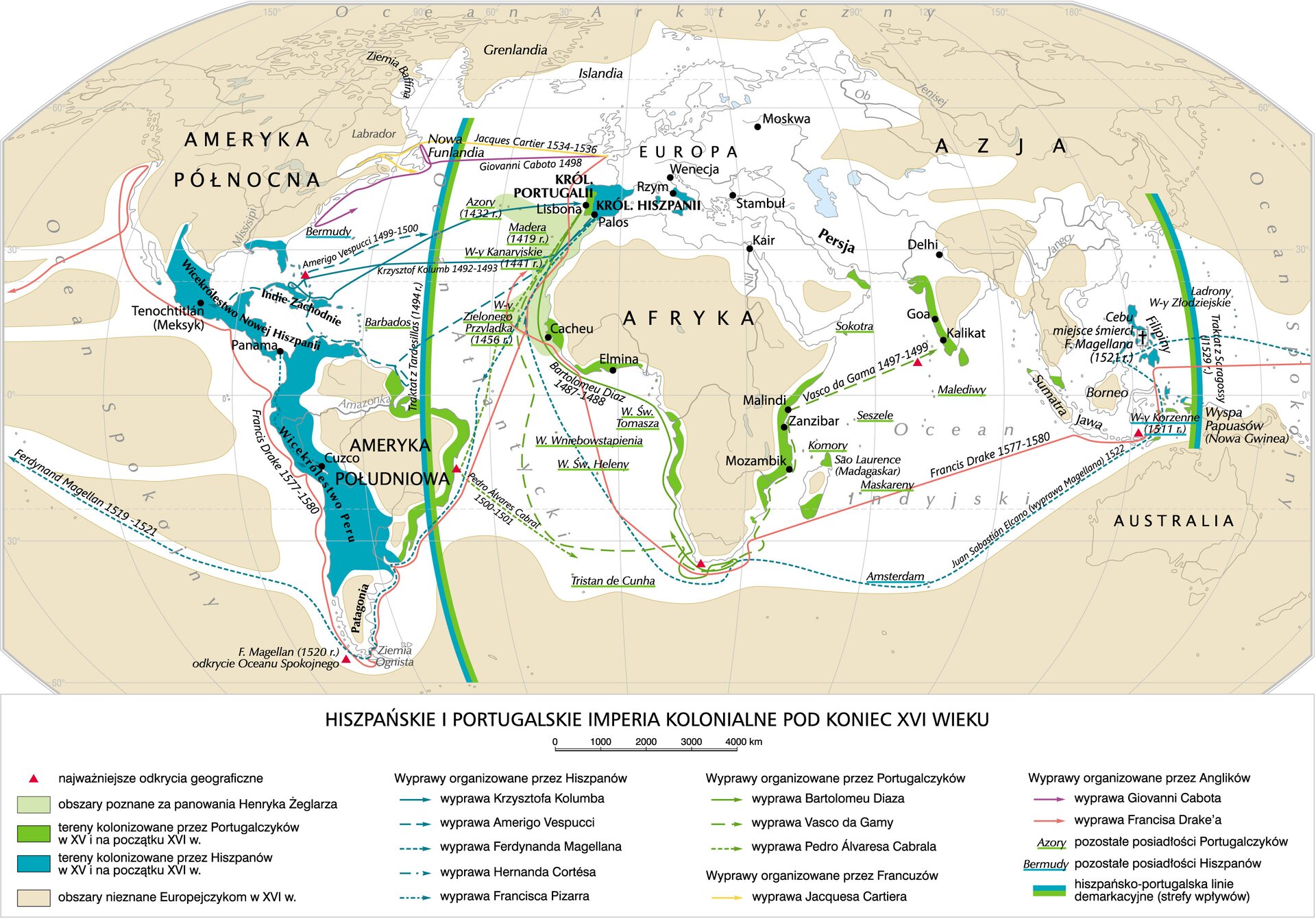
In the 14th century, Europeans began embarking on maritime expeditions the time of which is now called the Age of Discovery. These initiated the process of colonialismcolonialism, i.e., conquests and takeovers of economically underdeveloped states. At the first stage of colonialism, until the early 16th century, it was limited mainly to expeditions led by Portugal and Spain. From the very beginning, the Portuguese dominated the trade on the coasts of Africa, today’s Brazil, and in the Indian Ocean basin. There, they founded numerous trading poststrading posts which brought them significant profits mainly due to sugar cane cultivation. Spanish colonists, supported by the Catholic Church, focused their conquests on the lands of Central and South America, creating two viceroyalties there, with capitals in Lima and Mexico. Unlike the Portuguese, they very quickly developed settlement there, building commercial and administrative centers, and even establishing monasteries and universities.
Another country to join the [colonial]pojecie‑ref={Colonialism} race were the Netherlands. Being well aware of the benefits of trading with coloniescolonies, the Dutch initially tried to develop their cooperation with the Spanish dominions in America. When it was interrupted, they started to profit from piracypiracy, driving the Portuguese away from some of the dominions (Cape Province, Ceylon) and taking over their commercial models (the establishing of trading poststrading posts).
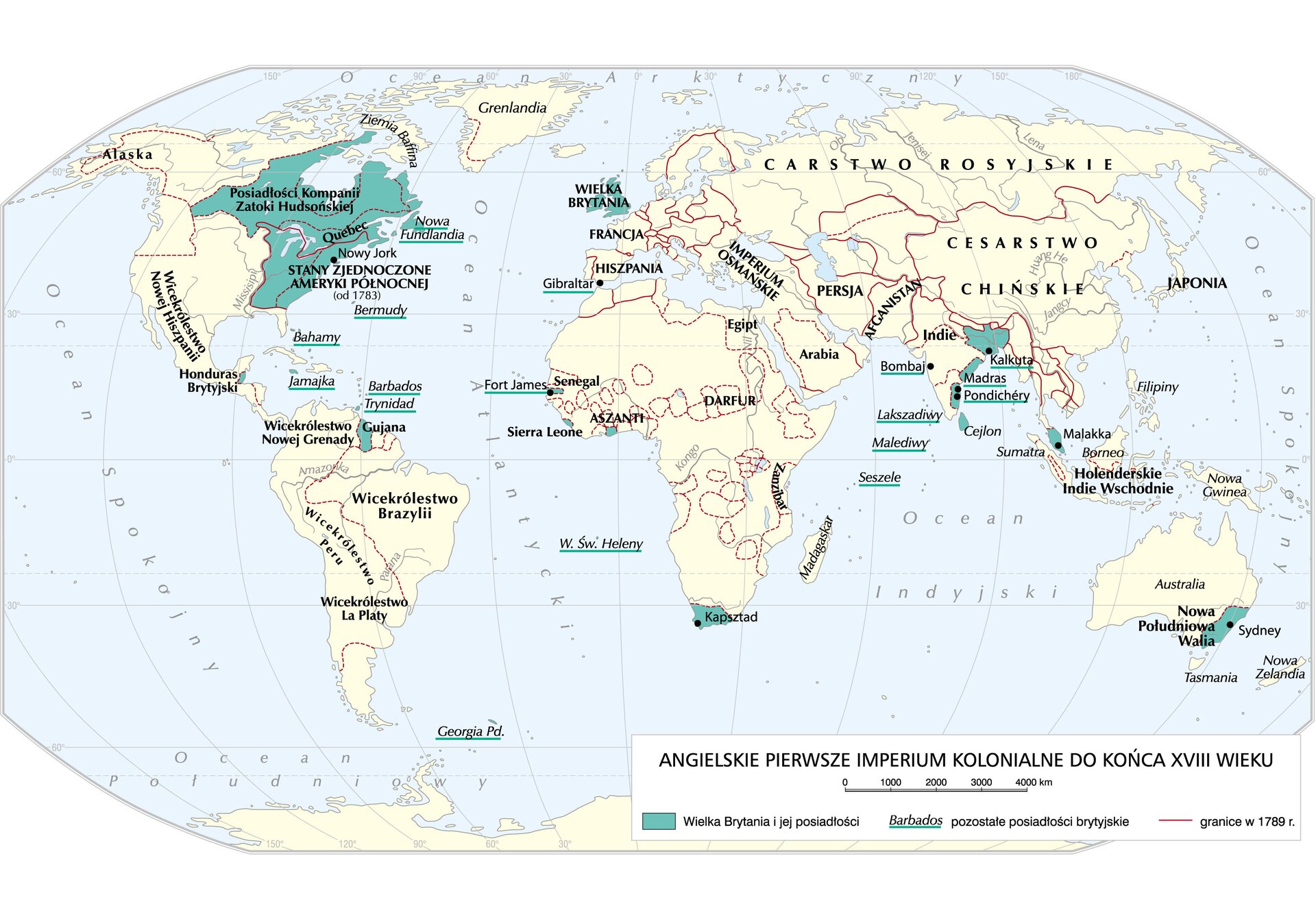
England joined the colonialcolonial expansionexpansion relatively late. Although its presence on the seas and oceans was visible as early as in the 16th century, it was only the conquest and founding of the coloniescolonies on the so‑called ‘sugar islands’ (Barbados and Jamaica) in the mid‑17th century that began the slow process of building the colonialcolonial empire. Britain turned into this empire only in the 19th century, when it had established dominions in almost every corner of the world.
The last major European player to join the colonialcolonial rivalry was France, when it founded its first overseas dominions in the 17th century in the territory of today’s Canada. However, it was not until the expansionexpansion to the Caribbean islands – Haiti, Martinique, and Saint Lucia, as well as to the dominions in the Far East, that it really began to count in the competition of the overseas powers.
Rivalry between European countries translated also into activities in overseas territories. In 1756, the Seven Years’ War broke out, which became the first conflict that had a global reach. Military actions took place in Europe, but also in North America, India, and the Caribbean islands.
Read about the most important events of colonialismcolonialism.
Describe a colonialcolonial empire of a randomly chosen European country. What was the significance of having an empire for that country?
You can use the maps below.
Match the terms to their explanations.
maritime robbery carried out by private ships at the request of and as authorized by a ruler. Privateers were paid some or all of the spoils they took., the territory of a state, within the British Empire, which was intermediate between a self-governing colony and an independent state. The status of ‘dominion’ meant the highest degree of autonomy that a territory could achieve within the United Kingdom., a state taking over new territories, most often through conquests., a policy of conquering and taking over underdeveloped countries by economically developed ones. Its aim was to maintain the subordination of these countries and to use their human resources and raw materials., illegal acts of violence on the seas and oceans committed by private ships.
| British dominion | |
| Colonialism | |
| Piracy | |
| Privateering | |
| Expansion |
Keywords
colonialism, British dominion, trading post, piracy, privateering, the Caribbean
Glossary
Kolonie – posiadłość państwa, która znajduje się poza jego granicami, ale bezpośrednio mu podlega.
Faktoria – położona w koloniach placówka handlowa, do której dostarczano towary i produkty z państw kolonialnych.
Dominium – terytorium państwa, w ramach imperium brytyjskiego, mające charakter pośredni między samorządną kolonią a niezależnym państwem. Status dominium oznaczał najwyższy stopień autonomii, które mogło osiągnąć terytorium w ramach Wielkiej Brytanii.
Kolonializm – polityka podbojów i przejmowania państw słabo rozwiniętych przez rozwinięte gospodarczo. Jej której celem było utrzymanie w zależności siebie tych krajów i wykorzystywanie ich zasobów ludzkich i surowcowych.
Tubylec – osoba należąca do rdzennej grupy ludności zamieszkującej dany obszar, np. Aborygeni w Australii.
Piractwo – inaczej rozbójnictwo morskie, bezprawne akty przemocy na morzach i oceanach dokonywane przez prywatne statki.
Korsarstwo – rozbójnictwo morskie prowadzone przez statki prywatne na zlecenie i z upoważnienia władcy. Wynagrodzeniem korsarzy była część lub całość zdobytych łupów.
Ekspansja – zajmowanie przez państwo nowych terytoriów, najczęściej dokonywanych na drodze podbojów.