Ecological factors
organisms have different environmental requirements ;
organisms are adapted to the conditions in which they naturally occur.
to differentiate between biotic and abiotic environmental factors;
to indicate abiotic factors and describe their effects on organisms;
Each species evolves in a specific environmental conditions, which are shaped by many external factors referred to as ecological factorsecological factors. These factors are constantly changing, as a result of what some individuals die, and those better adapted to the current conditions survive and reproduce.
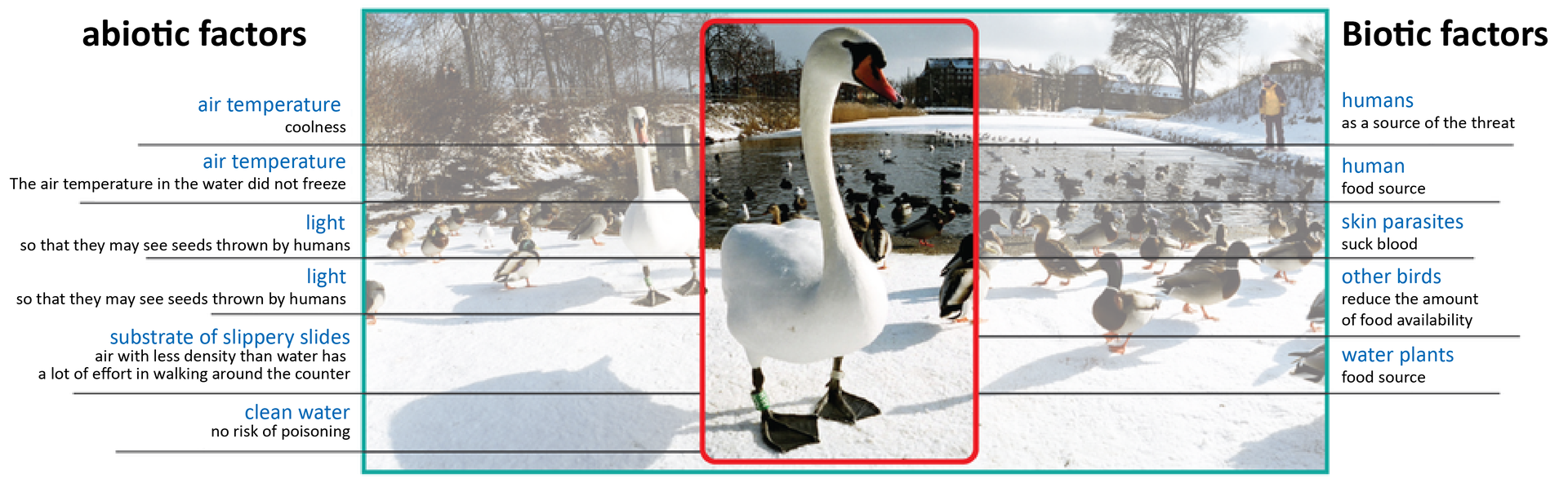
Ecological factors can be divided into bioticbiotic, i.e. those, which sources are co‑occurring organisms in a certain area, and abioticabiotic, resulting from the interaction of inanimate elements of the environment. Biotic factors include availability of food, presence of predators, occurrence of pollinating organisms, creation of a microclimate characteristic for a specific plant community, e.g. forest. The most important abiotic factors include the availability of oxygen, water, light and temperature.
Ecological factors and the intensity with which they affect organisms depend largely on latitude, altitude, depth, in case of water reservoirs, distance from the sea and type of ecosystem.
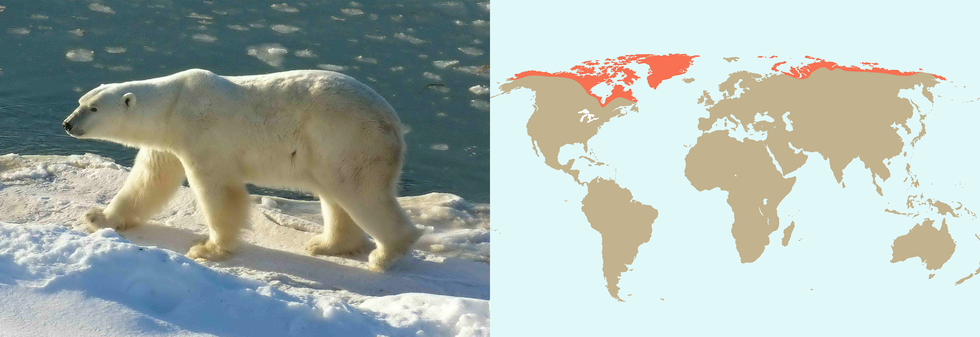
The Malay bear is the smallest of bears - it reaches the size of a large dog. It has a short, shiny, skin‑adhering dense fur without twisted wool hair. Its feet are naked. Polar bear is the biggest of them all. It is about 10 times larger than the Malay bear. It has thick fur with a strongly developed wool layer. Its coat is colourless or yellowish. The skin of this bear is black and there is a thick layer of fat beneath it. Its feet are very hairy, and the ears are short, hidden in a fur coat.
Show on the example of both species of bears the connection between their living environment and body structure.
How can we explain what ecological factors are? Indicate all the correct answers.
- genetically determined factors that affect the phenotype of a typical individual from a given population
- environmental conditions affecting the development of a given population
- the sum of abiotic and biotic factors acting on a given population
- actions taken to preserve the values of the natural environment
Move the following items to the appropriate category
presence or absence of predators, temperature, total rainfall, height above sea level, average insolation, population density, availability of food, soil moisture, landform
| abiotic factors | |
|---|---|
| biotic factors |
Match the ecological factor to the characteristic it affects.
skin color in humans, the occurrence of resistance to certain diseases in a given population, fat tissue thickness, formation of territorial behaviors, formation of water-storing tissue
| insolation | |
| climate | |
| presence of pathogenic organisms | |
| frequent droughts | |
| population density |
Summary
Organisms are influenced by biotic factors, which originate from other organisms, and abiotic factors – by the impact of an inanimate natural environment.
Keywords
ecological factors, biotic factors, abiotic factors
Glossary
czynniki abiotyczne – czynniki ekologiczne związane z fizycznymi i chemicznymi warunkami środowiska, np. temperatura, wilgotność gleby
czynniki biotyczne – czynniki ekologiczne związane z oddziaływaniem innych organizmów, np. oddziaływanie pasożytów, obfitość lub brak pokarmu
czynniki ekologiczne – warunki środowiska mające wpływ na rozwój i rozmieszczenie organizmów