Electrical equipment
that electrical devices require an electric power supply;
that some devices should be plugged into an electrical outlet and others should have batteries.
explain where electricity comes from at home;
specify electric power sources;
match a device to its appropriate power source;
build a simple electrical circuit;
carry out an experiment to check whether a substance conducts electricity.
Electric current in our homes
The home has many electrical appliances. Each one is powered by electricity, but where do we get it? Our devices need to have the correct power sourcepower source with the correct voltage. The voltage value is given in volts and is shown with a „V”, eg 230 V means 230 Volts. This is the voltage of all the electrical outlets in Poland. Each electrical device displays what voltage it needs. The voltage in the outlet comes from a power station. In everyday life we also use other sources of electricity, differing in voltage and the type of current.
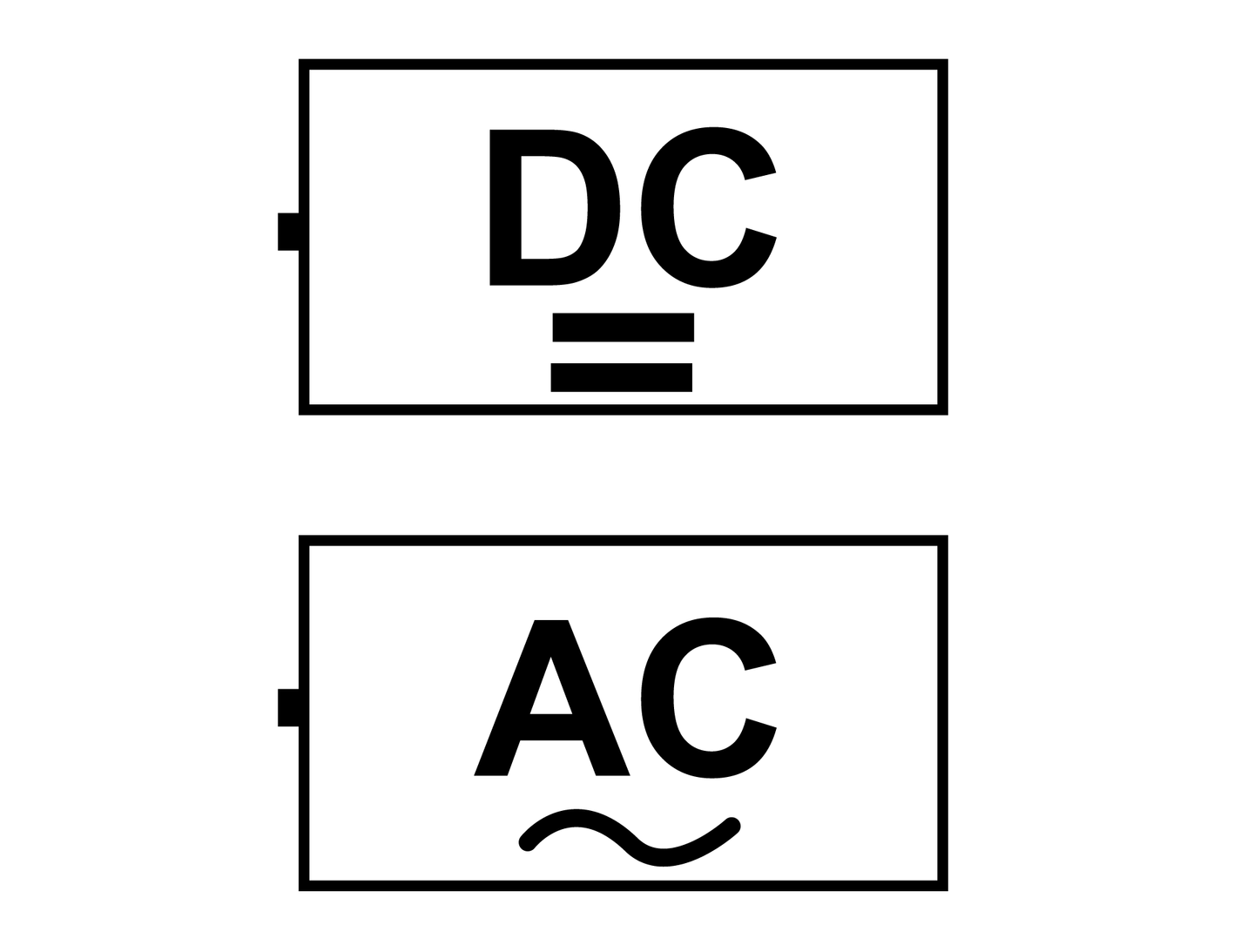
Direct Current and Alternating Current (DC/AC)
As we already know, around us we can find sources of two types of the current, DC and AC. The voltage of direct currentdirect current does not change. On the other hand in alternating currentalternating current the voltage changes very quickly (around 50 - 60 times per second, and sometimes much faster).
Direct current examples are batteries and rechargeable batteries. Such devices have the common name cell. Chemical reactions occur inside them, which allows them to generate electricity which allows them to power devices which require a little power. It is difficult to send direct current over long distances. Therefore, the current we use in our household sockets is alternating current. This current can be transmitted over long distances and thus power devices which require more power.
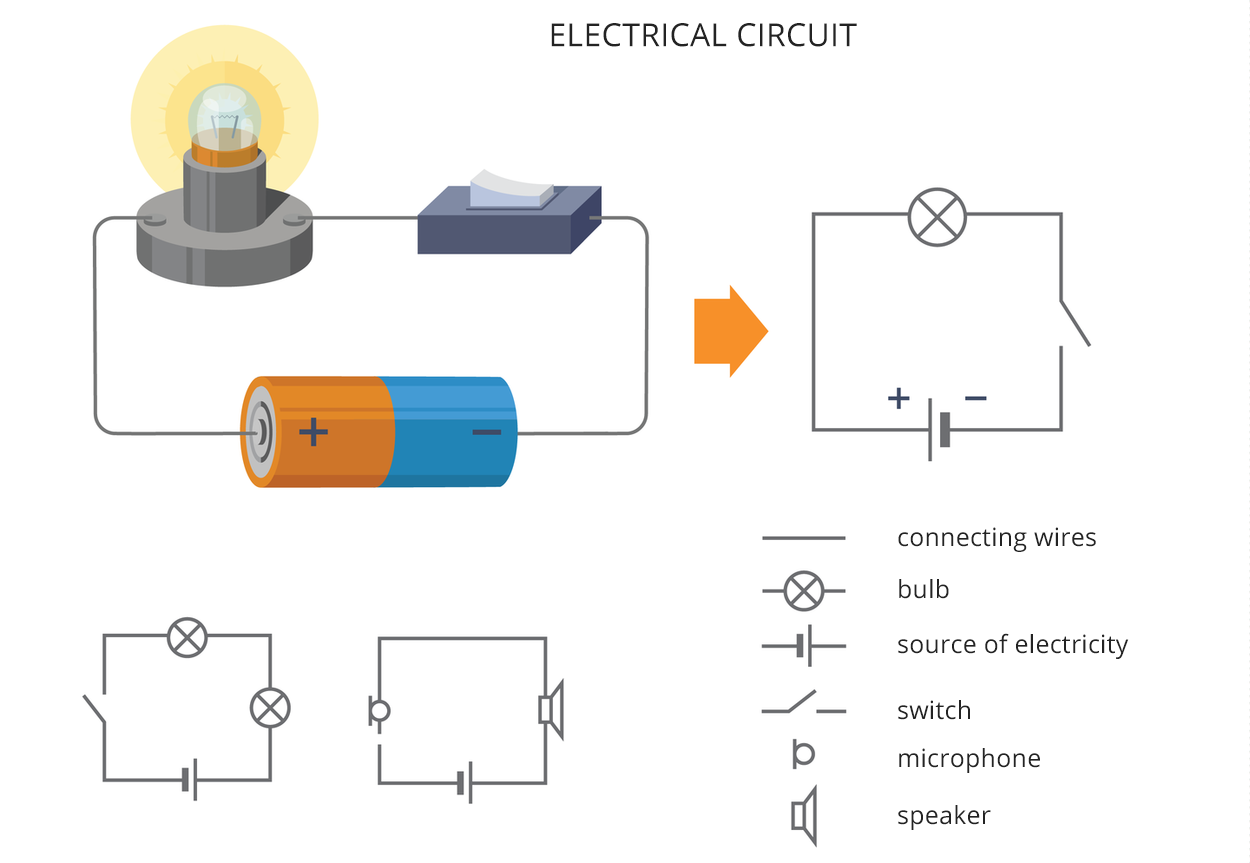
How does a bulb shine?
In order for the device to start working, it must be connected to the appropriate source of electricity using wires. It is therefore necessary to build an electrical circuitelectrical circuit. All electrical circuits, even the simplest ones, consists of several basic elements. These are:
a power source,
an electrical energy receiver (receivers),
electric wires.
The most important part of the electrical circuit is the power source otherwise known as the voltage source. Without a source of electricity, an electric current will not flow in the circuit and the electrical device connected to the circuit will not work. Another element in the circuit is the receiverreceiver. The receivers are all devices operating with the use of electricity, eg a light bulb, a TV set, an iron or an electric heater. Electric wiresElectric wires is nothing but a conductive wire.
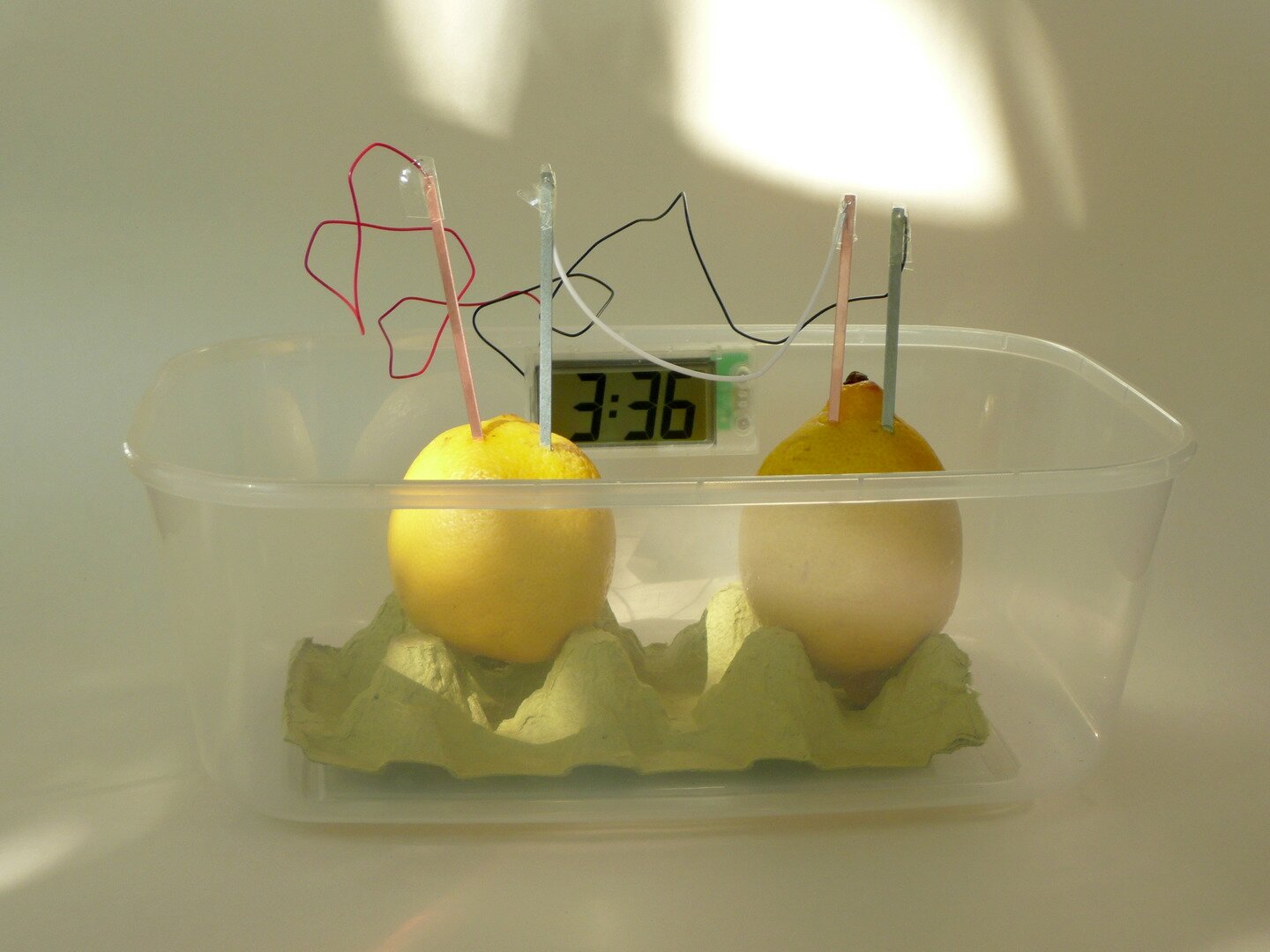
Construction of an electrical circuit.
a lemon,
a copper nail,
a galvanized (zinc) nail,
2 short wires,
an LED bulb.
Stick the nails in a lemon but make sure that they do not touch.
Attach a wire to each nail.
Connect the ends of the wires to the bulb. What do you see?
The lemon and the nails act as a power source. Thanks to this it serves as the basis for building an electrical circuit.
Conductor or Insulator?
Wondering why some materials are used to build electrical wiring, and others to create the insulation for these wires? The explanation is simple: the internal element is designed to conduct electricity, while the insulation should protect us from an electric shock, because it does not conduct electricity itself.
As you already know, some things conduct electricity very well. We call them conductorsconductors of electricity. Other things do not conduct electricity – these are called insulatorsinsulators.
Let's check together what objects around us are conductors and what objects are insulators? Let's use the electric circuit to find out, instead of using a circuit breaker, we will include various objects in the circuit.
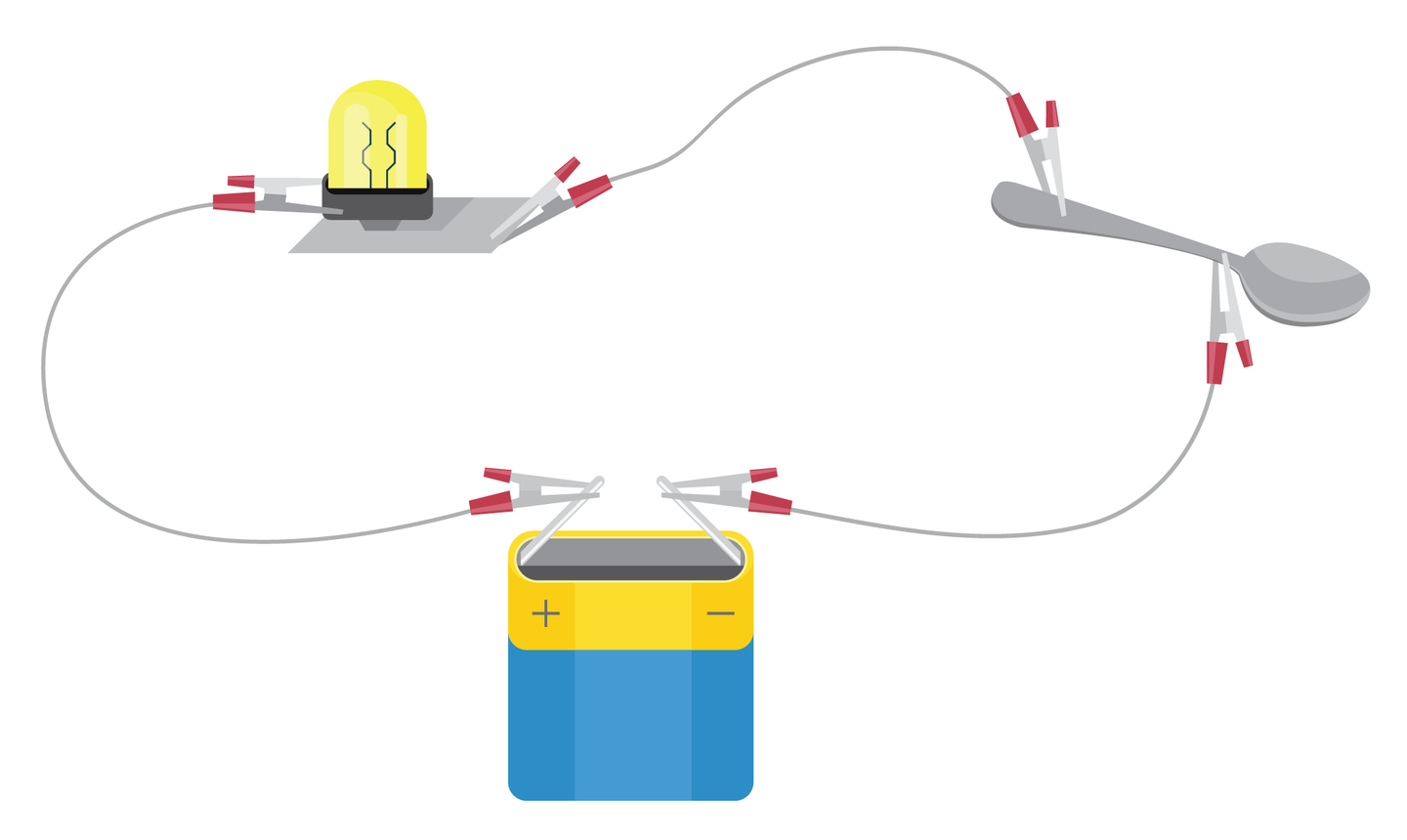
Detection of conductors
a battery
3 wires,
an LED bulb,
graphite,
an eraser,
an aluminium spoon,
a match.
Connect one of the battery terminals to the light bulb with a wire.
Connect the second wire to the other terminal of the battery, and the third with the bulb.
Connect the free ends of the wires to the various items. Make a note when the bulb shines.
If the material from which the object is made is an electric conductor, then the bulb will light up. If it is an electrical insulator, the bulb will not light up.
Match the device to the power source.
vacuum cleaner, TV remote control, a watch, bathroom scales, Microwave, refrigerator
| Direct current | |
|---|---|
| Alternating current |
Choose the most important element of the electrical circuit without which it will not work.
- source of electrical power
- receiver
- electric wires
Decide which statements are true and which are false.
| True | False | |
| For an electrical device it matters what kind of electric current and what voltage we supply it. | □ | □ |
| For an electric device it does not matter what electric voltage we will supply it with, only its type is important. | □ | □ |
| For an electrical device it does not matter what type of electric current we supply it with, only its voltage is important. | □ | □ |
| There is always an electric current in an electrical circuit. | □ | □ |
| The electric current can flow without electrical voltage in the circuit. | □ | □ |
| In order for the electric current to flow, it's circuit must be closed. | □ | □ |
Summary
The power source produces a current with a certain voltage.
DC or AC are used to power electrical equipment.
Each device needs a suitable power source for itself.
The electric circuit consists of at least a power source and its receiver, which are connected by wires.
In order for the current to flow through the circuit, the circuit must be closed.
Conductive materials are called conductors, while poorly conductive materials are insulators.
Keywords
electric circuit, insulator, receiver, alternating current, direct current, conductor, electric wire, power source
Glossary
izolator – substancja, która nie przewodzi prądu elektrycznego, np. tworzywa sztuczne, porcelana
obwód elektryczny – zestaw elementów elektrycznych połączonych ze sobą przewodami elektrycznymi, złożony co najmniej ze źródła prądu i odbiornika
odbiornik – każde urządzenie działające przy wykorzystaniu energii elektrycznej
prąd przemienny – prąd, którego kierunek i napięcie regularnie i bardzo szybko się zmieniają
prąd stały – prąd, którego napięcie nie zmienia się w krótkich przedziałach czasu
przewodniki – ciała dobrze przewodzące prąd elektryczny, np. miedź, aluminium, srebro
przewód elektryczny – przewód wykonany najczęściej z drutu miedzianego (lub innego przewodnika elektrycznego), pokrytego warstwą izolatora
źródło prądu – element obwodu elektrycznego wytwarzający napięcie, np. sieć energetyczna zakończona gniazdkiem elektrycznym, bateria, akumulator, dynamo