Gases – a repetition lesson
Links to the lessons: 1 , 2 , 3
Links to the abstracts: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
to ask questions and answer your friends' questions about gases and their properties.
to consolidate the material from the lessons: „Air – composition and properties pt 1”, „Air – composition and properties pt 2”, „Nitrogen”, „Noble gases”, „Oxygen: obtaining”;
to consolidate the vocabulary related to the theme of gases and their properties.
Before you begin solving the exercises, review abstracts „Air – composition and properties pt 1”, „Air – composition and properties pt 2”, „Nitrogen”, „Noble gases”, „Oxygen: obtaining” to recall the most important information and vocabulary. Then you will be able to check your knowledge. Good luck!
Before the lesson
Arrange a crossword, whose main password will be related to the content of lesson "Air – composition and properties".
Repetition
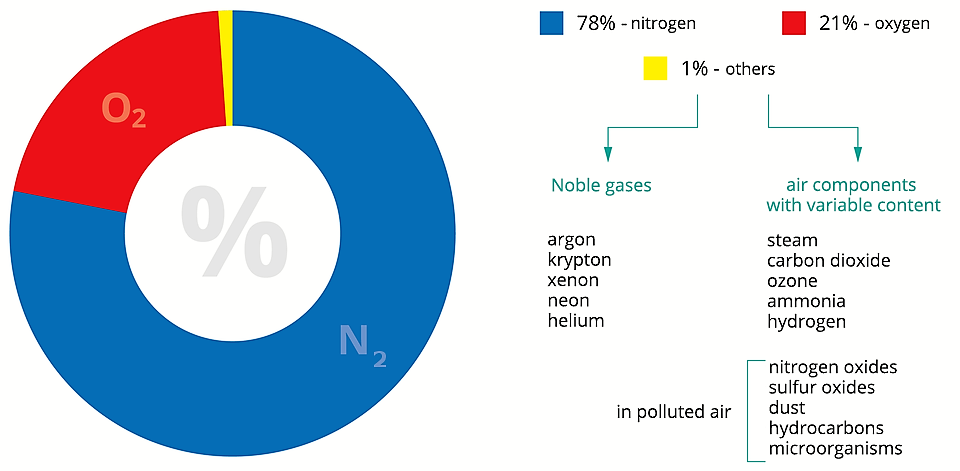
Replace the air components. Which one is the most? Then arrange the puzzle and check your knowledge.
Listen to the recording „Nitrogen” and write down questions you could ask your friend or colleague to check if he understood the text read. Also note the expected answers.
Present the properties of the gases listed below.
Properties of nitrogen:
Properties of noble gases:
Complete the reaction to obtain oxygen from potassium permanganate
2KMnO4, KMnO4, K2MnO4, K2MnO2
→ + MnO2 + O2
If you want to carry out a hydrogen peroxide () decomposition, which product will you use?
- yeast
- chalk
- onion
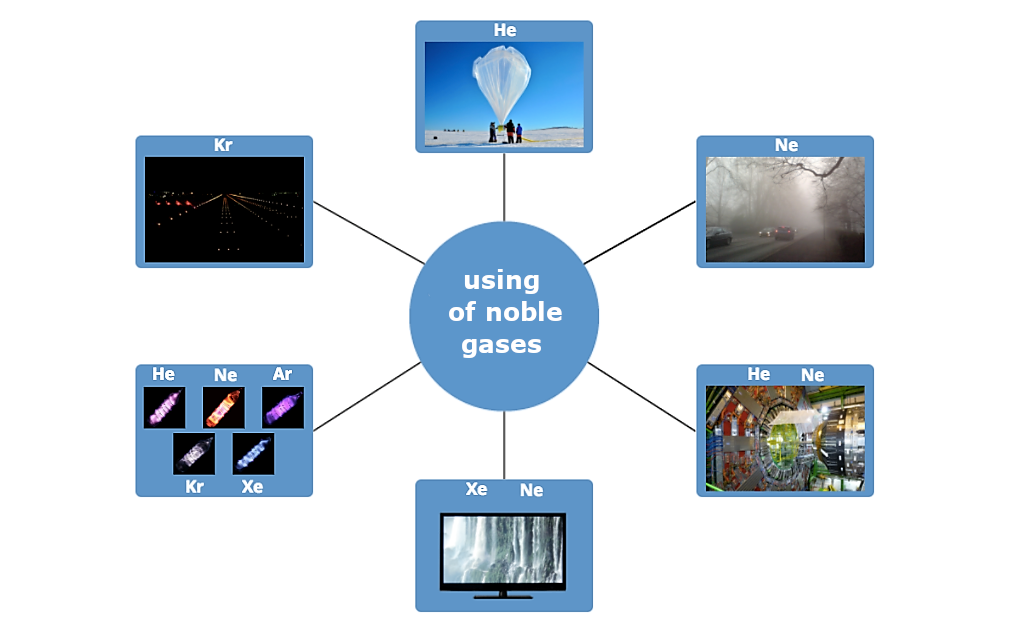
Do you know what noble gases are used for? Write down your suggestions on the board and compare them to the ideas of other students.
Complete a multiple-choice test question for the lesson "Noble gases".
Question: ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
Check the answer if all the drawn elements will describe the proper use of gases.
|
argon
|
breathing mixes in air tanks
|

|
|
oxygen
|
foam and powder extinguishers
|

|
|
carbon dioxide
|
is used in metallurgy, including for steel production
|

|
|
nitrogen
|
filling in computer hard drives
|

|
Match the pairs: English words and Polish definitions.
pierwiastek chemiczny z grupy helowców; po wodorze drugi najbardziej rozpowszechniony pierwiastek chemiczny we wszechświecie; jest niepalny;, pierwiastek chemiczny z grupy helowców; stosuje się go do produkcji lamp jarzeniowych (czerwona barwa), w urządzeniach elektronicznych, jednorodna mieszanina różnych substancji, głównie gazów, bez barwy, smaku i zapachu, stanowiąca atmosferę ziemską, pierwiastek chemiczny z grupy helowców o największym rozpowszechnieniu na Ziemi; jego zawartość w atmosferze wynosi 0,94% (procenty objętościowe);
| air | |
| argon | |
| helium | |
| neon |
Summary
The air is a homogeneous mixture of colourless and odourless gases.
The main components of the air are: nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon and other noble gases (0.94%), carbon dioxide and water in the form of steam.
For the first time, the air was liquefied by Polish chemists: Karol Olszewski and Zygmunt Wróblewski.
The air is compressible – you can easily reduce its volume. You can also expand them, or increase its volume.
The air does not conduct electricity.
Nitrogen is a chemical element of atomic number 7, belonging to the 15th group of the periodic table (nitrate group), has five valence electrons.
Nitrogen is used in many industries and medicine.
Noble gases show the least chemical activity among all known elements. This property is related to the durability of the electronic helium configuration.
Noble gases are used, among others in lighting technology.
Oxygen is the most common element in nature.
Oxygen is a colorless, odorless, slightly soluble in water, chemically active gas.
Oxygen can be obtained during thermal decomposition of potassium manganate(VII), hydrogen peroxide decomposition (in the presence of a catalyst) or water decomposition due to an electric current (water electrolysis).
The industrial method of obtaining oxygen is to distil liquid air.
Keywords
air, oxygen, nitrogen, noble gases, atmosphere, homogeneous mixture, helium, argon, krypton, xenon, radon, liquid nitrogen, neon, obtaining oxygen
Glossary
powietrze - jednorodna mieszanina różnych substancji, głównie gazów, bez barwy, smaku i zapachu, stanowiąca atmosferę ziemską
argon - pierwiastek chemiczny z grupy helowców o największym rozpowszechnieniu na Ziemi; jego zawartość w atmosferze wynosi 0,94% (procenty objętościowe); stosuje się go w procesach chemicznych wymagających obojętnego środowiska, np. podczas spawania, do wypełniania przestrzeni zespolonej w oknach oraz w mieszaninie do wypełniania żarówek razem z azotem
hel - pierwiastek chemiczny z grupy helowców; po wodorze drugi najbardziej rozpowszechniony pierwiastek chemiczny we wszechświecie; jest niepalny; stosuje się go do napełniania balonów, jako czynnik chłodzący w reaktorach jądrowych, a także składnik mieszaniny z tlenem w butlach tlenowych dla nurków
neon - pierwiastek chemiczny z grupy helowców; stosuje się go do produkcji lamp jarzeniowych (czerwona barwa), w urządzeniach elektronicznych
nadtlenek wodoru - 3‑procentowy roztwór nadtlenku wodoru ; stosowany do odkażania ran