How the blood vessels are build, how blood circulates
blood is a liquid tissue;
cardiovascular system of humans is a closed system of vessels;
blood participates in transporting nutrients and respiratory gases.
to present the connection between how organs of the cardiovascular system are build and what their functions are;
you will compare the build and the functions of arteries, veins and capillaries;
you will describe the blood flow in the systemic and pulmonary circulation;
The build of blood vessels
Blood is distributed all over the body using 3 types of blood vessels: arteriesarteries, veinsveins and capillariescapillaries. Their walls are composed of 3 layers of tissues. The outer layer protects the blood vessels, the middle layer, composed of smooth muscle tissue, shrinks them or widens them, meaning that it regulates the blood flow. The internal layer, called endothelium, is thin and smooth, which allows blood to flow.
In arteries, blood circulates under high pressure, which is why the muscle layer and the internal membranes are thick. Veins transport blood under low pressure. Their muscularis is thinner, and internal membrane creates valves. They prevent the blood from flowing backwards and allow it to pump against the law of gravity. There are connections between the arteries and the veins. The network of very thin blood vessels is called the capillaries. Their walls are build of only one layer of cells: simple squamous epithelium. This type of a structure allows the gas exchange to take place and allows various substances to penetrate to and from the vessels.
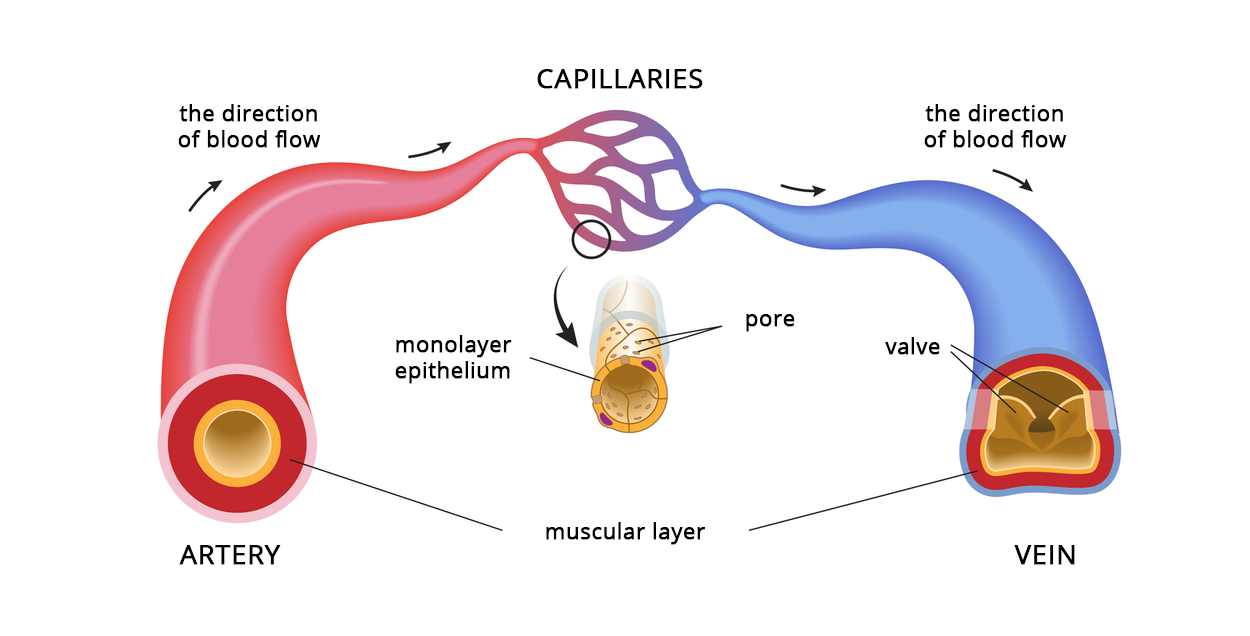
Blood vessels have combined construction. Explain, what significance to the blood flow have the following facts:
The internal membrane of the arteries creates the simple squamous epithelium;;
capillaries are made of only a single‑layered epithelium.
Blood circulation in the bloodstream
Blood flows in a closed circuit of vessels which is composed of 2 circulations: systemic and pulmonary.
In pulmonary circulationpulmonary circulation blood that has a lot of carbon monoxide and very little oxygen is introduced from the right chamber to pulmonary arteries. These arteries are divided into smaller ones until they become thin capillaries that wrap around the alveoli. Between the blood in the capillaries and the alveoli the gas exchange happens. Diffusion happens and blood gives away the carbon monoxide and absorbs oxygen. Oxygenated bloodOxygenated blood goes back via the capillaries which become bigger veins. Pulmonary veins conduct the oxygenated blood into the left atrium.
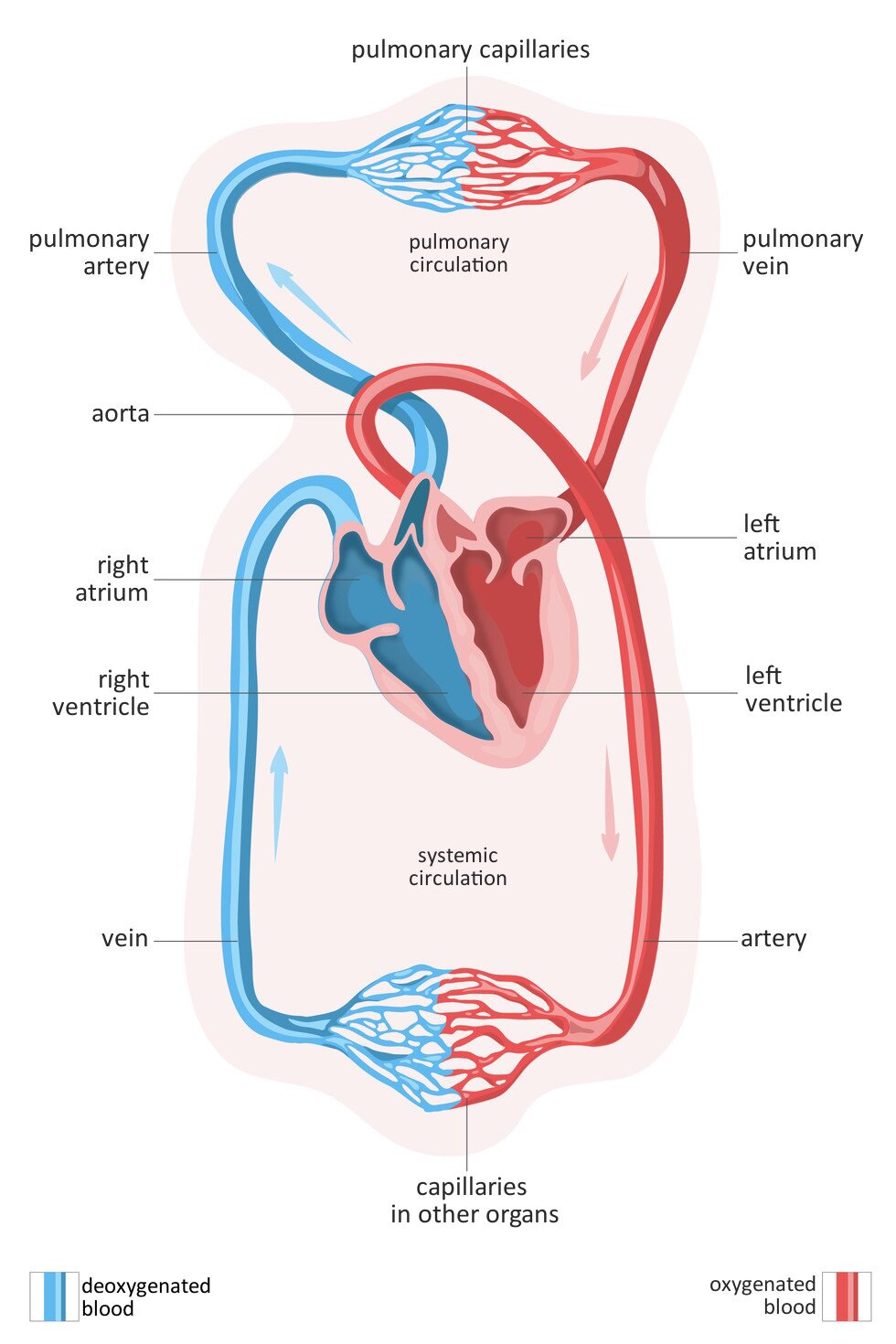
During the contraction of the left atrium, the blood flows into the left chamber, where the systemic circulationthe systemic circulation begins. Next, from the left chamber, it flows to the biggest artery of the body – aortaaorta. This is divided into smaller arteries coming closer to the cells of the body and forming the network of capillaries. Through them, oxygen and nutrients are transported towards the cells, whereas the products of metabolism are absorbed. Diffusion of respiratory gases takes place in the cells. It is also called the internal gas exchange: oxygen enters the tissues, whereas the carbon dioxide is transferred from the tissues into the capillaries. Deoxygenated bloodDeoxygenated blood is taken to the vein capillaries, which form bigger veins. Main veins from upper and lower part of the body transport the blood with carbon dioxide into the right atrium.
Before performing the show „Pressure Measurement” by the school nurse, write down the research question and the hypothesis. Make observations during the task, and finally - conclusions.
Assess, how correct the following statement is: All arteries in human cardiovascular system transport oxygenated blood.
Select the correct sentences.
- Artery is another name for a vein.
- Exchange of substances between blood and cells takes place in capillaries.
- Blood in veins flows at low pressure towards the heart.
- Blood in arteries flows at high pressure towards the heart.
Summary
Cardiovascular system includes the heart and blood vessels: Veins, arteries and capillaries.
Arteries lead blood from the heart, whereas veins lead blood to the heart.
Capillaries are wrapped around cells, provide them with nutrients and participate in gas exchange.
Blood circles in 2 circulations: systemic and pulmonary.
Select a blood vessel in which the blood has a lot of oxygen and little nutrients.
Keywords
veins, arteries, bloodflow
Glossary
aorta – największa tętnica organizmu; wyprowadza krew z lewej komory serca, należy do dużego obiegu krwi
komora – jedna z 4 jam serca zaopatrzona w silnie umięśnione ściany, których skurcz wypycha krew do krwiobiegów – dużego (lewa komora) lub małego (prawa komora)
krew odtlenowana – krew uboga w tlen, bogata w dwutlenek węgla
krew natleniona – krew bogata w tlen, uboga w dwutlenek węgla
krwiobieg duży – inaczej krwiobieg ustrojowy; system naczyń krwionośnych rozpoczynający się w lewej komorze, prowadzący krew tętnicami w kierunku narządów ciała (innych niż płuca), gdzie zachodzi wymiana gazowa wewnętrzna; krew pozbawiona tlenu wraca do serca żyłami do prawego przedsionka
krwiobieg mały – inaczej krwiobieg płucny; system naczyń krwionośnych rozpoczynający się w prawej komorze, prowadzący krew tętnicami w kierunku płuc, gdzie zachodzi wymiana gazowa zewnętrzna; krew naleniona wraca do serca żyłami płucnymi do lewego przedsionka
naczynia włosowate – najcieńsze naczynia krwionośne oplatające komórki; dostarczają składniki odżywcze, uczestniczą w wymianie gazowej, odbierają z komórek produkty przemiany materii
tętnice – naczynia krwionośne transportujące krew z serca (komór) w kierunku komórek ciała
żyły – naczynia krwionośne zaopatrzone w zastawki; transportują krew z komórek ciała do serca (przedsionków)