Human genetic diseases caused by chromosomal mutations
that sexual reproduction is the cause of genetic variability;
that certain diseases are the result of errors that occur in the DNA.
to distinguish different chromosome mutations;
to provide examples of human diseases caused by mutations.
Chromosomal mutationsChromosomal mutations are changes in the structure of single chromosomes or the number of chromosomes in a cell. Such mutationsmutations are usually caused by an incorrect propagation of chromosomes to gametes during meiotic division. If chromosomes of one of the pairs do not separate but move together during meiosis, then one of the gametes receives both of these chromosomes after the division, and the other receives neither. Consequently, after fertilisation with such gametes, an individual referred to as trisomic may be formed, with three chromosomes of such pair (one from the correct gamete and two from the incorrect one), or monosomic, with only one chromosome from the pair.
Most embryos with chromosomal mutations die already at an early stage of development. Only a few chromosome mutations are not fatal, but they always cause serious genetic diseases.
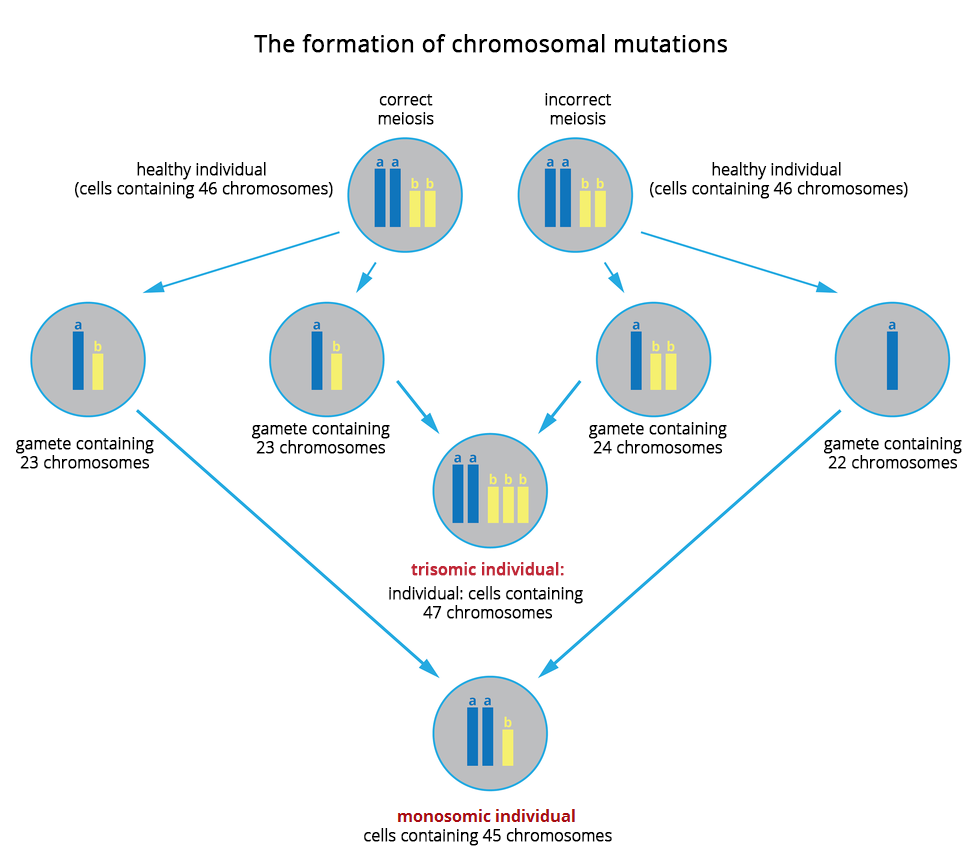
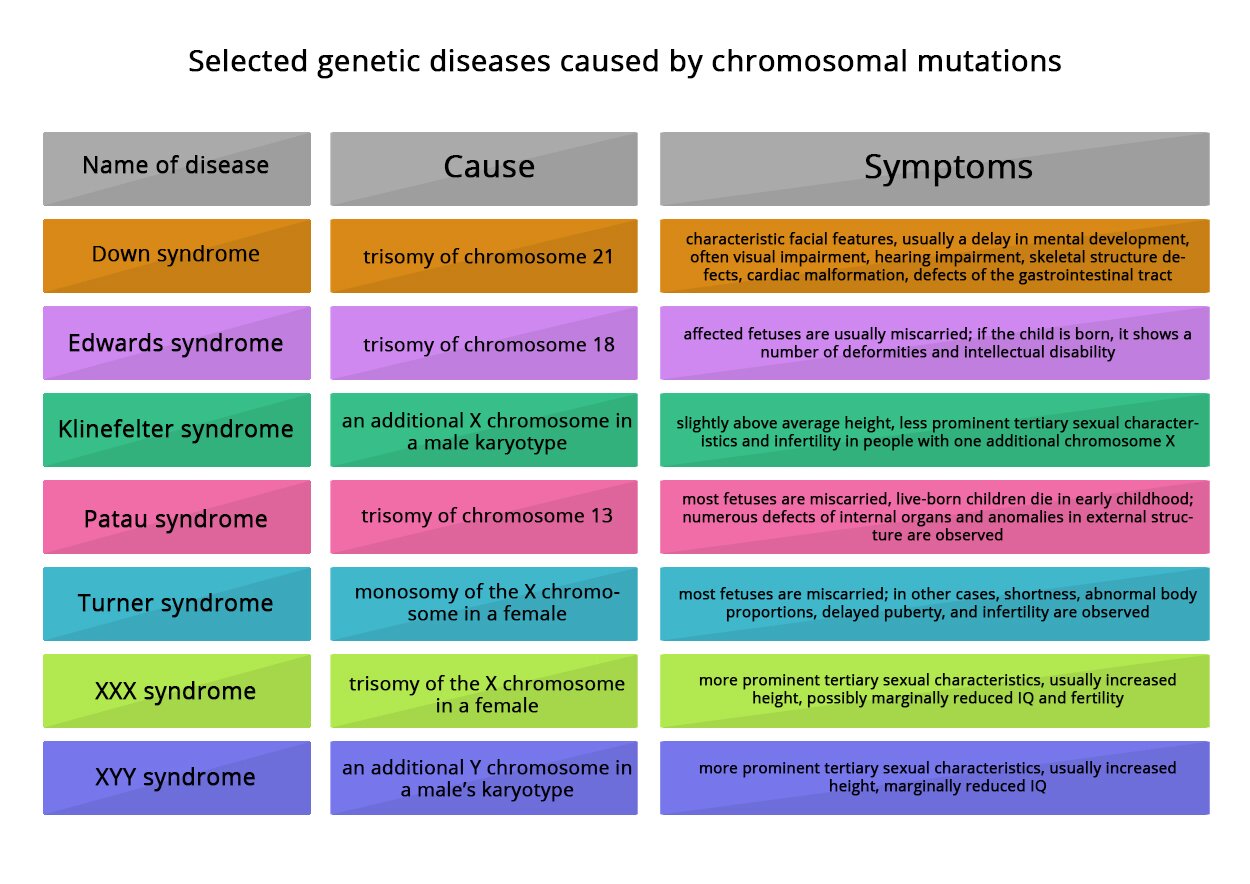
Match the description to each of the following terms.
an organism containing a single set of all chromosomes, an organism that has a double set of all chromosomes, an organism that has an additional chromosome in a given homologous pair, an organism that has a triple set of all chromosomes, an organism that lacks one chromosome from a given homologous pair
| haploid | |
| diploid | |
| triploid | |
| monosomic | |
| trisomic |
A certain woman expects a child. Both she and her husband are healthy. Still, she is very afraid because her sister was born with Down's syndrome. Is there an increased risk of being born with this disease for the unborn child of this woman?
- No, because Down syndrome is triggered by the dominant allele. If a woman and her husband are healthy, they will not pass that gene to the child.
- No, because Down's syndrome is usually the result of an error during meiosis. The fact that the woman's sister is ill does not cause an increased risk to the child.
- Yes, because Down syndrome is triggered by the recessive allele. A woman can be the carrier of this allele and not know about it.
- Yes, because Down syndrome is triggered by a group of several genes. The woman's child can inherit part of these genes from the mother and the rest - from the father.
Summary
Chromosome mutations are changes in the number or structure of chromosomes.
Keywords
chromosome mutations, genetic diseases, Down syndrome
Glossary
mutacja – nagła, trwała zmiana w informacji genetycznej organizmu, polegająca na zmianie struktury lub ilości materiału genetycznego
mutacja chromosomowa – jeden z typów mutacji; zmiana struktury lub liczby chromosomów, wywołująca dziedziczną zmianę cech organizmu
zmienność genetyczna – naturalne różnice w sekwencji DNA, występujące u osobników danego gatunku, będące wynikiem rozmnażania płciowego i mutacji