In the deep sea
how water density, temperature, pressure and salination affects water life;
the living conditions in an open body of water.
to describe the conditions prevalent in the deap sea;
to explain why there are is no plant life in the ocean depths;
indicate how animals have adapted to life at large depths.
Living conditions in the deep sea
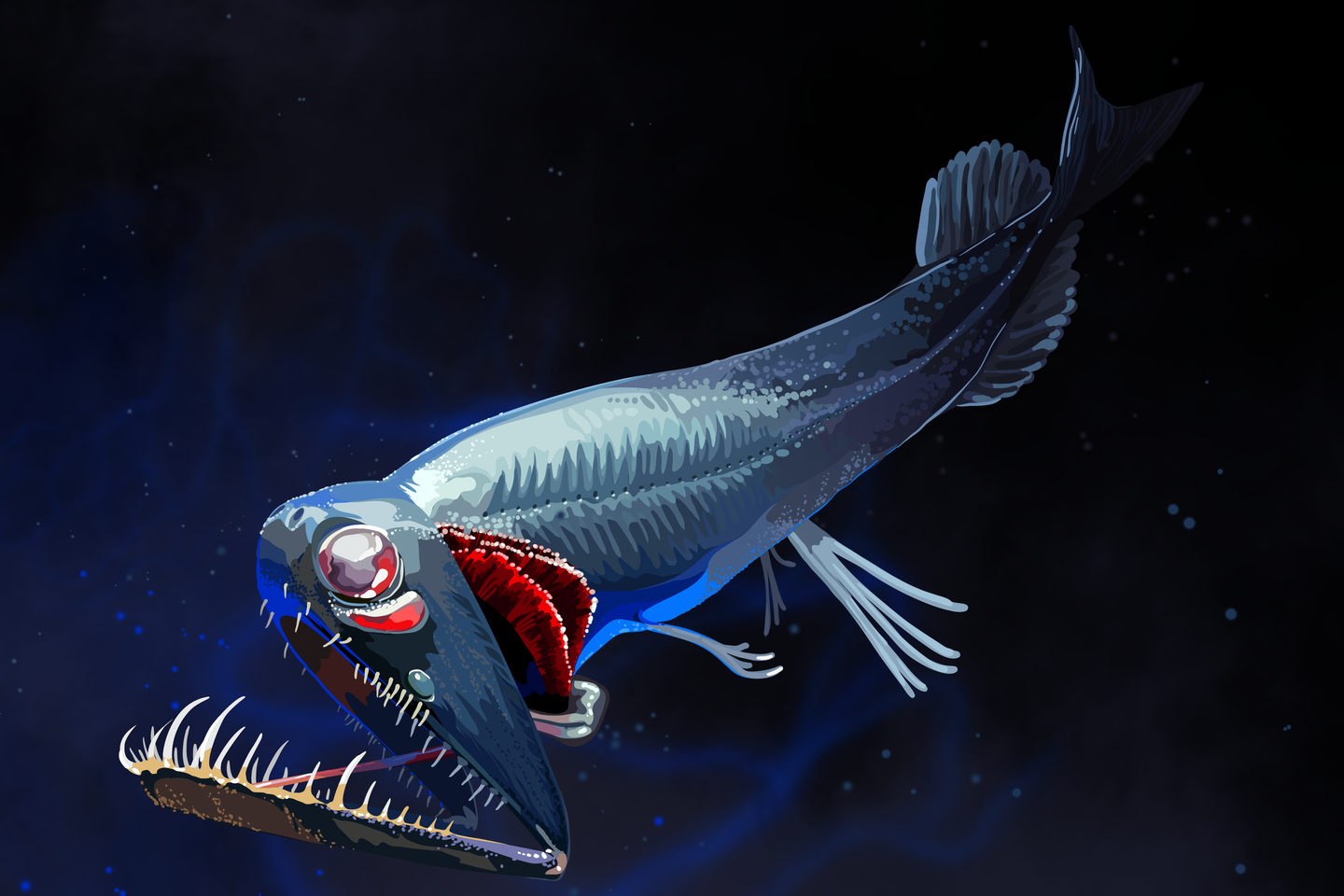
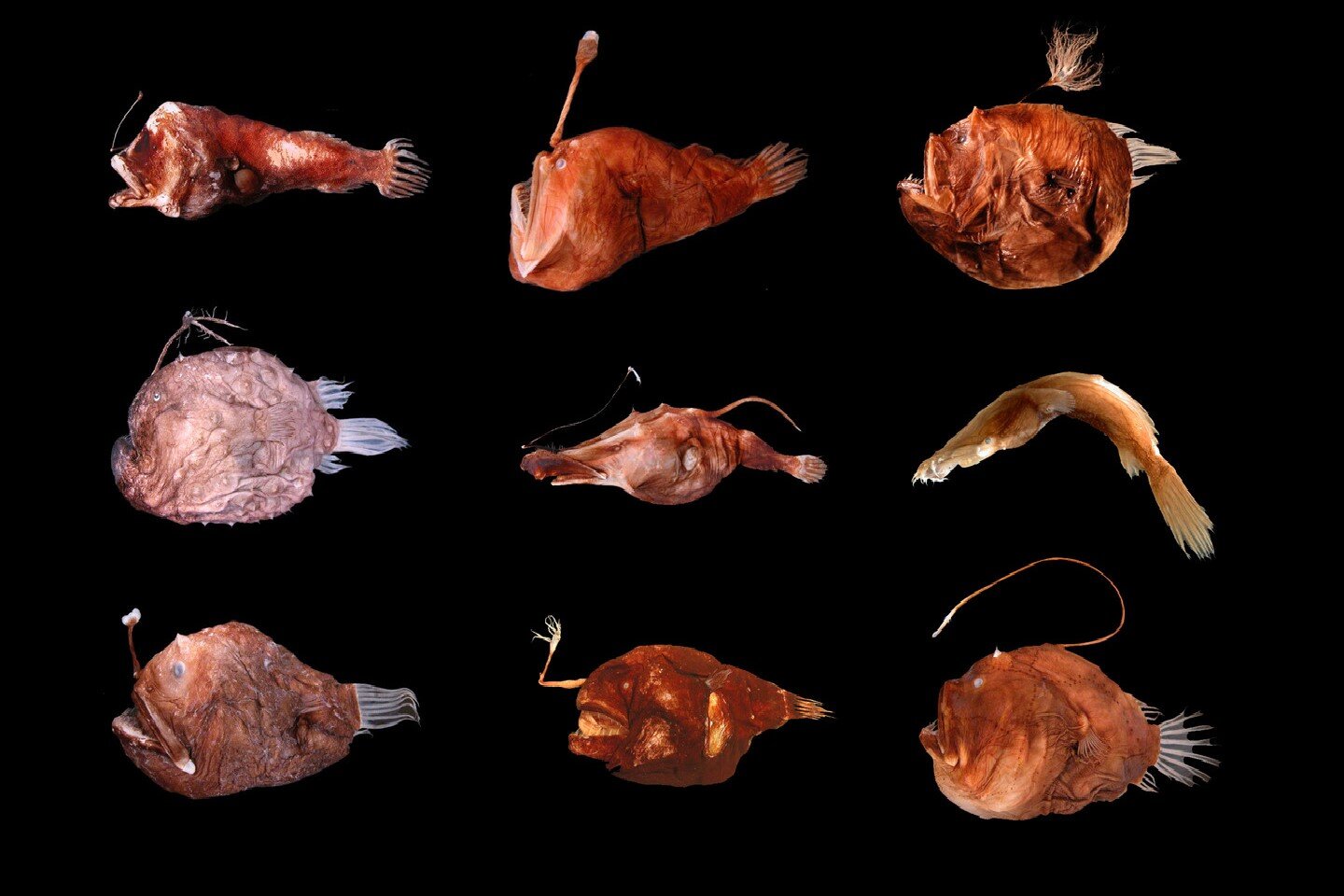
Sunlight doesn’t reach oceanocean waters at the depth of 1000 m below the surface. There is absolute darkness. No plant life can survive in this zone. However, there are animals that feed on plant and animal remains that fall from surface water layers that are reached by sunlight. Other animals that live in the deep sea are predators. Many animals have developed various light‑emitting organs that are useful for hunting or searching for a mate. Certain animals have completely lost the organ of sight. Others have developed huge eyes so that they may receive even the weakest optical stimuli.
An additional difficulty for animals living in the deep sea is the pressure that rises as depth increases. In the ocean trenches, water pressure is 1000‑times higher than air pressure! Organisms that live near the surface cannot withstand such pressure, as their bodies would be crushed. The deep‑sea organisms, on the other hand, aren’t able to surface, as they would be ripped apart by the internal pressure that protects their bodies from being crushed in the depths.
The deep ocean bed and ocean trench beds are among the places on the globe that have been studied to the least extent. Due to technical difficulties, the catching of marine organisms and the extraction of mineral resources from these depths have so far been developed only to a small extent.
Deep‑sea organisms
The variety of organisms that live in the deep sea and ocean trenches still remain largely undiscovered, but it’s still greater than was expected. There is a particularly large variety of invertabrates that consume the smallest nutrient particles from silt.
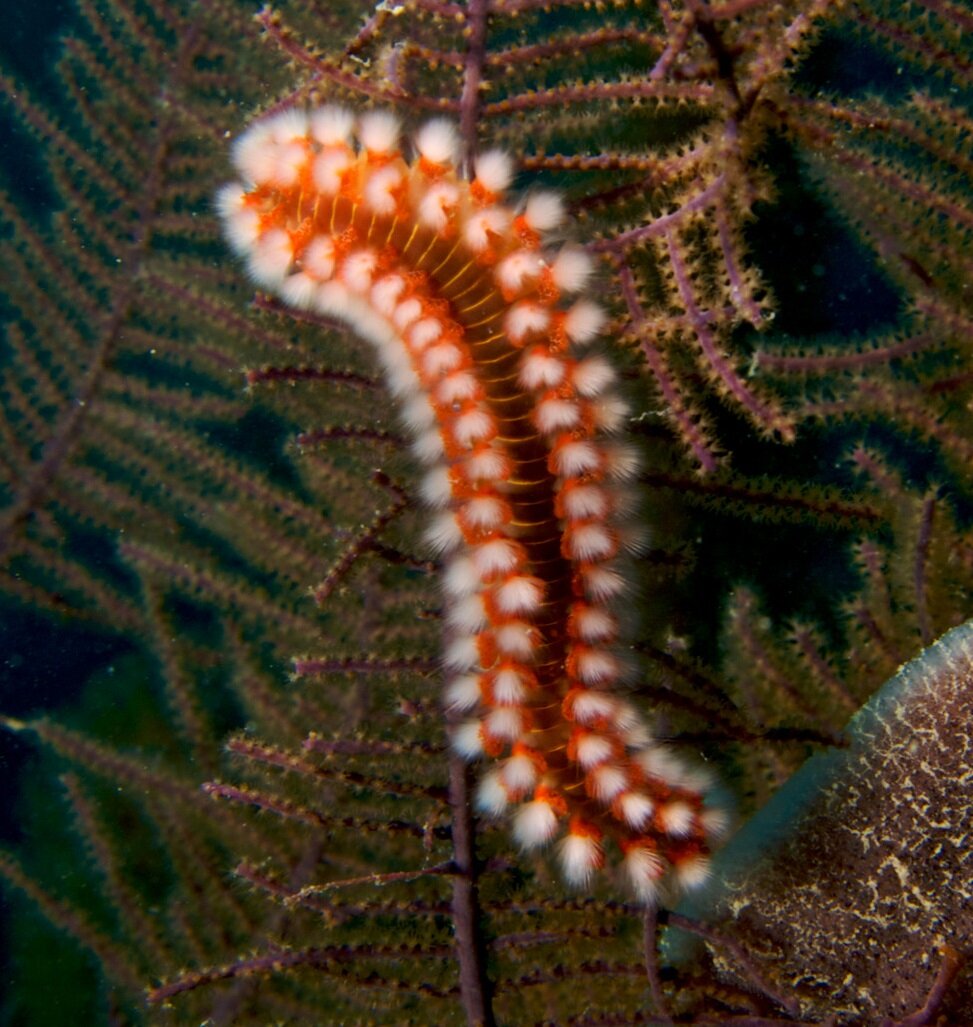
Marine annelids are organisms that slightly resemble earthworms, but are equipped with numerous bristles. They crawl on the bed or float in water, consuming small organisms or their remains. They are the primary source of nutrition for other animals.
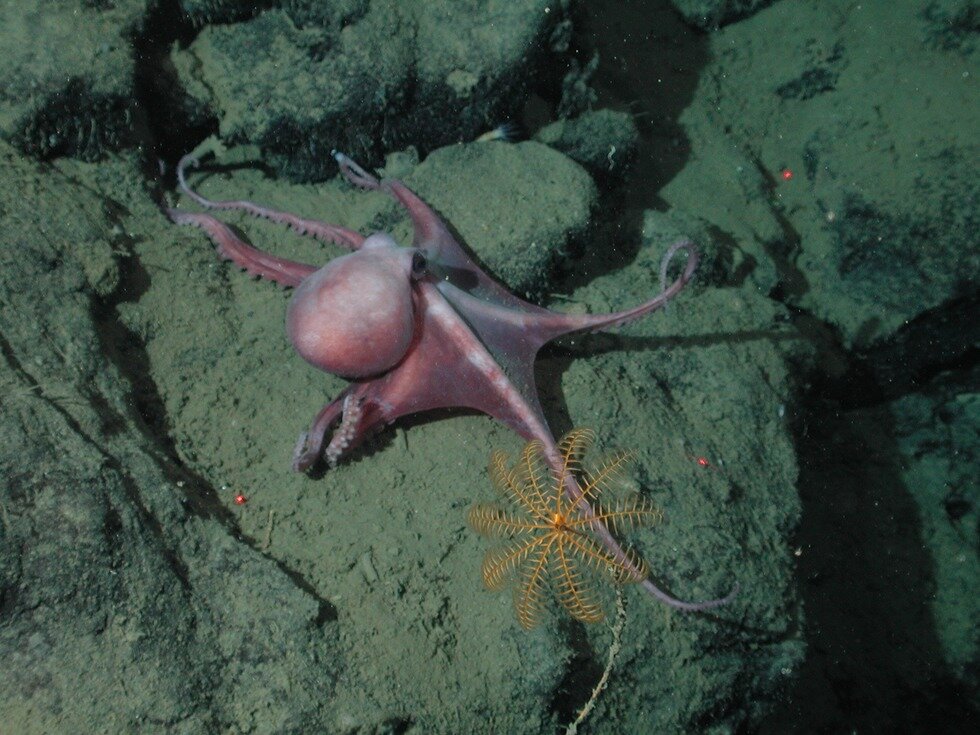
Many species of cephalopods can also be found in the ocean depths, primarily octopi which have a soft body and eight tentacles of equal length and squids which have an elongated body and ten tentacles, two of which are visibly longer.
Deep‑sea fish can be found up to the depth of 8000 metres below sea level. They are very diverse in terms of their appearance and what they feed on.
Which of the following is not a real ocean?
- Northern
- Arctic
- Atlantic
- Indian
- Pacific
- Southern
Summary
The deep sea is a part of marine waters where the sunlight does not penetrate.
The deep sea is characterised by extremely high pressure.
Deap‑sea animals feed on dead organic matter that comes from near‑surface water layers, bacteria and other animals.
Keywords
light‑emitting organs, ocean, deep sea
Glossary
ocean – wielka część hydrosfery stanowiąca odrębny fragment wszechoceanu; najczęściej wyróżnia się 4 oceany, ale są też klasyfikacje wyróżniające 3 (nie wydziela się wtedy Oceanu Arktycznego) lub 5 oceanów (wody wokół Antarktydy uważa się wówczas za Ocean Południowy)