Local government
The territorial division of Poland includes three levels of local government: gminas (communes), poviats and voivodeships.
You will be able to explain the essence of local government and discuss its importance to democracy.
You will be able to describe the territorial division of Poland.
You will be able to name the organs of local government and describe how they are elected.
According to the Constitution the inhabitants of the units of basic territorial division form a self‑governing community in accordance with law. These inhabitants, directly or through the representatives they have chosen, manage the affairs of the community and carry out other tasks in the field of public administration, assigned toassigned to the local government by the legislatorlegislator.
The Constitution of the Republic of PolandArticle 15
The territorial system of the Republic of Poland shall ensure the decentralization of public power.
The basic territorial division of the State shall be determined by statute, allowing for the social, economic and cultural ties which ensure to the territorial units the capacitycapacity to perform their public duties.
Article 16
The inhabitants of the units of basic territorial division shall form a self‑governing community in accordance with law.
Local government shall participate in the exercise of public power. The substantialsubstantial part of public duties which local government is empowered toempowered to discharge by statute shall be done in its own name and under its own responsibility.
Source: The Constitution of the Republic of Poland.
The local government reform was one of the most important in Poland after 1989.
Initially, the reform was limited to the level of the commune. The basis for the reform was the constitutional amendmentconstitutional amendment of 8 March, 1990 and the statute on local government adopted on the same day. In 1998 the second stage of the reform was introduced, which included the reform of the territorial division of the country. Poviats were introduced and the number of voivodeships was reduced from 49 to 16. As of 1, January, 1999 there is a three‑level local government in Poland: commune – poviat – voivodeship.
Local government in a free Poland
Decentralization – a reduction in the authority of national governments over policymakingpolicymaking by endowingendowing its citizens or their elected representatives with more power.
Legislative and executive bodies in different local government units
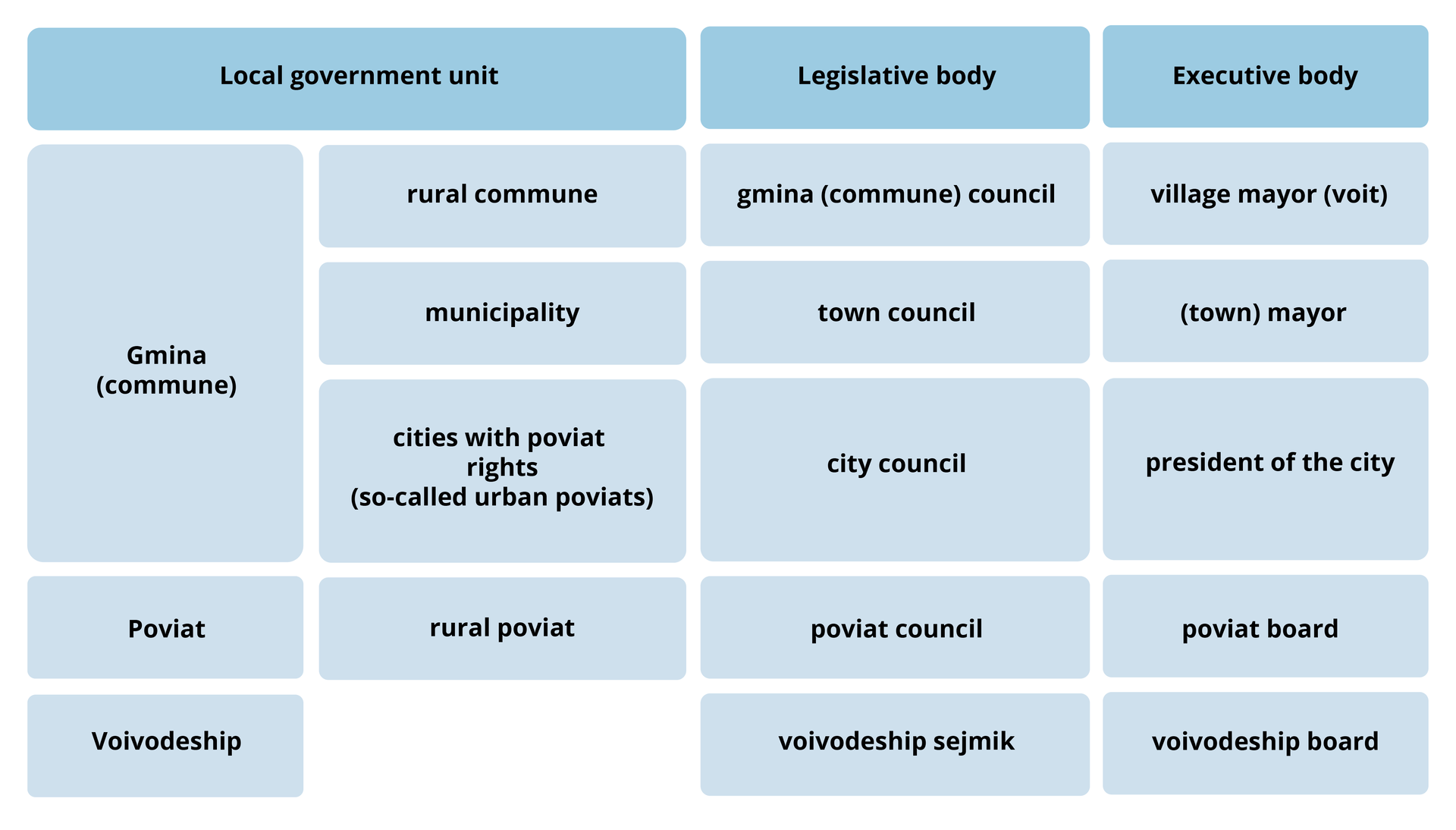
Local government elections are held every four years. The inhabitants of each unit of the local government vote for their representatives to each legislative body (on the commune, poviat and voivodeship level), and choose a voit, town mayor or president of the city.
Election of local government legislative bodies
Election of local government legislative bodies
Gmina (commune) council
Commune councils are elected in the majority system in single-mandate or multi-mandate constituencies, depending on the population of the commune.
Polish and European Union citizens who are over 18 and have permanent residency within the territory of the commune are both eligible to vote and stand for election.
Poviat council
Elections to poviat councils are held in a proportional system, in multi-mandate constituencies.
To participate in the distribution of seats in the council, the candidates have to be part of an election committee whose list gained at least 5% of votes in the poviat.
The right to vote and stand for election is granted to Polish citizens who are over 18 and have permanent residency within the territory of the poviat.
Voivodeship sejmik
Elections to the sejmik of the voivodeship are held in a proportional system, in multi-mandate constituencies.
To participate in the distribution of seats in the sejmik, the candidates have to be part of an election committee whose list gained at least 5% of votes in the voivodeship.
The right to vote and stand for election is granted to Polish citizens who are over 18 and have permanent residency within the territory of the voivodeship.
Election of local government executive bodies
Election of local government executive bodies
Gmina (commune)/urban poviat (city with poviat rights)
In rural communes, municipalities and cities with poviat rights executive bodies are one-man posts. Village and town mayors, as well as presidents of cities with poviat rights are elected directly by the inhabitants of the commune.
To be eligible to stand for election the candidate has to be over 25. The candidate doesn’t have to be a permanent resident of the commune in which he decides to run.
Poviat
The executive body in the poviat is of collegial character. The poviat board, headed by a staroste, is appointed by the commune council.
Voivodeship
The voivodeship board consists of five people: the marshal of the voivodeship, one or two deputy marshals, and other members. It is appointed by the sejmik of the voivodeship.
In modern democratic states, the power is divided between the state and the local government authorities – representing the interests of the local community, elected and controlled by the community. From 1, January 1999, Poland has a three‑level territorial division of the state. Communes, poviat and cities with poviat rights are managed by the local government only, and at the voivodeship level the competences are divided between local government units (voivodeship sejmik and board) and government administration bodies (voivode).
Create a single-choice question connected to the lesson's subject. Ask your classmate to answer it.
Question: ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
Listen to the abstract recording to review the material and new vocabulary. Then do the vocabulary exercise. Match the pairs: English and Polish words.
stałe zamieszkanie, ustawodawca, jednomandatowy (wielomandatowy) okręg wyborczy, kolegialny, zbiorowy, nowela konstytucyjna, poprawka (do konstytucji), znaczny, tworzenie polityki, uprawniony do
| legislator | |
| substantial | |
| empowered to | |
| (constitutional) amendment | |
| policymaking | |
| collegial | |
| single-mandate (multi-mandate) constituency | |
| permanent residency |
Keywords
territorial division, (rural) gmina (commune), municipality, (rural) poviat, voivodeship, decentralization, collegial, city with poviat rights (urban poviat), commune/town/city/poviat council, voivodeship sejmik, village/town mayor, voit, president of the city, poviat/voivodeship board, voivode
Glossary
przypisane do
ustawodawca
zdolności, możliwości
znaczny
uprawniony do
rozdzielać
nowela konstytucyjna, poprawka (do konstytucji)
tworzenie polityki
wyposażać
kolegialny, zbiorowy
codzienne
radzić sobie z
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie słówka: single‑mandate (multi‑mandate) constituency
jednomandatowy (wielomandatowy) okręg wyborczy
stałe zamieszkanie
jednoosobowy
stanowisko