Poland is us. Democracy
You will find out what the origins of democracy were.
You will be able to name and explain the underlyingunderlying principles of the democratic rule.
You will know who Cleisthenes was, and be able to explain what ostracism was in ancient Greece, as well as what it is today.
You will be able to explain the difference between direct and indirect democracy, and give examples of the forms they take.
Origins of democracy
The word democracy comes from ancient Greece. It originates from two words: demos – the people and cratos – power, the authorities or government. The meaning of the word was “the power of the people”. The most important values to the Greek democracy were the freedom and equality of the citizens.
Take a look at the infographics presenting the basis for democratic rule, as well as its ultimateultimate goals.
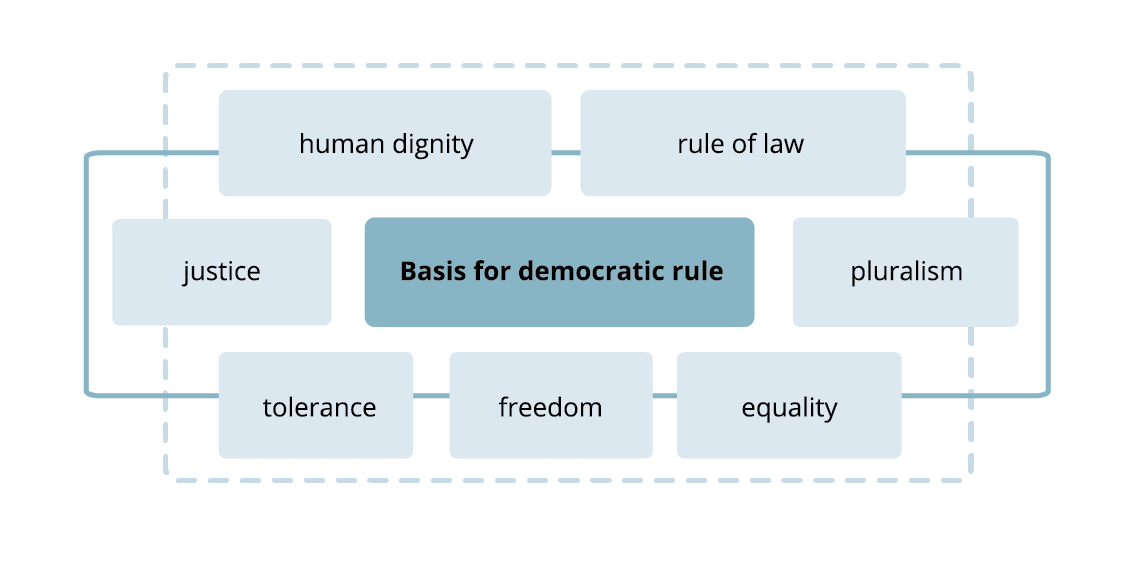
You have already studied the meaning of most of these words, so let us just remind you that:
pluralism is means “multiplicity/diversity”, e.g. many political parties with different programmes operating in the political system;
the rule of law means “compliance withcompliance with applicable law” by all citizens, but also, even more importantly, by all institutions, organizations and state authorities.
A political system, a state, political parties, all social organizations and institutions deserve to be called democratic if they include and implement these values in their programmes and actions.
Cleisthenes lived at the turn of the 6th and 5th centuries BC. He carried outcarried out reforms that became the foundation of Athenian democracy. One of the most interesting ideas of Cleisthenes was ostracism. Citizens of Athens, by voting, could remove from their country a person whose views they found threatening to democracy. Their votes were castvotes were cast on pottery shardspottery shards (broken pottery), hencehence the name (potsherd - ostracon).
Today, ostracism means:
exclusion from a social group
hostilityhostility/dislike towards the person rejected by a group
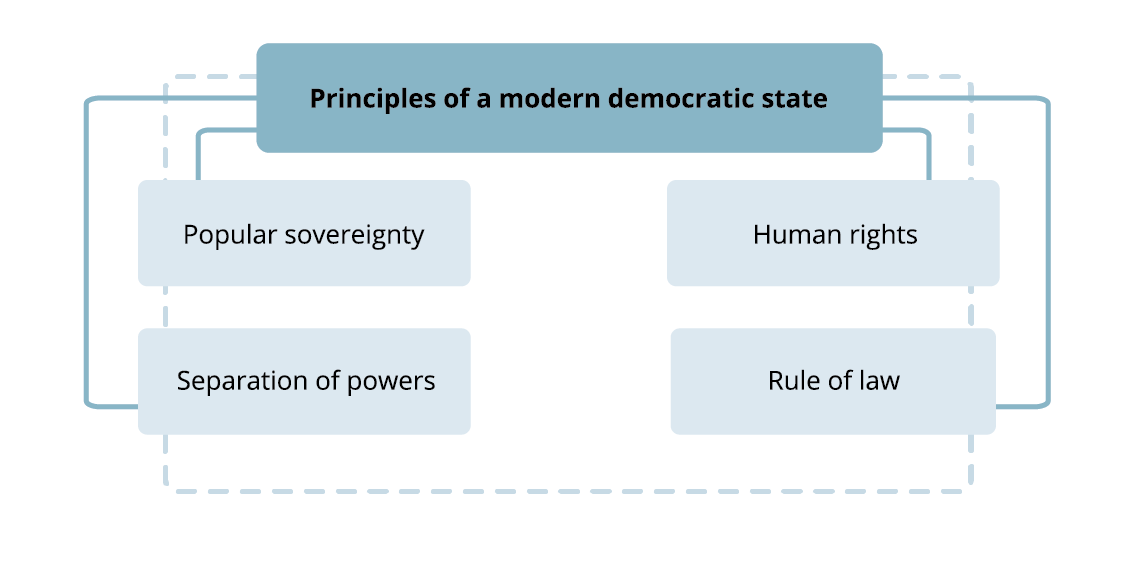
You will find out the meaning of these terms in the next few lessons.
Forms of democracy
Two forms of democracy have evolved in the historical development of societies: direct and indirect (representative) one.
Direct democracy
The origins of direct democracy are connected with the political system of ancient Athens. Every Athenian citizen personally took part in governing of the state, participating in the deliberationsdeliberations of the popular assembly (Ecclesia). Direct democracy, as a way of exercising political power, was possible under conditions of a small area of the city‑state (polis) of Athens and a small number of citizens. In modern democratic states elements of direct forms of government have been preserved. One of them is a referendum.
Remind yourself what the referendum is and complete the definition.
local, electorate, indirect, all politicians, worldwide, nationwide, proposal, direct
A referendum is a .............................. vote in which an entire .............................. has the opportunity to decide on a particular ............................... There may be a .............................. referendum (concerning for example the construction of a landfill or a sewage treatment plan) or a .............................. referendum (concerning for example changes to the Constitution).
Representative democracy
Representative democracy is a system in which decisions on behalf ofon behalf of citizens are made by representatives chosen by the citizens through free elections (e.g. deputies, councilors). Indirect democracy is typical of most modern democratic states, including Poland. As the number of inhabitants of modern countries exceedsexceeds the number of citizens of ancient Athens many times, direct democracy could not function effectively.
Indicate, in which of the presented situations the principles of direct democracy have been applied, and in which - the principles of representative (indirect) democracy. Justify your choice.
| Situation | Direct democracy | Representative democracy |
| A general meeting of members of the school sports club was called. Almost everyone came to the meeting. An important decision was made to change club colors. | □ | □ |
| Elections were closed. The school electoral commission counted the votes and informed, which students will be members of the school council board this year. | □ | □ |
| Each class has selected a student to attend meetings with the school management. Consultations will concern the most important issues related to school life. | □ | □ |
| The form teacher together with the students decided to award prizes. On special cards, each student pointed to three people who, in his opinion, should be recognized for their work for the benefit of the class. | □ | □ |
The school management wants to organize extracurricular foreign language classes for all students. What language should be chosen? It has been decided, that students themselves should be consulted on the issue. The school management has two options to find out, what the students’ opinion is:
- Organize a referendum.
- Organize a meeting with class representatives and, after a discussion, make the decision by voting.
Democracy is not only a political system, but most importantly - active, responsible citizens. You learn the principles and mechanisms of democracy at school already. Through participation in activities undertaken by the school community, you learn independence, decision making, responsibility for yourself and others. The student government is, by legal definition, the whole school community, it is YOU. The fate of the school and the future of the state also depends on you. Remember that the stability and quality of democracy depend on us.
Listen to the abstract recording to review the material and new vocabulary. Then do the vocabulary exercise. Match the pairs: English and Polish words.
zasadniczy, najważniejszy, rozważania, w imieniu, przekraczać, przeprowadzać, dominujący, przeważający, odłamki garncarskie, oddawać głosy
| dominant | |
| underlying | |
| to carry out | |
| pottery shards | |
| to cast votes | |
| deliberations | |
| on behalf of | |
| to exceed |
Keywords
direct/indirect (representative) democracy, freedom, equality, justice, tolerance, pluralism, rule of law, human dignity, popular sovereignty, human rights, separation of powers, ostracism, referendum
Glossary
dominujący, przeważający
zasadniczy, najważniejszy
starożytny
ostateczny
w zgodności z
przeprowadzać
odłamki garncarskie
oddawać głosy
stąd
wrogość
rozważania
w imieniu
przekraczać