Przeczytaj
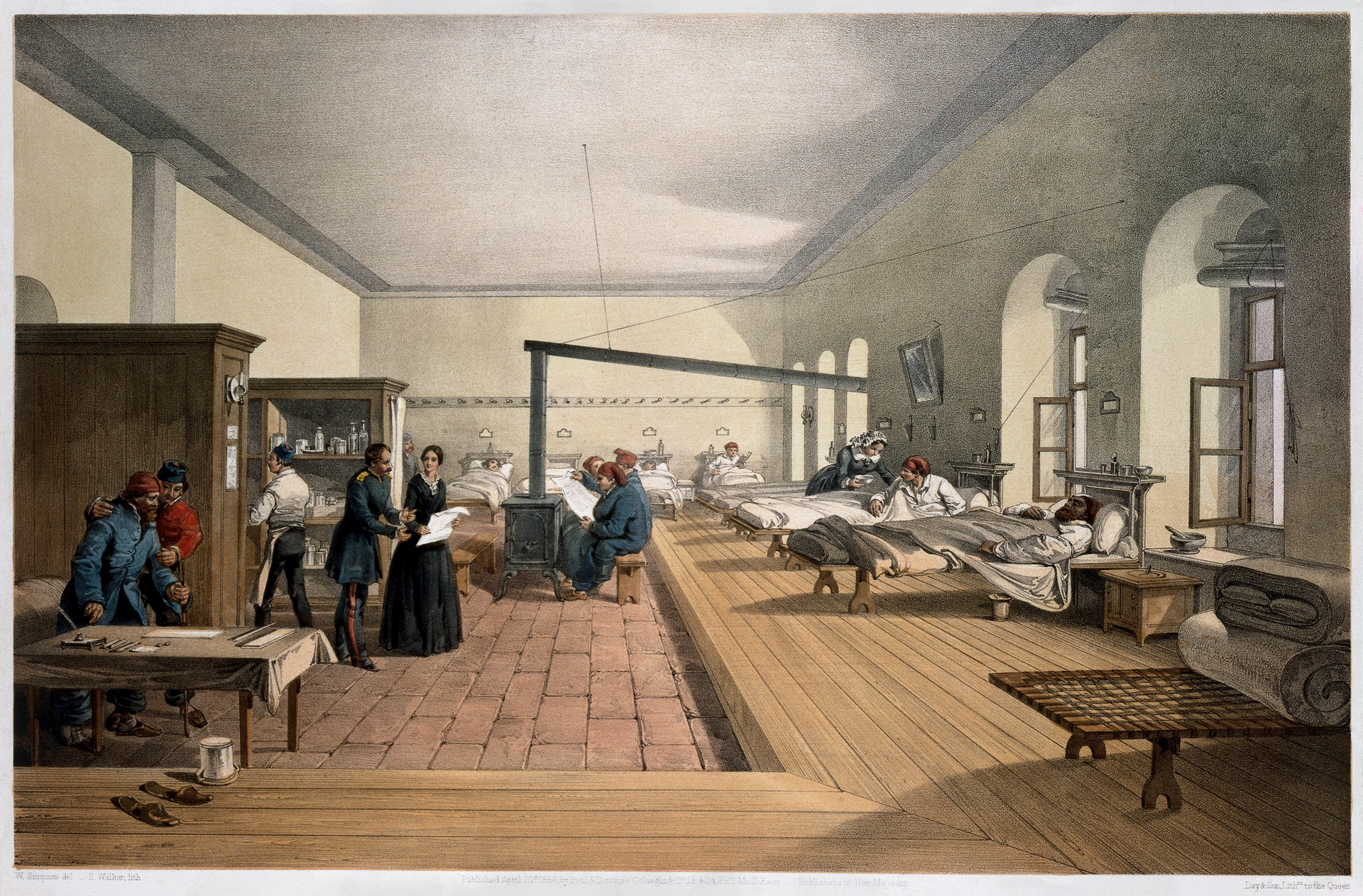
The picture below depicts the ward in which Florence Nightingale worked in Scutari, Turkey during the Crimean War. Notice the wounded in beds in the background. The figure of a woman on the left, is presumably Florence. You are going to study the text on the life of the nursing pioneer Florence Nightingale to learn more about this inspiring figure.
Poniższe zdjęcie przedstawia, jak wyglądał oddział, w którym pracowała Florence Nightingale w Scutari, w Turcji, podczas wojny krymskiej. Zwróć uwagę na rannych leżących w łóżkach w tle. Postać kobiety po lewej stronie to przypuszczalnie Florence. Zapoznaj się z tekstem o życiu pionierki pielęgniarstwa, Florence Nightingale, aby dowiedzieć się o niej więcej.
Study the text and do the exercises below.
Florence Nightingale - the Nurse who CaredFlorence was born in Italy on May 12, 1820. Her parents gave her the name inspired by her birthplace: Florence in Italy. Nightingale’s parents were affluentaffluent and she could therefore be well‑educated. 1. ___. She learnt Greek, Italian, Latin, French, German, history, maths, literature, and philosophy. She could marry a rich gentleman, but declined the offer, possibly due to her inner voice telling her to follow a different career path and decided to dedicate herself to helping others instead. Even though nursingnursing was at that time socially underrated, Florence disregarded her family’s opinion and decided to train in this field as she felt she had a vocation forvocation for it.
Florence attended a nursing school at Kaiserwerth in Germany in 1850 and in 1851. Three years later, in 1854, Nightingale went to Scutari, Turkey when the Crimean War broke out. 2. ___. The omnipresent dirt, stink, and soldiers laying in their own excrementsexcrements; the view was horrifyinghorrifying. During that time she improved the sanitary conditions of soldiers. Such rudimentary issuesrudimentary issues as clean clothing, bedding, ventilation, regular bathing, reducing overcrowding, or providing nutritious meals for patients made the difference. It seemed that previously soldiers were dying mainly of poor sanitary conditions. The spread of the news of her successful lowering of the death rate made her famous in her motherlandmotherland. Nightingale cared for the wounded even at night. This earned her the nickname ‘Lady with the Lamp’ and the respect of the medical personnel and patients.
In 1855, Florence developed brucellosisbrucellosis, an incurable illnessincurable illness that affected her until her final days. In 1856, when the Crimean War was over, she met with Queen Victoria and Prince Albert to discuss the roles of nurses. Thanks to the statistical data she collected when working in Turkey, she managed to change their mindsetmindset on this matter. Nursing began to matter. Influencing the royal couple was only the beginning of her activism. 3. ___. She also set up a nursing school – the Nightingale Training School at St. Thomas Hospital in London in 1860. Two years later, in 1862, her efforts led to establishing a school for midwivesmidwives at King’s College Hospital. However, Florence’s nursing training wasn’t confined toconfined to England only. In the 1870s she provided training to an American nursing pioneerpioneer, Linda Richards, who then dedicated herself todedicated herself to developing nursing standards in the U.S.
4 . ___. She was respected and admired. In 1883 she was awarded the Royal Red Crossthe Royal Red Cross. In 1907 she was the first woman awarded the Order of Meritthe Order of Merit. Nightingale died in 1910. She was even offered a funeral and burial place in Westminster AbbeyWestminster Abbey, but her family respected her decision to be buried in Hampshire instead.
Two years after her death the International Committee of the Red Cross began to award Florence Nightingale’s Medal to nurses. She inspired and initiated immense change to elevateelevate the status of nurses from uneducated pauperspaupers to well‑trained and educated women, able to show empathy and care for all wounded regardless of their social status. This must have won the public’s heart. 5. ___. Such a person was Florence Nightingale, the pioneer of modern nursing.
Źródło: Katarzyna Piotrowska, licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0.
2. 1. She attended a local primary school where she learnt the basic skills such as writing and drawing., 2. Next, she published Notes on Nursing which provided practical advice to caretakers., 3. On arrival there, the conditions in which the wounded were treated shocked her and the accompanying nurses., 4. She even gave the first medals to the most distinguished nurses., 5. Putting oneself before the others and being able to sacrifice oneself for the sake of others, 6. Her father placed emphasis on her receiving extensive education., 7. Nightingale was among those whose success came during her lifetime.
3. 1. She attended a local primary school where she learnt the basic skills such as writing and drawing., 2. Next, she published Notes on Nursing which provided practical advice to caretakers., 3. On arrival there, the conditions in which the wounded were treated shocked her and the accompanying nurses., 4. She even gave the first medals to the most distinguished nurses., 5. Putting oneself before the others and being able to sacrifice oneself for the sake of others, 6. Her father placed emphasis on her receiving extensive education., 7. Nightingale was among those whose success came during her lifetime.
4. 1. She attended a local primary school where she learnt the basic skills such as writing and drawing., 2. Next, she published Notes on Nursing which provided practical advice to caretakers., 3. On arrival there, the conditions in which the wounded were treated shocked her and the accompanying nurses., 4. She even gave the first medals to the most distinguished nurses., 5. Putting oneself before the others and being able to sacrifice oneself for the sake of others, 6. Her father placed emphasis on her receiving extensive education., 7. Nightingale was among those whose success came during her lifetime.
5. 1. She attended a local primary school where she learnt the basic skills such as writing and drawing., 2. Next, she published Notes on Nursing which provided practical advice to caretakers., 3. On arrival there, the conditions in which the wounded were treated shocked her and the accompanying nurses., 4. She even gave the first medals to the most distinguished nurses., 5. Putting oneself before the others and being able to sacrifice oneself for the sake of others, 6. Her father placed emphasis on her receiving extensive education., 7. Nightingale was among those whose success came during her lifetime.
Study the sentences below and choose the correct ending for each sentence.
Answer the questions. Write 3‑4 sentences to each question. Use the information from the text and your own ideas.
What changes did Nightingale introduce in caring for the wounded?
According to the text, why was Florence Nightingale given the nickname ‘Lady with the Lamp’?
Do you think that what Florence Nightingale did was significant? Why? Why not?
Słownik
/ ˈæfluənt /
zamożny/zamożna (wealthy)
/ ˌbruːsəˈləʊsɪs /
bruceloza, gorączka śródziemnomorska (an infectious disease that can spread from animals to humans and gives symptoms similar to flu)
/ kənˈfaɪn tuː /
ograniczać do (limit to)
/ ˈdedɪkeɪtɪd hɜːˈself tuː / / ˈdedɪkeɪt wʌnˈself tuː /
poświęcił/poświęciła się czemuś [poświęcać się czemuś] (commit herself to [commit oneself to])
/ ˈelɪveɪt /
podnieść rangę czegoś (make something more important)
/ ˈekskrəməntS / / ˈekskrəmənt /
odchody, ekskrementy (faeces, solid waste material that is released from a person’s body)
/ ˈhɒrɪfaɪɪŋ /
przerażający/przerażająca (very shocking)
/ ɪnˈkjʊərəbl̩ ˈɪlnəs /
nieuleczalna choroba (a disease that can’t be cured)
/ ˈmɪdwaɪvz / / ˈmɪdwaɪf /
położne [położna] (women trained in assisting women in childbirth)
/ ˈmaɪndset /
sposób myślenia (a person’s way of thinking)
/ ˈmʌðəlænd /
ojczyzna (a person’s native land)
/ ˈnɜːsɪŋ /
pielęgniarstwo (the profession of providing care to the sick)
/ ˈpɔːpəz / / ˈpɔːpə /
ubodzy [ubogi/uboga] (very poor people)
/ ˌpaɪəˈnɪə /
pionier/pionierka (a person who is among the first to do something)
/ ˌruːdɪˈmentri ˈɪʃuːz /
sprawy [sprawa], kwestie podstawowe [kwestia podstawowa] (most basic matters)
/ ˈsækrɪfaɪs /
poświęcać (give up something valuable in order to help someone else)
/ səbˈstænʃl̩ sʌm /
znaczna kwota (a considerable amount of money)
/ ði ɔ:dər əv ˈmerɪt /
Order Zasługi (a special honour given to British people in recognition of their outstanding service)
/ ðə ˈrɔɪəl ˈred ˈkrɒs /
Krzyż Królewskiego Czerwonego Krzyża (a British military award given to women in recognition for their outstanding service in military nursing)
/ vəʊˈkeɪʃn̩ fɔː /
powołanie do (a calling, strong feeling one should do a particular job)
/ ˈwestmɪnstə ˈæbi /
Opactwo Westminsterskie (Gothic church in Westminster, London where important national events such as coronations are held)
Źródło: GroMar Sp. z o.o., licencja: CC BY‑SA 3.0