Southern Europe - Mediterranean culture, tourism
that the natural environment in Southern Europe is conducive to settlement;
that great cultures developed in Southern Europe, whose achievements had a significant effect on the developent of the civilisation in Europe;
to be able to point out the most outstanding natural and cultural features of Southern Europe on a thematic map;
to demonstrate the role and significance of tourism;
to use information sources to describe selected tourist attractions in Southern Europe.
Southern Europe – areas of early settlement
The origins of European civilization are considered to have come from the succesful movement of the older Asian civilisation to younger colonies situated in the islands of the eastern Mediterranean. Around 6000 BC settlers from Asia Minor began to enter eastern areas of Southern Europe. The Asia Minor Peninsula is separated from Europe by the Bosphorus and Dardanelles, which at their narrowest point are around 1km wide. It is likely the incomers included shepherds and farmers from the Fertile Crescent, that is, a place where many plants and animals had been previously cultivated.
The following infographic gives information on the development of agriculture in Southern Europe.
Southern Europe – the great cultures of the Mediterranean basin
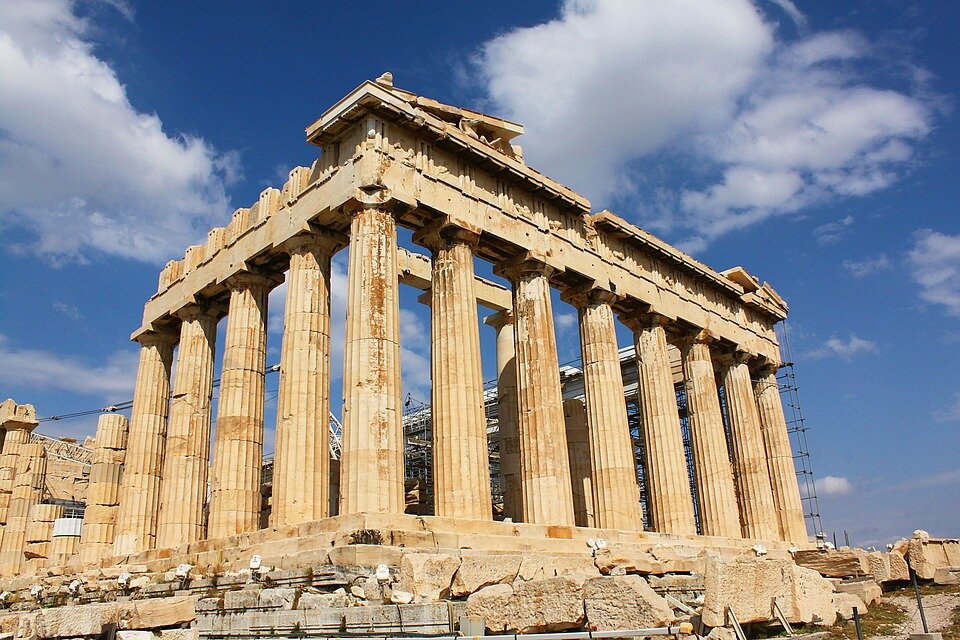
The oldest culture of the Mediterranean is considered to be the Minoan culture from Crete. Preserved documents show that in the seventeenth century BC the inhabitants of Crete ruled over this entire known marine area. The history of Ancient Greece covers a period of more than a thousand years. The Golden Age of Greek city states lasted from VIII to the IV centuries BC. The beginning of the era is marked by the first Olympic Games, which occurred in 776 BC. At that time, the Greek city states were colonising many famous places such as: Naxos, Messina and Syracuse in Sicily, Massilia (now Marsailles), Napolis (Naples). The expansion of Ancient Rome began from the third century BC into areas occupied by the Greeks and their city states. The final phase is considered to be the capture of Syracuse, which was defended, amongst others, by Archimedes in 212 BC. In the following centuries there came the phenomenon of interpenetration of Greek and Roman culture.
Choose which country is shown on the physical map below.
- Serbia
- Bosnia and Hercegovina
- Spain
- Bulgaria
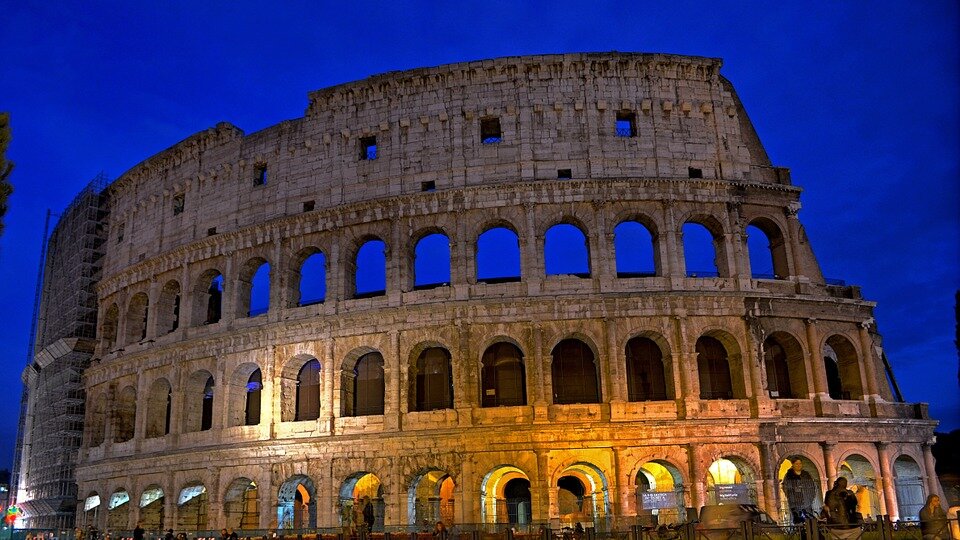
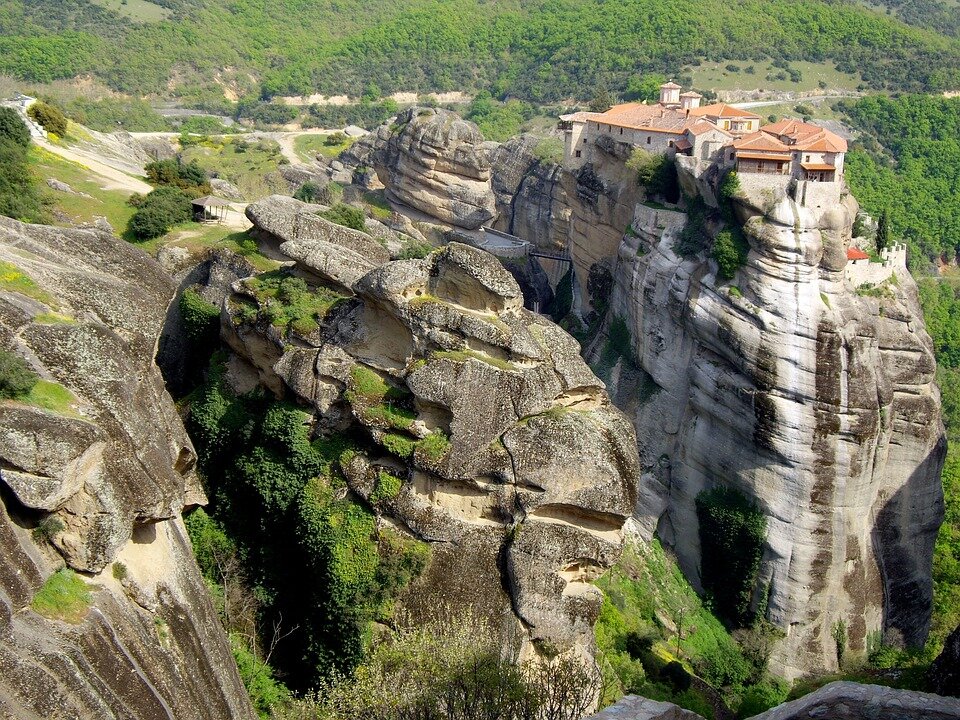
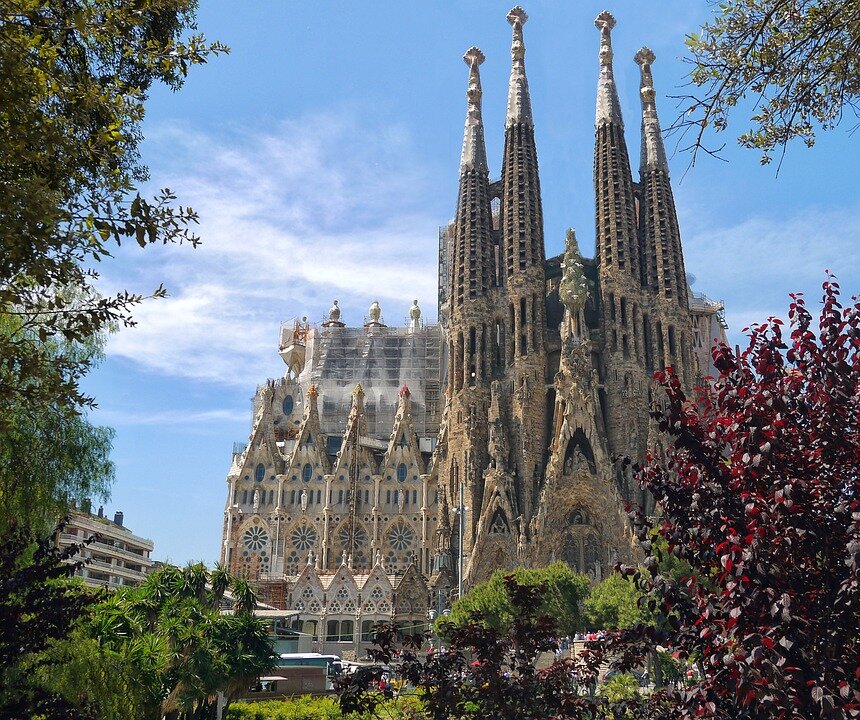
Southern Europe – tourist attractions
The following factors are used to define a tourist attraction in Southern Europe:
warm Meditteranean climate which encourages relaxing by the water;
a concentration of unusual cultural values that are connected to the history of our continent;
diverse terrain and interesting vegetation.
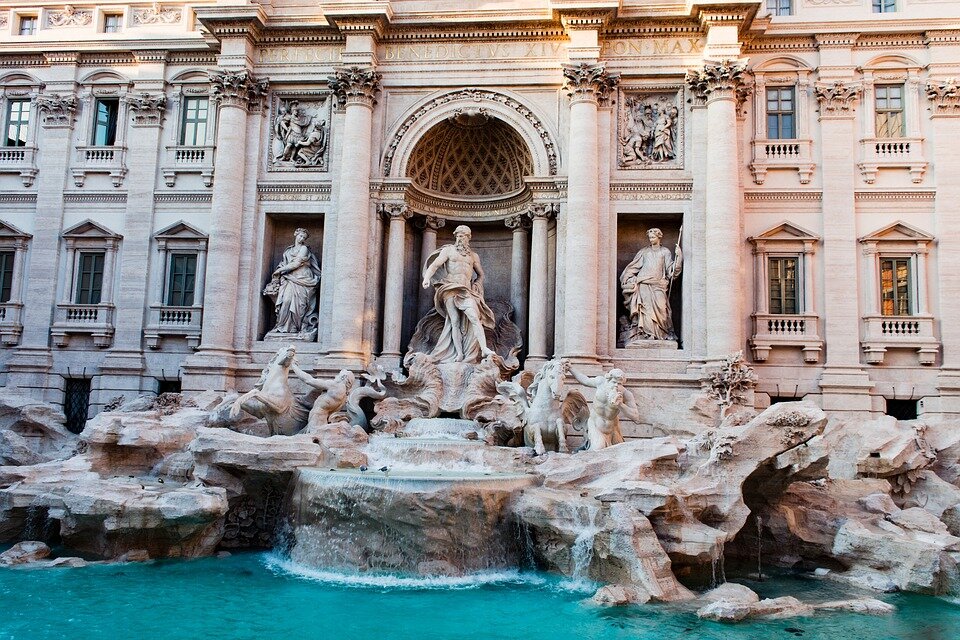
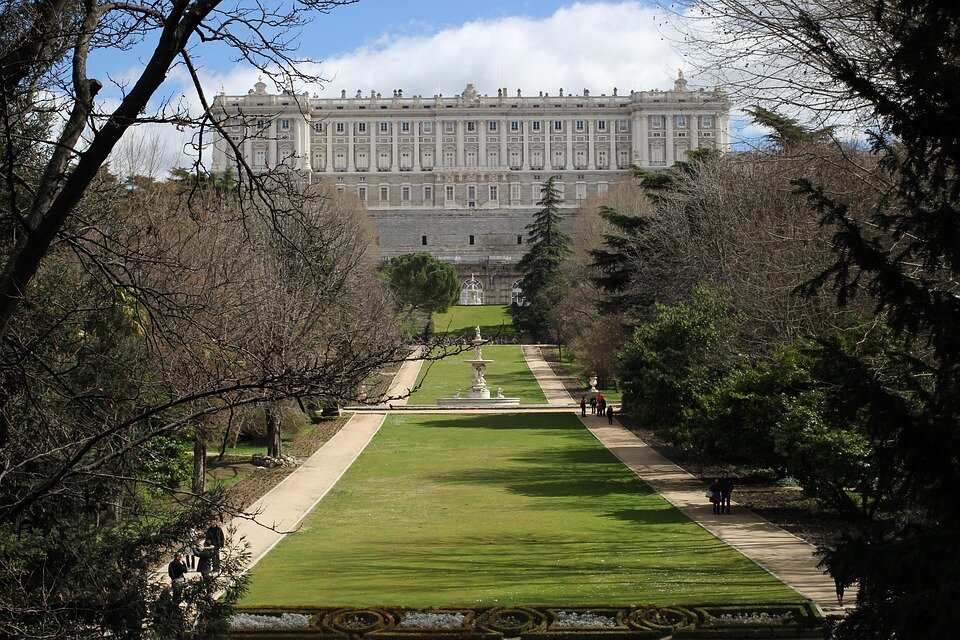
The map shows cities, centres, monuments and other objects that have been selected and added to the UNESCO World Cultural and Natural Heritage List. The map does not show the full cultural richness of Southern Europe. Many smaller items are not included, such as: the Isle of Capri, karst regions of the Balkan Peninsula, the Rock of Gibraltar – the Columns of Hercules. Each location marked on the map above has a long and rich history. Today, a number of cities in this area are known as the great centres of European culture because of their importance to tourism. These are: Athens, Rome, Florence, Venice, Madrid, Barcelona, Istanbul. Southern Europe is one of the most visited regions in the world by tourists. It yields around 20% of global income from tourism.
Based on the knowledge you have gained, complete the following exercises.
Select which of these four photographs shows the Swiss Guard at the Vatican City
- A
- B
- C
- D




From the list of cities, match the corresponding historic sites.
Florence, Istanbul, Venice, Madrid, Athens, Rome
| ruins of the Parthenon | |
| Basilica and St Mark's Square | |
| the Seven Hills | |
| Florence Cathedral | |
| Bosphoros Strait | |
| Prado Museum |
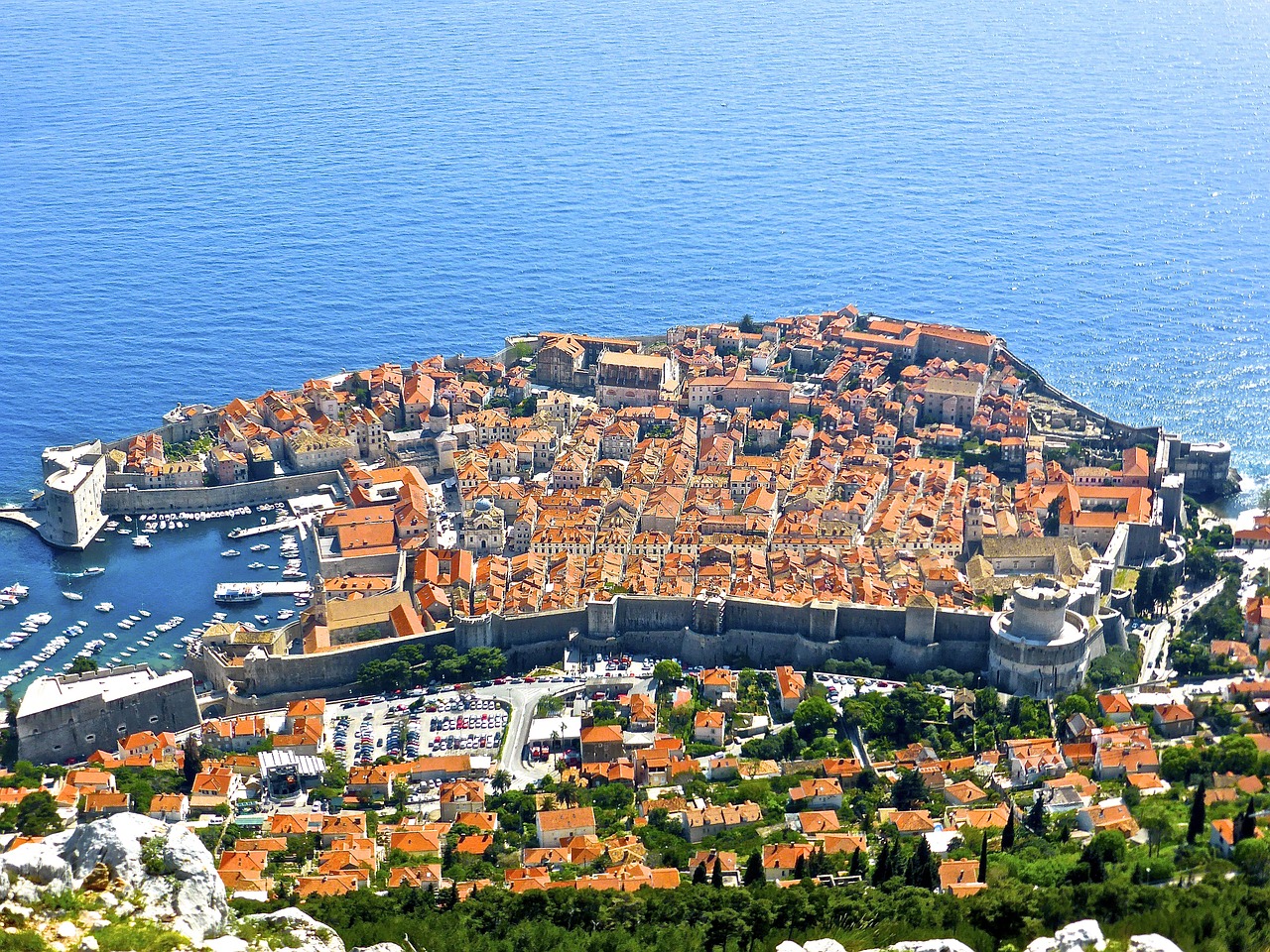
Which city of Southern Europe is this::
- Athens
- Venice
- Dubrovnik
- Naples

Keywords
Southern Europe, Mediterranean basin, UNESCO
Glossary
Kultura minojska – kultura kreteńska to jedna z najstarszych kultur epoki brązu w obszarze Morza Śródziemnego powstała na Krecie około 3000 p n e .
Partenon – w latach 447‑432 p.n.e. wybudowano na szczycie Akropolu - wielką świątynię wzniesioną na chwałę bogini Ateny, patronki miasta, której pomoc uratowała Greków przed Persami. Partenon został zbudowany z inicjatywy Peryklesa. Świątynia stoi w miejscu dwóch innych świątyń: Hekatompedonu i niedokończonego tzw. starszego Partenonu, który został zburzony przez Persów.
Lista Światowego Dziedzictwa Kulturowego i Przyrodniczego UNESCO – lista obiektów dziedzictwa kulturowego i dziedzictwa naturalnego o „wyjątkowej powszechnej wartości” dla ludzkości prowadzona przez organizację wyspecjalizowaną ONZ UNESCO - United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization.






