Structure and biological functions of fats
the structure of esters and what esterification consists in.
to classify fats in terms of their origin and state of aggregation, giving examples;
to list food products that are sources of fats;
to list elements that build fat molecules;
to classify fat into esters and provide justification;
to write down semi‑structural formulae of some fats;
to name given fat based on its semi‑structural formula;
to discuss functions of fats.
Think of possible uses of fats apart from food and cosmetics industry. In which products can you find them?
Types of fats
Think about fats that you encounter every day. Can you classify them in some way?
Classification of fats due to their origin.
| Vegetable fats | Animal fats |
|
Olive oil Linseed oil Peanut butter Cocoa butter |
Lard Fish oil Butter Fatback Tallow |
Classification of fats due to their state of aggregation.
| Solid fats | Liquid fats |
|
Tallow Salo Butter Lard Peanut butter Cocoa butter |
Linseed oil Soy oil Rapeseed oil Sunflower oil Olive oil Fish oil |
Fats are classified in terms of their state of aggregation and origin.
Structure of fats
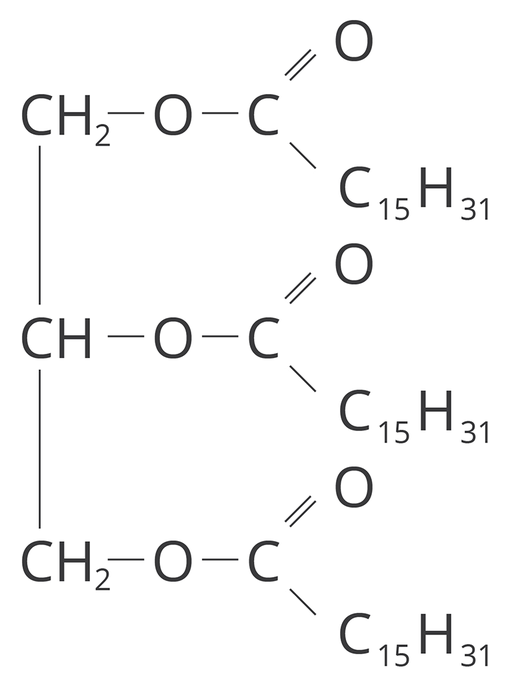
Esters are compounds that are responsible for lovely fragrance of flowers or fruits. Also fatsfats are classified as esters, although they do not smell lovely. These essential components of our daily diet are naturally found – in meat, fish and oil plants. They are chemically obtained in estrification of glycerol and higher carboxylic acids.
Fats are esters of glycerol and higher carboxylic acids. Fat molecules may contain acid radicals of various fatty acids.
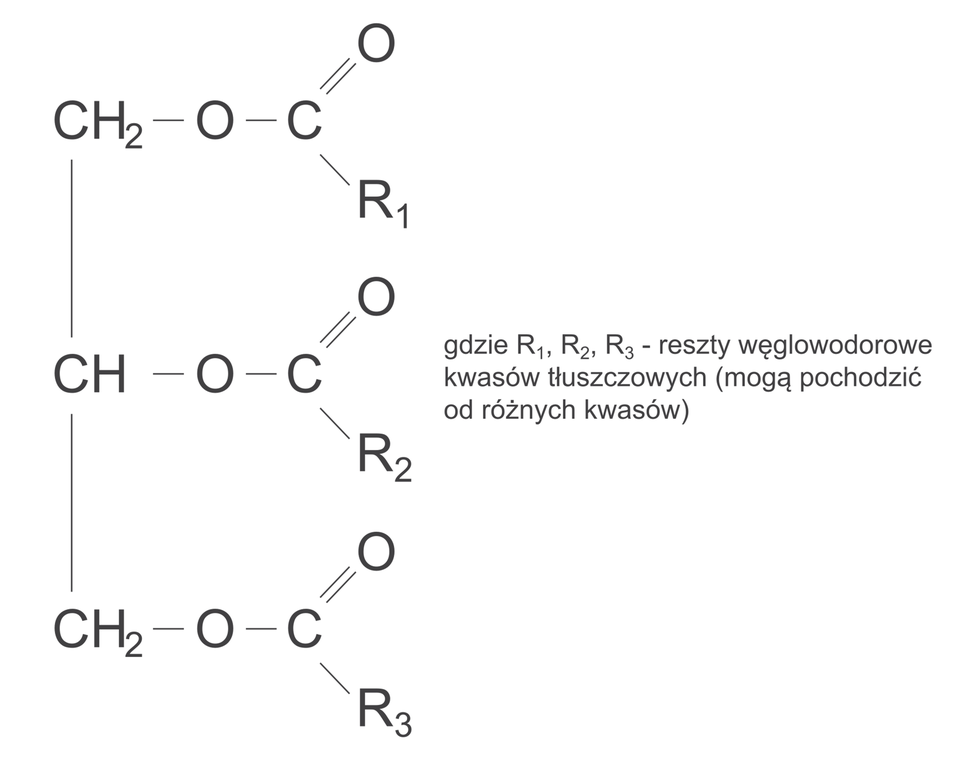
1. where R1, R2, R3 - hydrocarbon radicals of fatty acids (may come from various acids)
How to name fatty compounds
Rules for creating names of fat molecules
A fat molecule is formed in a chemical reaction from glycerol and three fatty acid molecules. Names of fat molecules are derived from common names of alcohol and fatty acids, e.g. glycerol tristearate.
Names consists of two parts or may be more complex, depending on the quantity of various fatty acids that made up given fat molecule.
The first part of the name is derived from the alcohol’s name, namely glycerol and the second is always derived from the name of fatty acid.
If there are three acid radicals of one acid, prefix tri (three) should be added the to acid’s name. It denotes the quantity of fatty acid radicals, for example glycerol tristearate.
If there is more than one type of fatty acid in the fat molecule, we start forming the name from the fatty acid with the shortest carbon chain. Analogously, we add prefix di (two) to the acid’s name from which there are two acid radicals, for example glycerol dioleate palmitate, glycerol dipalmitate stearate, glycerol palmitate oleate stearate.
Occurrence and biological functions of fats
Which food products contain fats?
In the store you can easily find sunflower, rapeseed, soy, coconut, nut, linseed, grape seed or avocado oil as well as olive oil obtained in various ways. These fats commonly used in the kitchen are found in seeds of plants such as: rapeseed, sunflower, soy, olives, or less frequently nuts, coconut, grapes and avocado. Oils and olive oils are obtained in various processes.
Animal fats are found in meat and milk. Lard is obtained as a result of melting fatty parts of pig, while butter – is churned.
Think of answer to the following question: “Why do we eat more fats in winter?” Write down your suggestions below.
What is the significance of fats for living organisms?
Fats have a very important function in living organisms. Have you wondered why we eat more fats in winter? First of all, fats provide energy to organisms. Fat layer under the skin prevents heat loss and protects internal organs from damage. Fats also transport vitamins soluble in fats: A, D, E and K.
In times of fast foods it is important that we know the rules of rational diet. Obesity is affecting more and more people and is the cause of many diseases. So – what is the matter with fats? Eat them or not to eat them?

1. Oily and lean fish
2. Eggs
3. Avocado
4. Walnuts
5. Brazil nuts
6. Almonds
7. Ground flaxseed
8. Olive oil
9. Rapeseed oil
10. Nut oils
11. Linseed oil
12. sources of essential fatty acids
As you already know, fats are essential element of our diet. However, it is not advisable to eat too much solid fats, such as lard and butter. Why? Solid fats are mainly esters of saturated fatty acids that increase concentration of cholesterol in blood. It is recommended to provide the body with vegetable fats, which are mostly esters of unsaturated acids named as essential fatty acids (EFA). Have a look at an interactive illustration and check what products contain large amounts of these compounds.
Select true statements.
- Most vegetable fats are liquids, and most animal fats are solids.
- Natural fat molecules found in animal tissues and seeds of oil plants usually contain acid radicals of various fatty acids.
- Glycerol tristearate is a liquid fat.
- Fats are made of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen.
- There are 6 double bonds between carbon atoms in the glycerol trioleate molecule.
Select true statements.
- Fats are solvents of many substances that are essential to organisms, for example vitamins A, D, E, K.
- Fats store water.
- Olive oil is obtained from seeds.
- Fats accumulated in adipose tissue protect against excessive heat release.
- In plants fats are found mostly in seeds and fruits. In animal organisms they occur as a separate fatty tissue.
Select products that are sources of fats.
- Fastfood: hamburger and fries
- Donut with whipped cream
- Bread
- Tomatoes
- Fish, salmon
- Nuts






Summary
Fats are esters of glycerol and higher carboxylic acids.
Fats can be divided – due to their state of aggregation – into solid and liquid ones.
Fats are classified – due to their origin – into vegetable and animal fats.
Names of fat molecules are derived from common names of alcohol and fatty acids.
The first part of the name is from the alcohol’s name, namely glycerol and the second is always derived from the name of fatty acid.
Fats are essential for proper functioning of the body.
Fats give us energy and protect internal organs. They also transport vitamins soluble in fats: A, D, E and K.
Fats are found in seeds of plants such as: rapeseed, sunflower, soy, olives, or less frequently nuts, coconut, grapes and avocado.
Animal fats are found in animal fat tissues and milk.
Keywords
fats, unsaturated fats, saturated fats, glycerol esters, higher carboxylic acids, fatty acid radicals, names of fat molecules, fatty acid
Glossary
tłuszcze – estry glicerolu i wyższych kwasów karboksylowych