The Arabs and the World of Islam
to indicate where Islam was Born;
to explain what are the Five Pillars of Islam;
to describe what spurred the development of Islam;
to define what the HejiraHejira, kharajkharaj, the Sharia lawSharia law and the RamadanRamadan are.

The Arabs were a herding people inhabiting the Arabian Peninsula. Their main occupations were husbandry and trade. They also guided European merchants through the lands of the Middle East and Mesopotamia. One of their most imortant cities and trade centers was Mecca. Its Kaaba temple, which, according to the legend, was supposedly erected by the Biblical Abraham (Ibrahim) and his son Ishmael (Ismail), considered by the Arabs to be their forefather, was its central point. The creator of Islam and its most important prophetprophet was Muhammad, alive in the sixth and seventh centuries. He believed that through his visions he maintained contact with God, who passed his will onto him. Based on that and the later teachings of Muhammad, the MuslimsMuslims (the followers of Islam) believe in one god, AllahAllah – the creator of the world, humanity, and everything that surrounds it. Much like the Christians, they believe that after one’s death they will be judged, and that the good will be admitted to heaven, and the wicked – banished to hell. The Muslims, while they acknowledge Moses and Jesus as prophets, believe that only the prophecies passed onto Muhammad contain the truth about God and humanity.
The revelations preached by Muhammad were not received with much interest by the people of Mecca. He was only joined by foreigners and people belonging to the lower social classes. They were attracted by Islam’s rejection of divisions and championing justice and equality for everyone. When Muhammad openly condemned polytheism, popular among the rich, he antagonized not only the wealthy, but also the local leaders. Thus, he had to flee; in 622 he left Mecca and headed to Medina. There, he found not only refuge, but also new followers, envious of the wealth and influence of their neighbors. The Hejira, as the event is known in the Arabic tradition, is considered by the Muslims to be the beginning of the new religion and the Muslim era.

The number of Muhammad’s followers grew quickly through numerous conquests and subduing the neighboring Arabic tribes. Eventually, by the end of Muhammad’s life, owing to his sizable army of over ten thousand, Mecca found itself under the rule of his followers as well. Having passed away in 632, the prophet had left no heirs. The community chose Abu Bakir to replace him, granting him the title of CaliphCaliph, meaning “successor”. Thus began the rule of the caliphs, during which Islam spread into the vast territories extending from Persia, through the Arabian Peninsula, Palestine, Egypt, and North Africa, to the Iberian Peninsula, in a mere few decades. The results of the conquest were astounding, and the followers of the new religion became a great force. They did not, however, impose their religion, culture or customs upon the defeated nations. They did not destroy their territories and civilization achievements either. The subdued, non‑Muslim people was, however, obliged to pay a special tax (kharaj) in exchange for protection.
The foundation of the Muslim faith is constituted by the so‑called five pillars of Islam. They are: the faith in one God and his prophet, five‑time‑a-day prayer, fasting during the holy month of Ramadan, alms, and pilgrimage to Mecca. The Muslims pray in mosquesmosques, and they consider the QuranQuran, or the teachings of Muhammad written down at the order of Abu Bakr, to be their holy book. It is also considered the most beautiful example of Arabic literature and the source of the Muslim Sharia law.
Match the respective pillars of Islam to their definitions.
the Islamic declaration of faith: there is no god but God. Muhammad is the messenger of God., the prayer recited five times a day while facing the direction of Mecca., the pilgrimage to Mecca that a pious Muslim needs to make at least once in their lifetime., the fasting during the ninth month of the Muslim month of Ramadan., the alms that a Muslim should donate to the poor.
| Shahada | |
| Salat | |
| Zakat | |
| Saum | |
| Hajj |
Learn more about the Quran – the Muslims’ most important book.
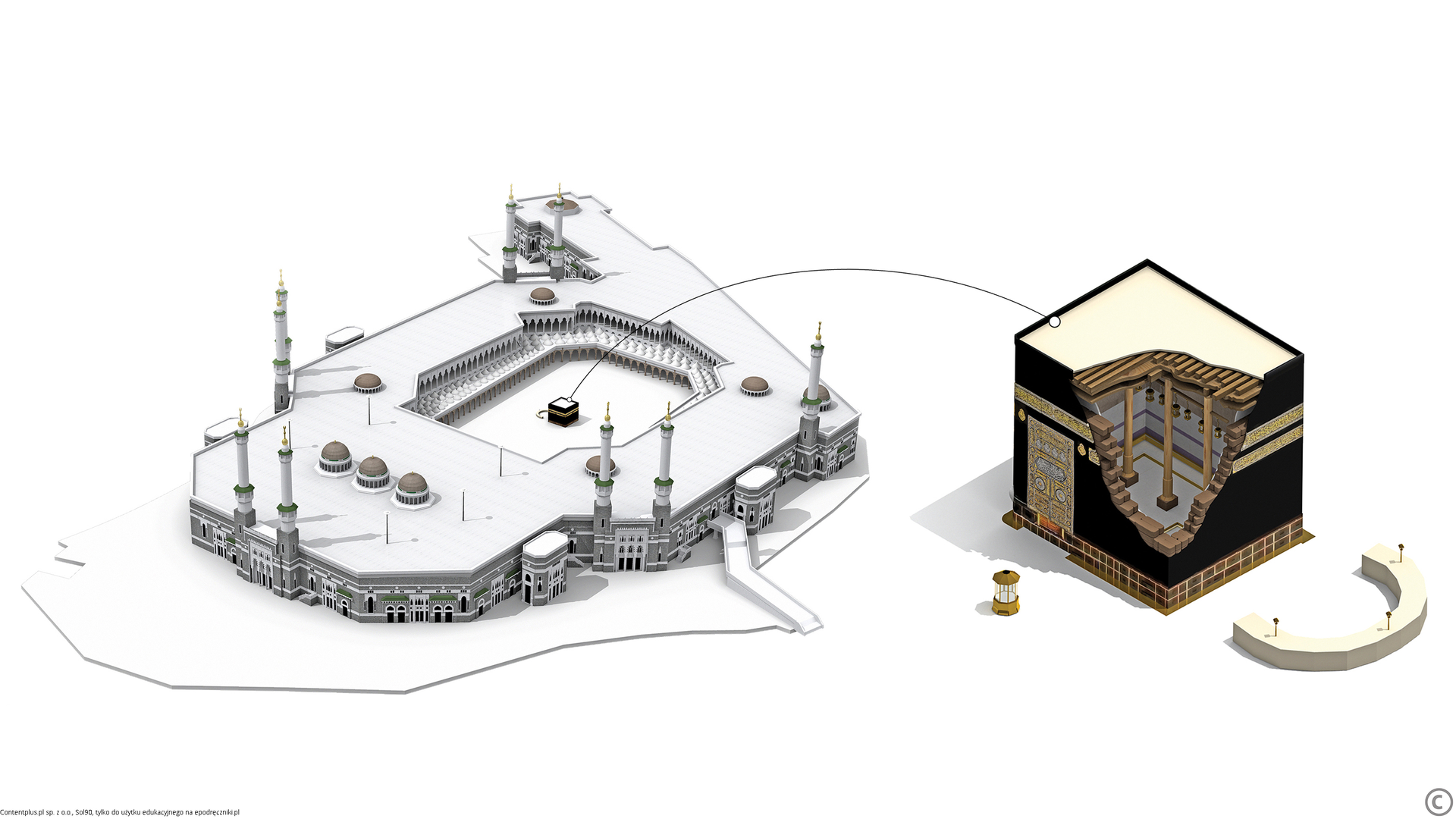
Take a close look at the image of the Al‑Masjid Al‑Haram mosque and the Kaaba temple in Mecca, and reflect upon the reasons why are they considered the most important holy sites by the Muslims.
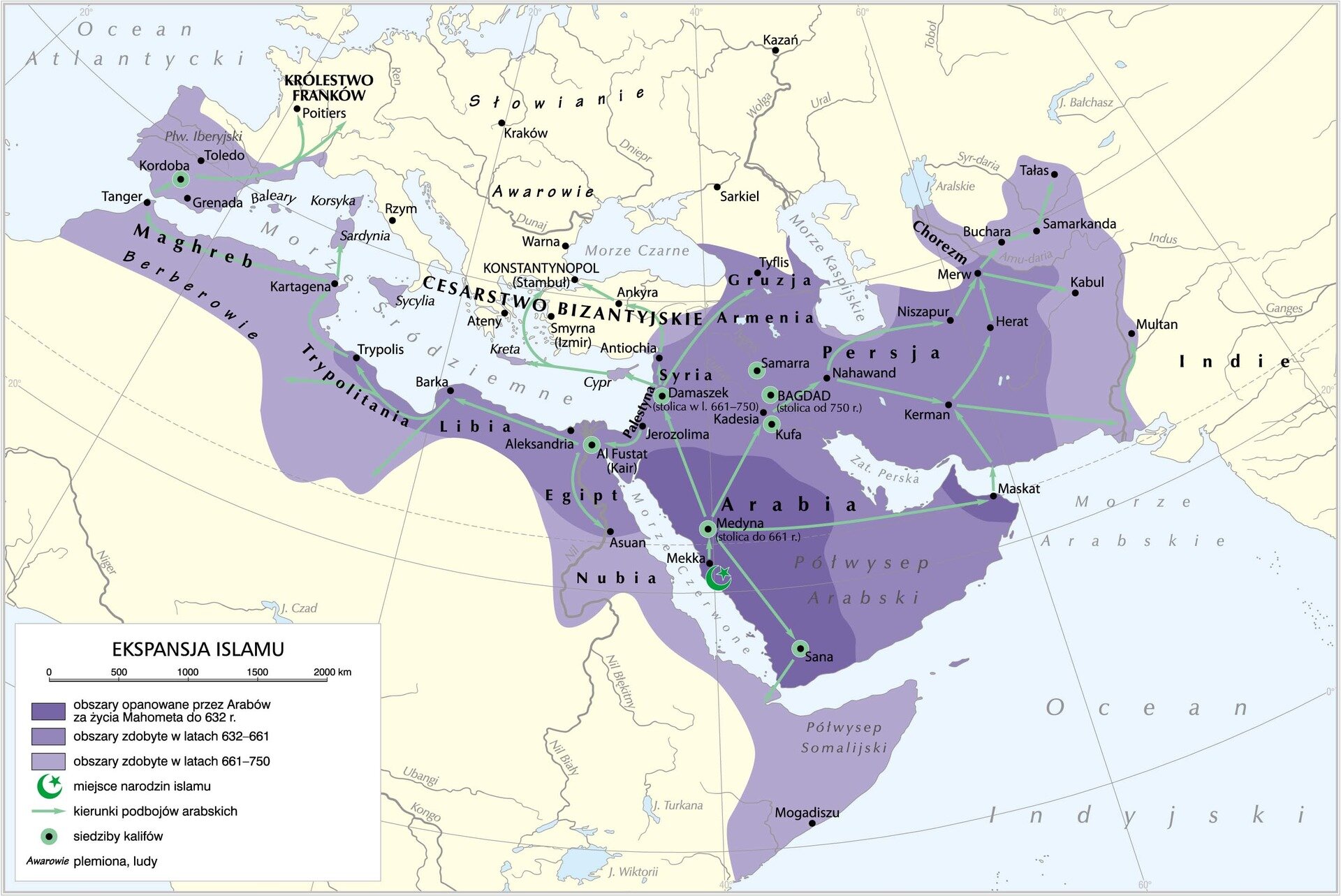
Study the map below and list the cities on the territory conquered by the Arabs during Mahomet’s lifetime.
Indicate the principles of Islam.
- Worshipping multiple gods.
- The duty to consume kosher food.
- Ban on alms.
- Obligatory fasting in a holy place.
- At least one pilgrimage to Mecca in one’s lifetime.
- Faith in one God.
Keywords
Muhammad, Islam, Muslim, Allah, Quran, Hijra, Ramadan, prophet, mosque, minaretminaret, caliph, ShahadaShahada, Arabs
Glossary
Politeizm – wiara w wielu bogów, którzy zajmują się odrębnymi sferami życia.
Monoteizm – wiara w jednego Boga, wykluczająca istnienie innych bóstw.
Prorok – dosłownie „osoba przemawiająca w czyimś imieniu”, w religiach były to osoby pozostające w kontakcie z Bogiem, który przez nie miał wyrażać swoją wolę i zamierzenia.
Koran – święta księga islamu, składa się ze 114 sur (rozdziałów). Według wiernych za jego twórcę uważany jest Allach, który objawił go prorokowi Mahometowi.
Szariat – prawo muzułmańskie regulujące zwyczaje religijne, prawo oraz postępowanie w codziennym życiu.
Szahada – muzułmańskie wyznanie wiary, jeden z obowiązków każdego muzułmanina.
Hurysa – w religii muzułmańskiej, piękna i wiecznie młoda kobieta o duchowej i cielesnej czystości, która czeka w raju na zbawionych wiernych.
Hegira – ucieczka proroka Mahometa i jego zwolenników z Mekki do Medyny. W islamie uznawana jest za początek istnienia tej religii.
Umma – wspólnota islamskich wiernych.
Ramadan – święty miesiąc dla muzułmanów, ustanowiony na pamiątkę początku objawień Mahometa.
Meczet – budynek, w którym oddaje się cześć Bogu. Potocznie określa się tak muzułmańskie świątynie.
Minaret – wysoka wieża znajdująca się przy meczecie, z której nawołuje się wiernych do modlitwy.
Kalif – tytuł następców Mahometa, będących przywódcami religijnymi i państwowymi muzułmanów.
Charadż – podatek narzucany podbitym, niemuzułmańskim ludom.
Islam – jedna z wielkich religii monoteistycznych, stworzona na początku VII w. przez uważanego za proroka Mahometa. Jej główne założenia są zawarte w świętej księdze Koranie.
Muzułmanin – inaczej mahometanin, wyznawca religii islamu.
Allach – imię Boga w religii islamskiej. W języku arabskim oznacza Boga.