The distribution of earthquakes
the internal structure of the Earth;
basic types of rocks and minerals;
the causes and consequences of the plate‑like structure of the Earth's crust.
using the map of world you will show the boundaries of tectonic plates;
determine the relationships between the location on the boundary of lithospheric plates and the occurrence of earthquakes;
locate places on a physical map of world at risk of earthquakes;
draw conclusions concerning the Pacific ring of fire;
determine the impact of earthquakes on human life;
provide examples of solutions on how to prevent tragic consequences of earthquakes.
Earthquakes are vibrations of the Earth's crust. Those that propagate within the Earth are called seismic waves. As a rule, they are a consequence of tension release resulting from the movement of the lithosphere plates. The frequent causes of earthquakes include volcanic eruptions. Moreover, they may occur as a result of collapse of cave ceilings or excavations in mines (the so‑called rock bumps), and (very rarely) the fall of relatively large meteorites. The largest and most powerful earthquakes are created at the contact zones of the lithosphere plates. They occur in the zones of subduction and sliding of the lithosphere plates along faults, often in the vicinity of active volcanoes and in spreading zones. The source of seismic wave propagation has been called the focal point or the focus of an earthquake It can be located at various depths, even several hundred kilometres. A place located on the surface of the Earth, directly above the focus of an earthquake, is the epicentre. In the epicentreepicentre, the shocks are felt the earliest and are the strongest. The magnitude of earthquakes is determined, among others, using the Richter scaleRichter scale. For example, earthquakes with a magnitude of 2.0 are delicate shocks felt by seismographsseismographs only, and occur hundreds of thousands of times on the Earth during the year. Whereas earthquakes with a magnitude of approximately 9.0 are catastrophic in effect, destroying entire cities on a large surface (thousands of kmIndeks górny 22), and they occur quite seldom – once every several, a dozen or so years.
Earthquakes are experienced all over the globe, but their impact varies geographically.
Earthquakes of such magnitude are relatively rare and occur once every 3–19 years. Earthquakes occur across the globe, but their impact is different depending on the geographical region. In the picture below, we present a cuboid representing a section of the Earth.
In areas of old, stiff continental disks and old mountains, earthquakes are very rare and weak. We call them aseismic areas. The opposite are seismic areas, i.e. where 90% of all earthquakes occur, including the strongest ones. To a great degree, seismic areas coincide with the zones of lithosphere plate collisions.
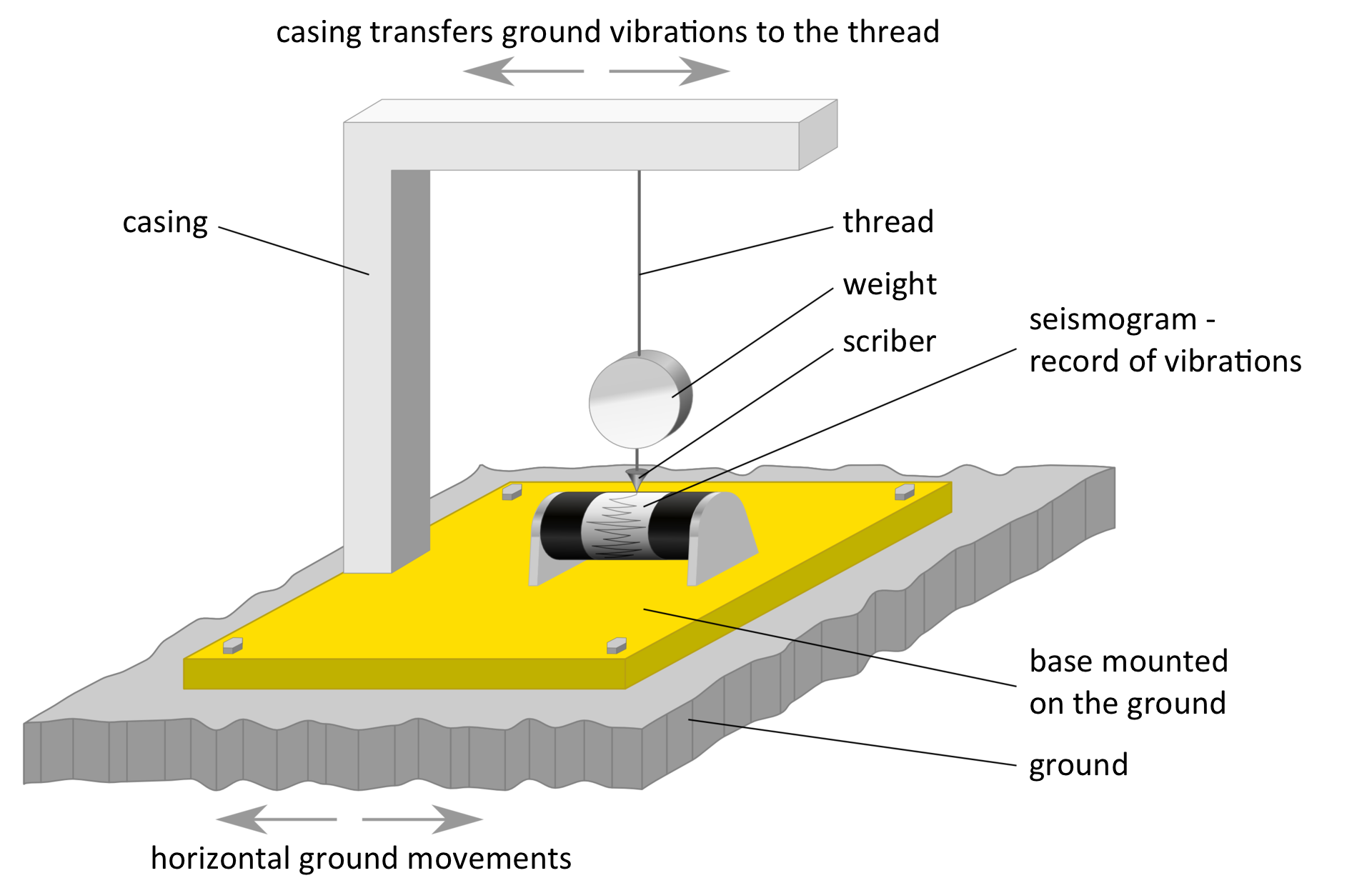
Virtually all earthquakes are recorded by seismological stations throughout the world. Special equipment is used to record them, the so‑called seismographsseismographs.
In which sphere of the earth vibrations are perceived as earthquakes?
- in the core
- in the atmosphere
- in the Earth's crust
- in the troposphere
- in the pedosphere
Choose areas where earthquakes are most common.
- rainforests
- bottoms of the oceans
- polar regions
- the zone of parallel plate displacement
- subduction zones
- Central Europe
Areas of earthquakes.
In the areas of old, stiff continental disks and old mountains, earthquakes are very ............ and weak. We call them ................ areas. Their opposite is made up of .............. areas, i.e. where 90% of all earthquakes occur, including all the strongest. Seismic areas coincide to a large extent with the zones of ...................... plate collisions.
Indicate the correct answer. Aseismic areas include:
- Greenland.
- Apennine Peninsula.
- Japan.
- West coast of South America.
Seismic areas include:
- Scandinavian Peninsula.
- Labrador Peninsula.
- Central Africa.
- West coast of North America.
The earthquake's fire, located at a depth of several to several dozen kilometers from its surface, is:
- hypocenter.
- epicenter.
- fault.
- seismic waves.
The magnitude of earthquakes is determined by the following scale:
- Mohs.
- Richter.
- Fahrenheit.
- Kelvin.
Keywords
earthquake, tectonic plate, Earth's crust, seismography
Glossary
epicentrum - miejsce na powierzchni Ziemi leżące dokładnie nad ogniskiem trzęsienia ziemi
sejsmograf - urządzenie do odczytywania i rejestrowania trzęsień ziemi
skala Richtera - jedna ze skal użytych do określenia wielkości trzęsień ziemi