The main causes of soil degradation
the distribution of climate zones and types of climate in the world;
how climate affects vegetation and soils found on Earth;
the difference between weathering and erosion;
what the geomorphic role of flowing water and wind is;
how to justify the need for responsible farming in environments characterised by serious shortage of freshwater resources.
name the causes of land degradation;
give examples of land degradation;
describe some situations where improper land use affects food production.
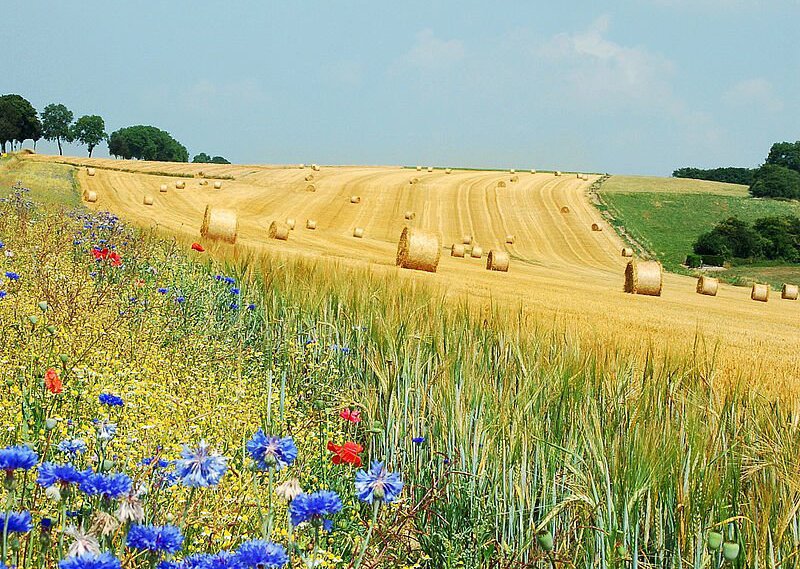
There are many causes of land degradation, which often overlap. The most common cause of land degradation is overgrazing, that is, when the animals eat plants so fast that vegetation has no chance to grow back. This leaves the soil bare, especially its humus layer. Wind and rainwater easily remove humus, which makes the soil lose its qualities. This is especially characteristic of arid and semi‑arid areas, such as the Sahel region of Africa. The effects of reckless deforestation are similar, only they can be seen much sooner.

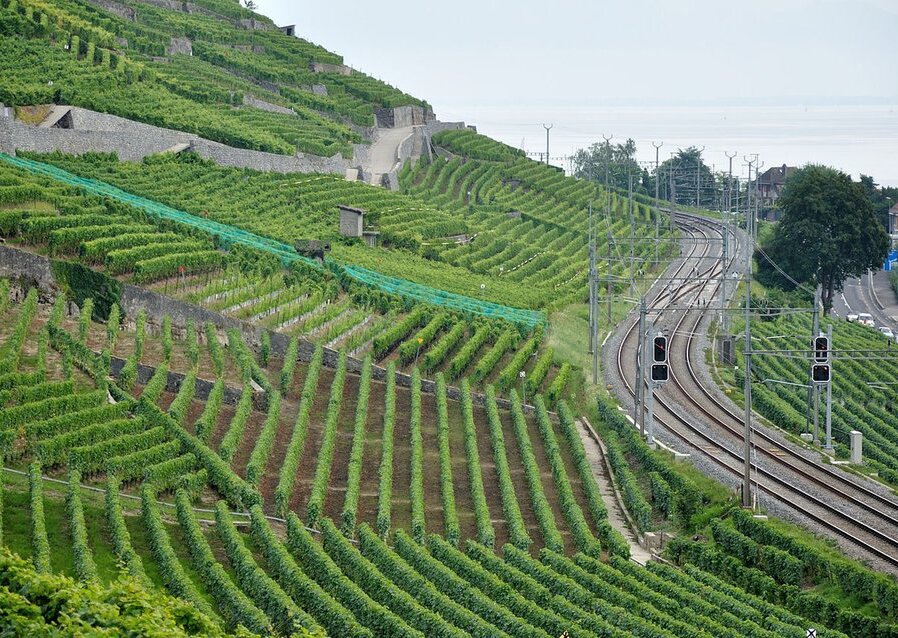
Improper agricultural practices also contribute to the deterioration of soil quality. Prolonged overexploitation of land leads to a reduction of the amount of humus. As a result, the soil becomes poorer in nutrients and its structure deteriorates, causing reduced water absorption, inhibiting the activity of soil‑dwelling organisms and weakening its chemical stability.
An obvious solution would seem to be to use fertilisers. Natural ones are the best, but unfortunately they are usually hard to come by in sufficient amounts. Synthetic fertilisers, on the other hand, can be counterproductive when used improperly. For instance, too much can poison the soil, killing soil micro‑organisms, activating heavy‑metal compounds and changing the pH (increasing acidity) of the soil, which makes it more difficult for plants to absorb nutrients. Over‑fertilisationOver‑fertilisation is typical of developed countries where intensive farming is popular.
Soil degradationSoil degradation may also derive from incorrect use of chemical plant protection products. When such substances, toxic by their very nature, penetrate the soil, they kill soil‑dwelling organisms, disturbing, as a result, soil formation processes.
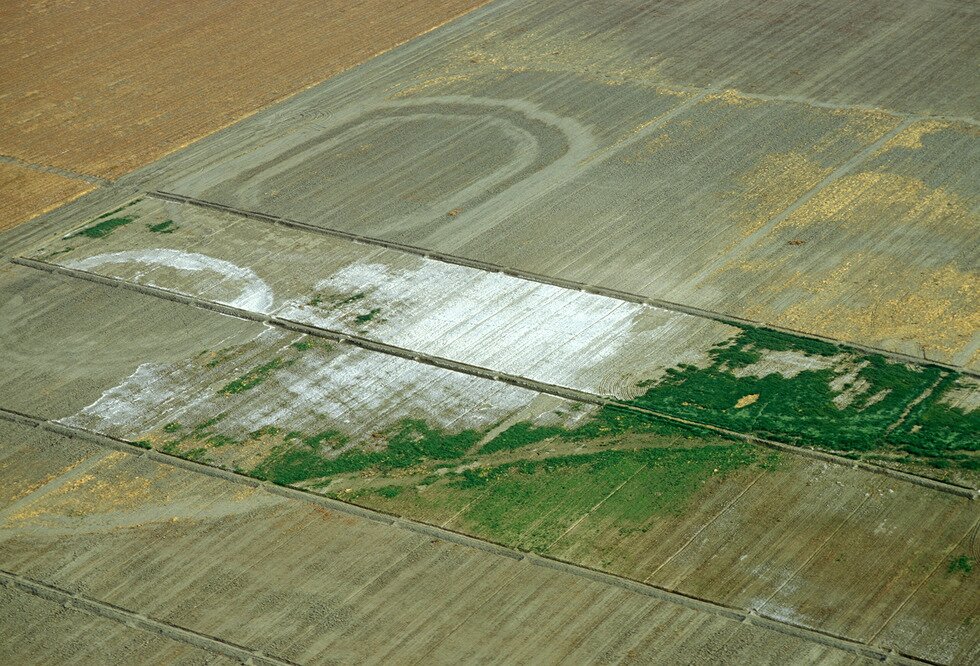

Even improper irrigation can have grave consequences. Water used in farming is often rich in salts. In the process of evaporation, only water particles enter the atmosphere, whereas mineral compounds remain in the soil. The amount of the latter grows with time, leading to soil degradation due to increased salinity. Soil salinitySoil salinity is a characteristic feature of arid areas in both developing and developed countries.

Soil degradation can be also caused by some types of agricultural machinery. Machines used for harvesting crops are usually large and heavy, so they compact the soil. This, in turn, hinders gas exchange, water absorption, movement of animals living in the soil, but also makes it easier for water to run over the soil instead of entering it. All these factors combined impair the quality of the land or, in other words, lead to its degradation. Owing to the costliness of agricultural machinery, this type of degradation is typical of developed countries.
In addition to factors contributing to the degradation of soils on a global scale, there are also others that can only be relevant locally, for example, plowing on the steep slopes. In the case of a field plowed along the slope, soil degradation occurs much faster as a result of washing out the humus out of it than in the case of a contour plowing.
In the list below, mark all consequences of improper agricultural practices that lead to land deterioration.
- soil salinity
- abundance of soil-dwelling organisms
- improving soil structure
- soil compaction by agricultural machinery
- increased soil acidity
- washing out the humus layer of the soil
Organize in the right order the main causes of soil degradation in the world, from the most common causes to the least common causes.
- Overgrazing
- Agricultural activity
- Deforestation
- Excessive use of vegetation
Match the cause of soil degradation with the right region.
dry areas of both poor and highly developed countries, dry and semi-arid areas, especially in Africa in the Sahel zone, highly developed countries using intensive farming
| over-fertilisation | |
| incorrect irrigation | |
| overgrazing |
Keywords
soil salinity, land degradation, overgrazing
Glossary
zasolenie gleb - występuje gdy ilość soli w glebie jest zbyt duża, co w konsekwencji powoduje degradację gleby
degradacja gleb - ogół procesów i zjawisk, które poprzez pogorszenie właściwości fizycznych (zniszczenie struktury), biologicznych (zmniejszenie ilości i jakości próchnicy lub chemicznych (np. zakwaszenie przez wymywania kationów zasadowych wapnia, magnezu, potasu) gleby istotnych dla roślin, wpływają ujemnie na jej żyzność, a więc i zasobność
przenawożenie - występuje gdy rośliny otrzymuja zbyt dużą dawkę nawozu. Jest wynikiem nieprawidłowego i nadmiernego stosowania wysokoprocentowych nawozów mineralnych.

