The process of decolonization
when the process of decolonizationdecolonization began;
what the UN’s stand was on the existence of coloniescolonies;
how decolonization proceeded in Africa and Asia;
what colonial conflicts there were;
what neocolonialismneocolonialism is.
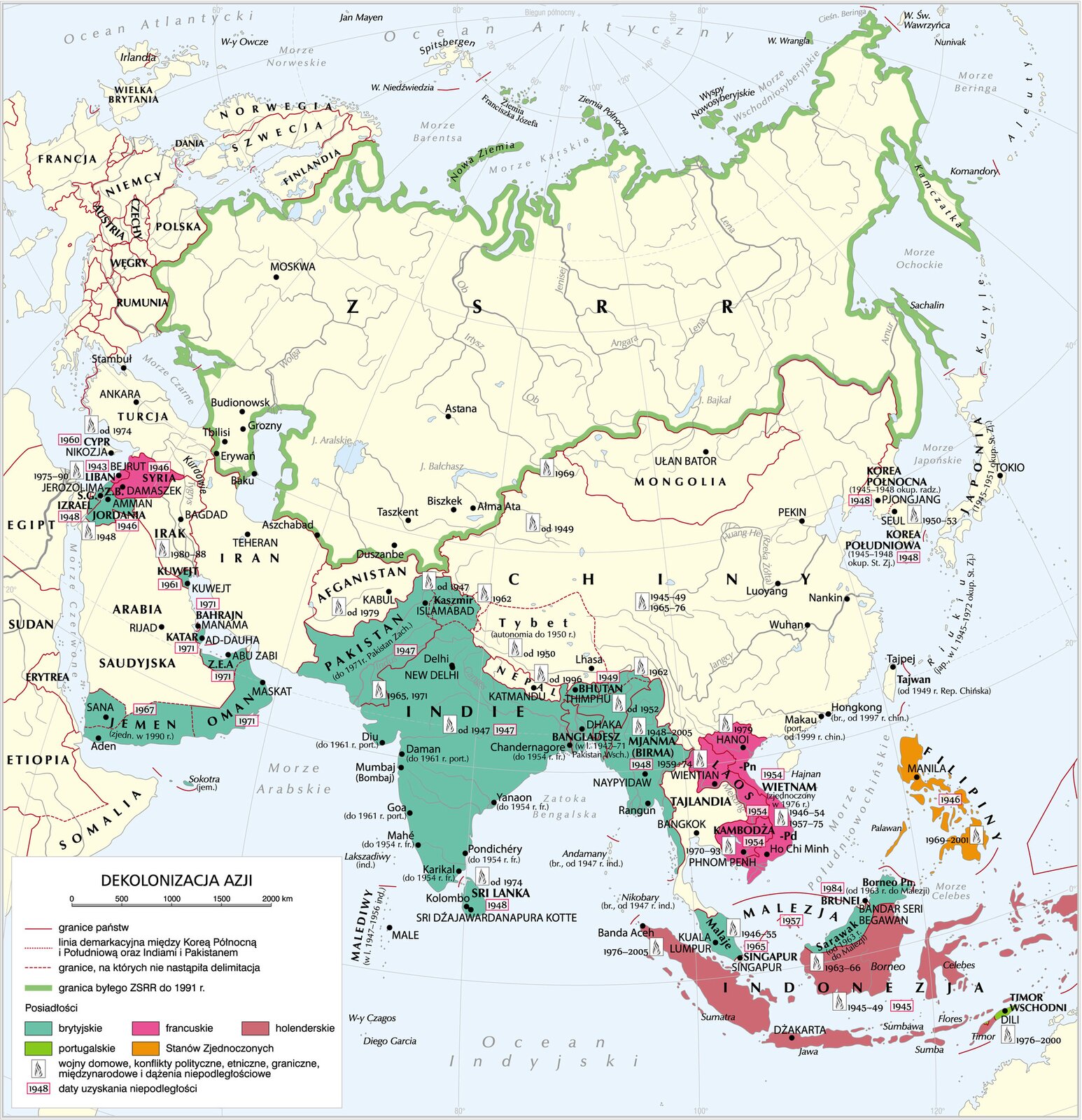
The Decolonization, i.e., liquidation of the colonial system, gained momentum after the end of World War II. Conducive to this process were the international situation and the post‑war weakening of the mother countries, as well as the activities of the UN which supported the nations’ ideas of self‑determination and striving for independence. Decolonization may also be said to have resulted from the post‑war transformations: economic development of the colonies, independence movements, and the colonial societies becoming self‑reliant. The process happened in various ways, and the colonial states would either be given their independence or have to fight for it in armed conflicts. The process of liberation of the colonies in Asia began in 1945 (Taiwan). Its culminating point was the gaining of independence by the ‘jewel in the British crown’ – India (1947). Mahatma Gandhi – the symbol of the passive resistance policy – played an important role in this. Subsequently, independence was gained by other British (Pakistan, Burma, Sri Lanka, Malaya), French (Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam), Dutch (Indonesia), and American territories (Philippines). A few years later, a similar path was followed by African countries which, due to the natural resources located in their territories, had remained dependent on the European mother countries for a longer period of time. However, there too, the growing national identity led to the colonial system’s collapse, whose decisive moment came with the announcement in 1960 (the ‘Year of Africa’ in which 17 countries became independent), by the UN, of the declaration of giving independence to the colonial states and peoples. The births of new countries often led to conflicts some of which lasted many years. These arose both between the former colonies and mother countries (e.g. the Indochina Wars), and between the young countries (e.g. the Indo‑Pakistani wars). In addition, the expansion of communism and attempts to introduce it often ended in conflicts. One of the most famous is the Vietnam War (1964–1975) in which, after years of fighting, the US army had to end its intervention and withdraw its forces, incurring huge losses. In other places too, it very quickly turned out that the gaining of independence was the beginning of problems for the newly formed countries. The lack of political elites, the spreading corruption, and the economic difficulties caused many of the ‘young democracies’ to quickly turn into bloody dictatorships engulfed in civil wars. This was particularly evident in Africa (Uganda, Angola, and Congo). Failure of the former colonies to cope with the new reality resulted in neocolonialism, i.e., dependence and external management of a state which, in theory, is independent and has all the attributes of sovereignty.
Why is Geneva associated with the peace process? What organization was created in the interwar period and had its headquarters there?

Match the terms to the definitions.
the process of liquidating the colonial system and liberating the nations striving for independence., a theory that proclaims the need for separate development of communities of different races., a modern form of colonialism that consists in making dependent and managing from the outside a state that theoretically is independent and has all the attributes of sovereignty., an international organization established in 1931, which brought together autonomous communities that maintained links with the British Crown., the legal status for colonies taken away from Germany and Turkey after World War I and then entrusted, under the supervision of the League of Nations, to the victorious countries of the Triple Entente., a policy of conquering and taking over underdeveloped countries by economically developed ones., a group of countries during the Cold War, which remained uninvolved in the conflict between the Western capitalist bloc (the First World) and the Eastern Communist block (the Second World). Over time, it has become a term for poor and underdeveloped countries.
| Colonialism | |
| Decolonization | |
| League of Nations mandate | |
| The Commonwealth of Nations | |
| Apartheid | |
| Neocolonialism | |
| Third World countries (the Third World) |
Keywords
Colonialism, apartheid, neocolonialism
Glossary
Kolonie – posiadłość państwa, która znajduje się poza jego granicami, ale bezpośrednio mu podlega.
Kolonializm – polityka państw rozwiniętych gospodarczo polegająca na utrzymywaniu w zależności politycznej i ekonomicznej krajów słabo rozwiniętych, wykorzystywaniu ich zasobów ludzkich i surowcowych.
Dekolonizacja – proces likwidacji systemu kolonialnego i wyzwalania się narodów dążących do uzyskania niepodległości.
Terytorium mandatowe – kolonie odebrane po I wojnie światowej Niemcom i Turcji, powierzone następnie pod nadzorem Ligi Narodów zwycięskim państwom Ententy. Były one podzielone na 3 kategorie (A,B,C) w zależności od poziomu samodzielności i rozwoju.
Brytyjska Wspólnota Narodów – organizacja międzynarodowa powstała w 1931 r. skupiającą autonomiczne społeczności utrzymujące związki z koroną brytyjską. Obecnie zrzesza ona niepodległe kraje.
Rada Powiernicza ONZ – jeden z organów ONZ, którego zadaniem miała być kontrola nad terytoriami mandatowymi do momentu ich niezależności od dawnych metropolii.
Apartheid – teoria głosząca konieczność osobnego rozwoju społeczności różnych ras. W odniesieniu do tej doktryny funkcjonował oparty na segregacji rasowej system polityczny panujący w Republice Południowej Afryki do połowy lat 90. XX wieku.
Neokolonializm – współczesna forma kolonializmu polegająca na uzależnieniu i kierowaniu z zewnątrz państwem, które jest w teorii niepodległe i dysponuje wszystkimi atrybutami suwerenności.
Państwa Trzeciego Świata (Trzeci Świat) – grupa państw w okresie zimnej wojny, które pozostały niezależne w konflikcie między blokiem zachodnim, kapitalistycznym (pierwszy świat) a wschodnim, komunistycznym (drugi świat). Z czasem termin ten zaczął oznaczać ubogie i słabo rozwinięte kraje.