The spectacle in the sky
that light propagates in a straight line;
that light has the ability to reflect, refract and disperse;
that the sun is the main source of light on Earth.
describe the effect of a prism;
discuss the colors that make up white lightwhite light;
discuss the conditions necessary for t he creation of a rainbow.
Is white light… white?
The sunlight seen by man is white. It turns out, however, that it is not just one colour. In fact, it is a mixture of many parts seen by us as different colors. The full range of light reaching us from the sun consists of a whole range of colors available to human sight, namely: red, green and blue, and all the colors between them – there are infinitely many of them. How do we know it? It has been proven a long time ago with a glass object called a prismprism. The phenomenon that we observe thanks to the prism is called the dispersion of light.
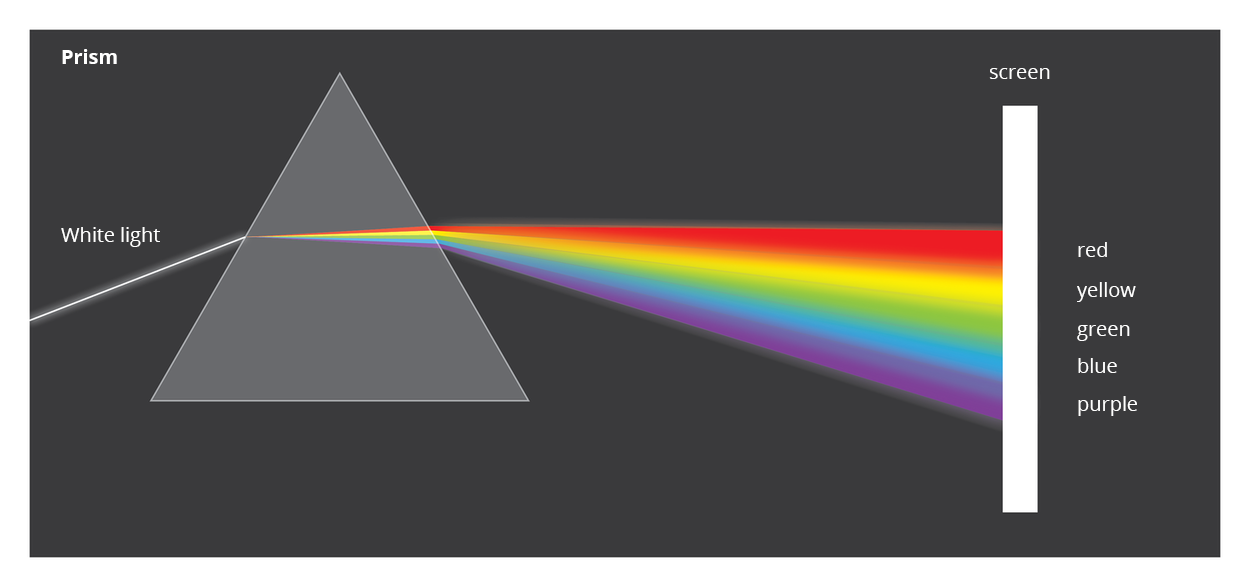
Before you watch the movie „White light dispersion”, write down the research question and the hypothesis. Make notes while watching the movie, and finally make conclusions.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film ilustrujący przykład eksperymentu, w trakcie którego rozszczepiamy światło białe, najlepiej klasycznej żarówki, na płycie CD.
Can we prove that light dispersion if we do not have a prism? Yes, we can do simple observation for this.
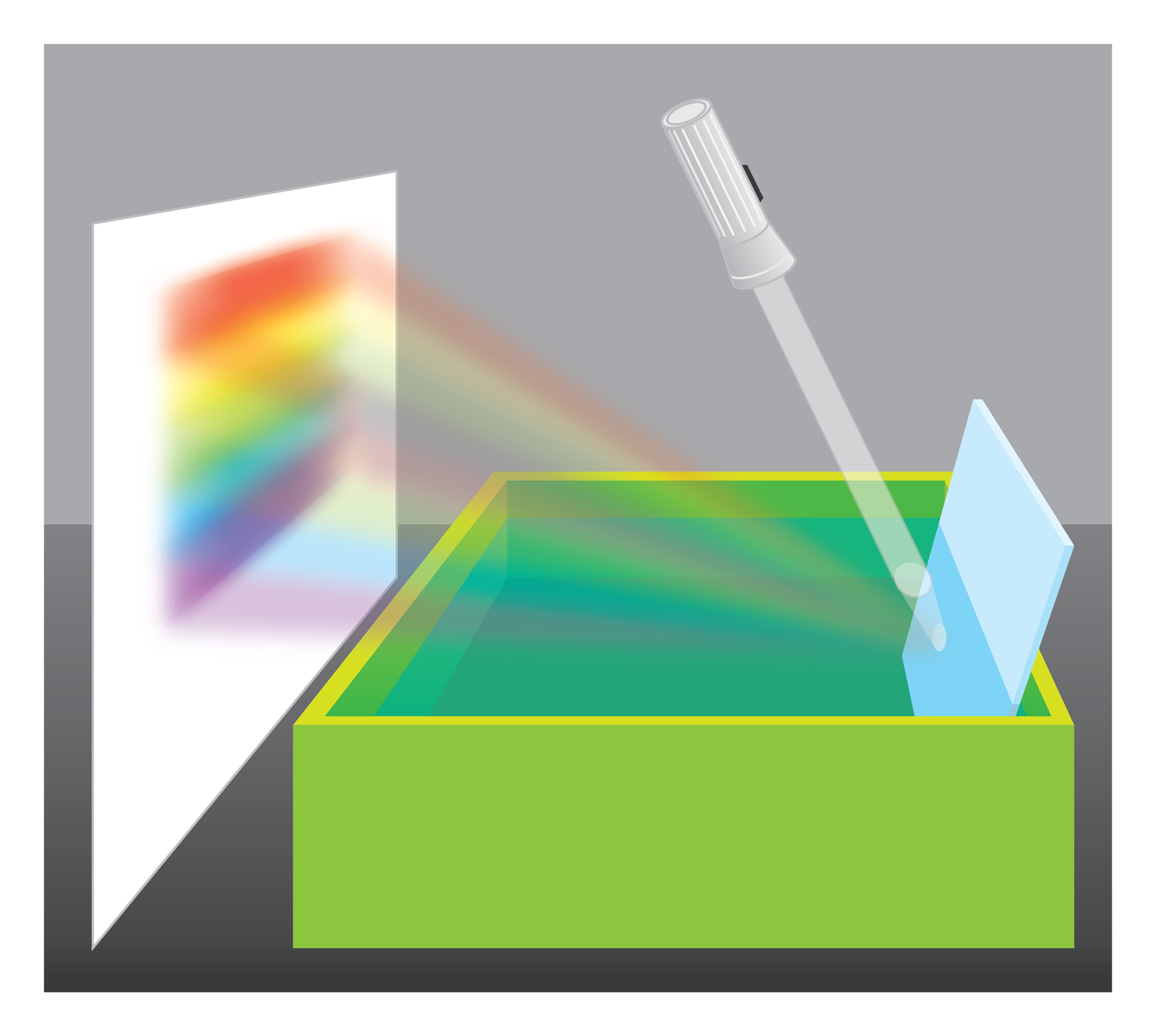
Splitting white light into its component colors.
bowl,
sheet of paper,
mirror,
lamp or flashlight with white light.
Attach the card to the wall.
Pour water into a bowl.
Immerse the mirror so that it is half immersed in water.
Light the flashlight at the mirror in the place where the water line is. Adjust the mirror so that the light falls on the card. What are you seeing?
White light, going through the water, breaks down and splits. On the screen, we can see the colors that make up white light. As a result of splitting the white light, we get multicolored stripes flowing smoothly from red, through orange, yellow, green and blue to violet.
How is it that we see colors? Well, every object either shines itself, or absorbs or reflects light. For example, we see a book with a red cover because it absorbed most of the light, except for the red color, which was reflected and hit our eye.
Is a rainbow connected with the dispersion of light?
Not only the prism splits the light. Water drops also have this property. As a result of the sunlight falling on the border of air and water, it diffuses. When the drops of water float in the air during falling rain, while the cloud is illuminated by the sun's rays, a very impressive phenomenon appears called a rainbowrainbow.
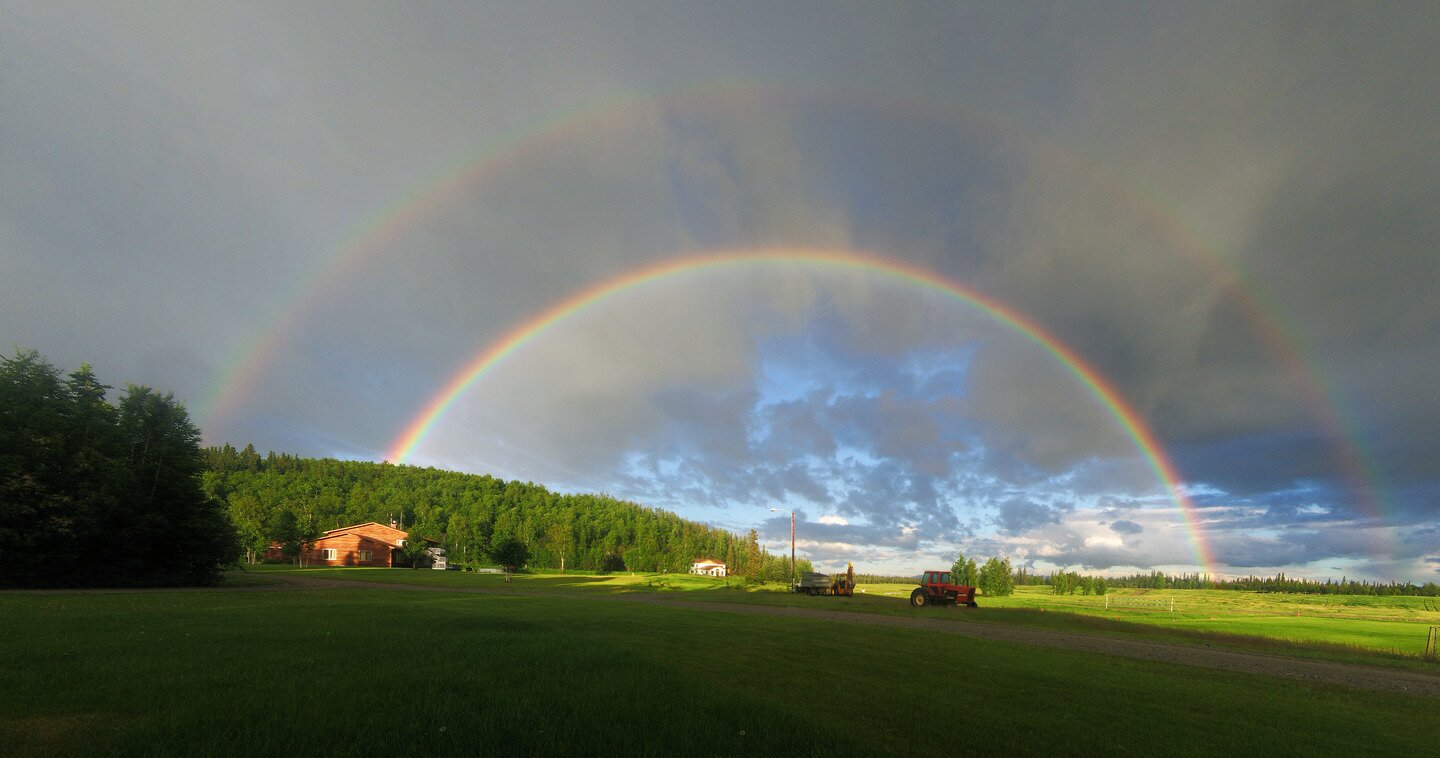

It is worth remembering that a rainbow does not exist in a particular place. It is only an image perceived by the observer. A few people watching the rainbow from different places at the same time see it a bit differently.
Another light phenomenon in the atmosphere is a halohalo. It is a luminous circle that surrounds the sun or moon. The part of the sky visible inside the circle is clearly darker than the rest. Halos are caused by the refraction of light on ice crystals or inside them, in cirrus clouds.Explain under what circumstances you can see the dispersion of light.
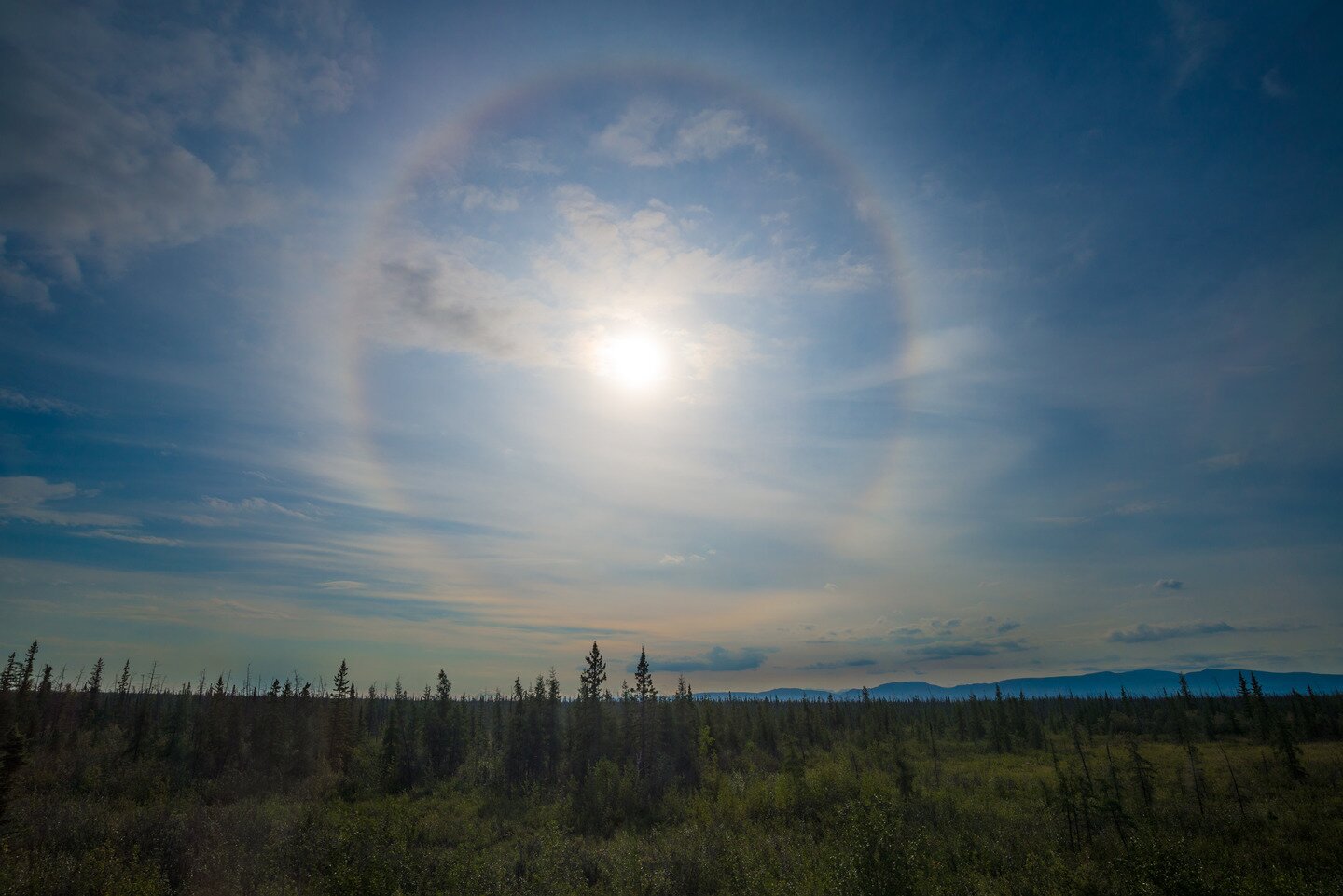

Select the conditions that must be met to observe a rainbow.
- The sun should not be too high above the horizon.
- The observer should stand with his back to the Sun and face to the cloud.
- The air temperature should be at least 15 ℃.
- On the opposite side of the horizon there should be a cloud from which it rains.
- The observer should be on a high mountain or in an airplane.
Based on the lesson information, fill in the text below.
dispersion, ice crystals, water droplets
Halo, like the rainbow, is a light phenomenon resulting from the ............................ of light. In the case of a rainbow, the light splits on the border of the ............................ and air. Halo arises in a similar way, but in this case the refraction of light occurs on ............................ or inside them.
Summary
White light can be split into its component colors.
A device used for splitting light is the prism.
The splitting of light is related to the formation of optical phenomena, e.g. rainbow and halo.
Keywords
white light, prism, rainbow, halo
Glossary
halo – zjawisko w atmosferze mające postać świetlistego kręgu wokół tarczy Słońca lub Księżyca; powstaje w wyniku załamania światła w kryształkach lodu budujących chmury pierzaste
pryzmat – bryła z przezroczystego materiału o dwóch ścianach nachylonych względem siebie pod kątem odpowiednim dla rozszczepienia światła
tęcza – zjawisko mające postać barwnego kręgu widocznego po przeciwnej stronie niż Słońce; powstaje w wyniku rozszczepienia światła białego w kropelkach wody
światło białe – światło docierające do nas ze Słońca; zawiera wszystkie barwy podstawowe i barwy pośrednie