Vascular tissue
all organisms are made of cells;
basic life processes take place in the cells;
most of plant cells have chloroplasts, cell wall and vacuoles.
identify plant tissue;
discuss the basic functions of individual plant tissues;
show the relationship between the structure of tissues and the function they perform;
how to perform microscopic observation of plant tissues.
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie dźwiękowe abstraktu dotyczące tkanki przewodzącej
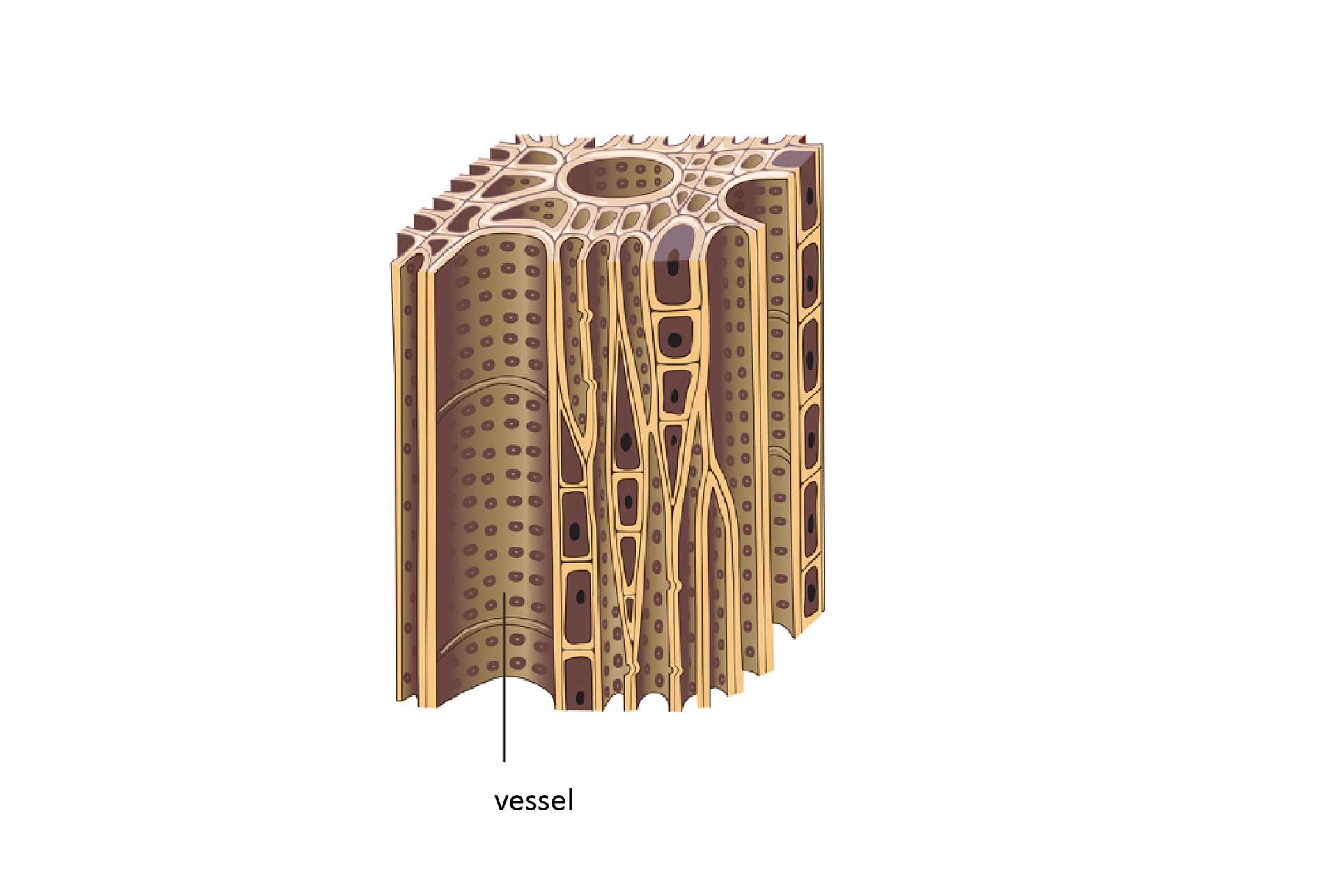
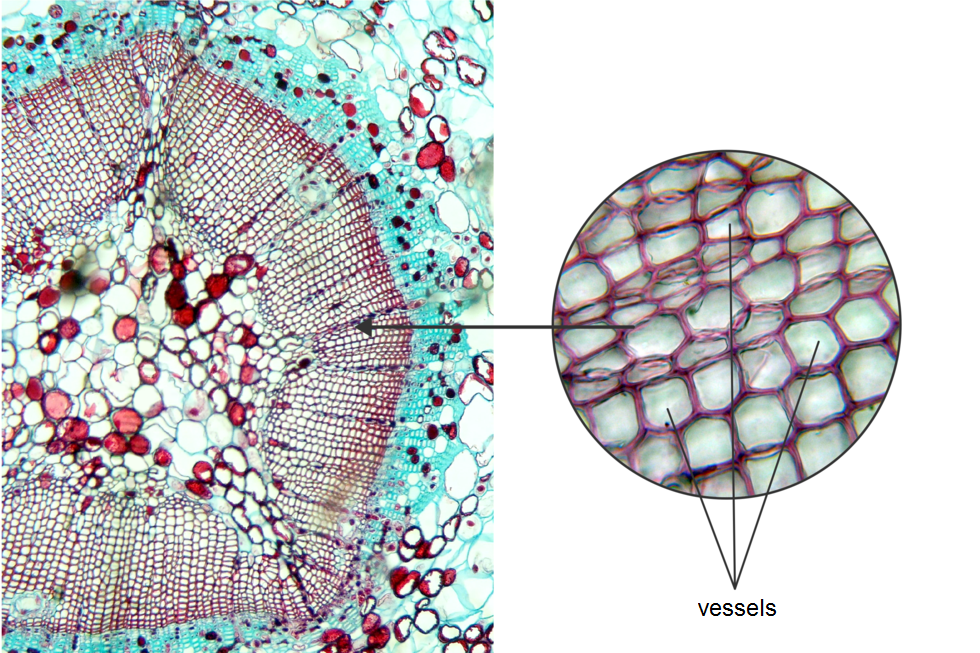
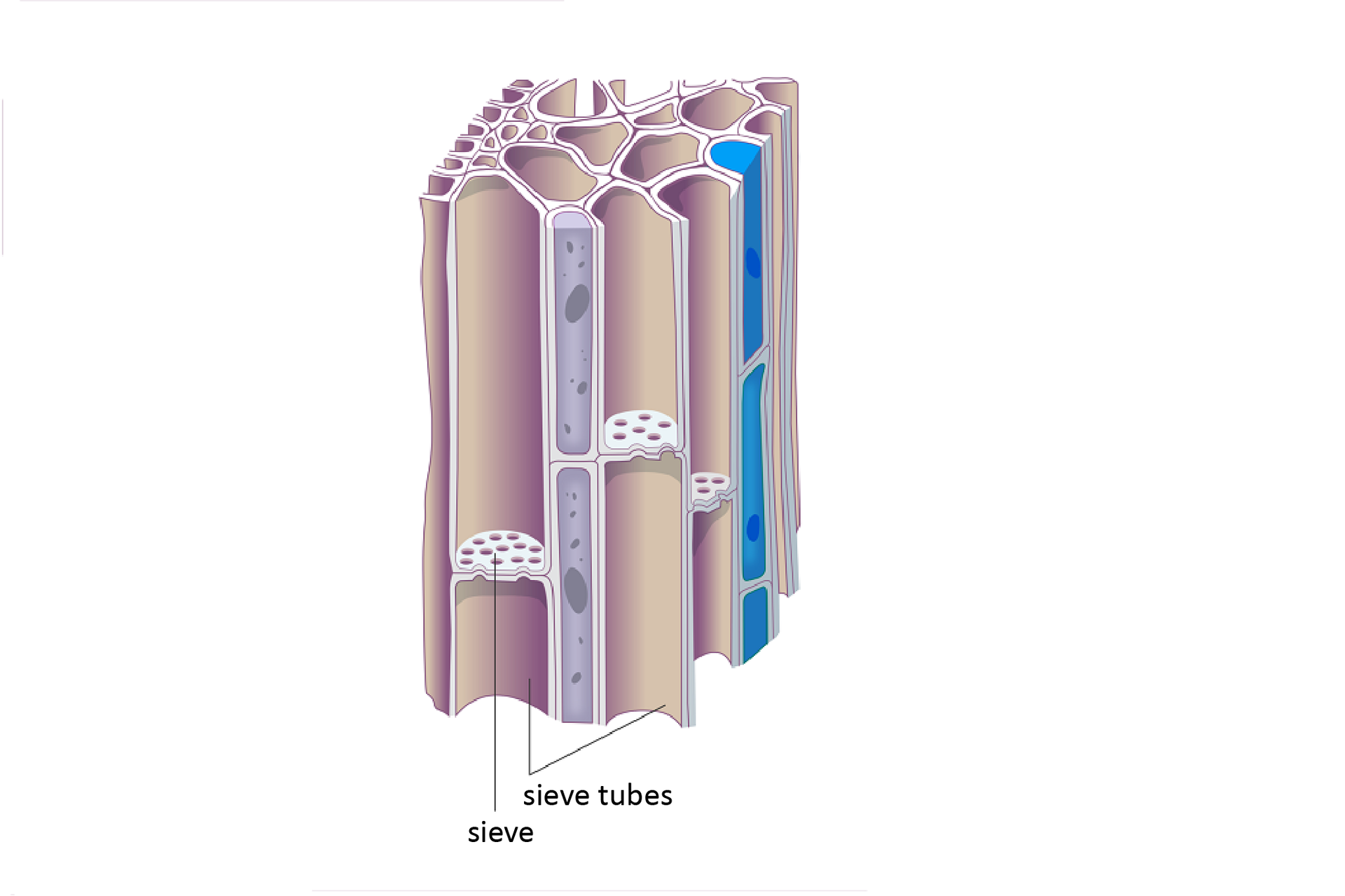
The taller the plant, the harder it is to supply the cells located on top with the necessary amount of water and nutrients.They deal with this using vascular tissuesvascular tissues, which form long vascular bundles running along the plant. Typical vascular tissuestissues occur in vascular plants, i.e. ferns and seed plants.
Wood (xylem) it is built of dead, woody and hollow cells arranged one above the other. Their transverse cell walls have disappeared, so they resemble long tubes called vessels. They are leading the water along with minerals from the roots through the stem to the leaves, flowers and fruits.
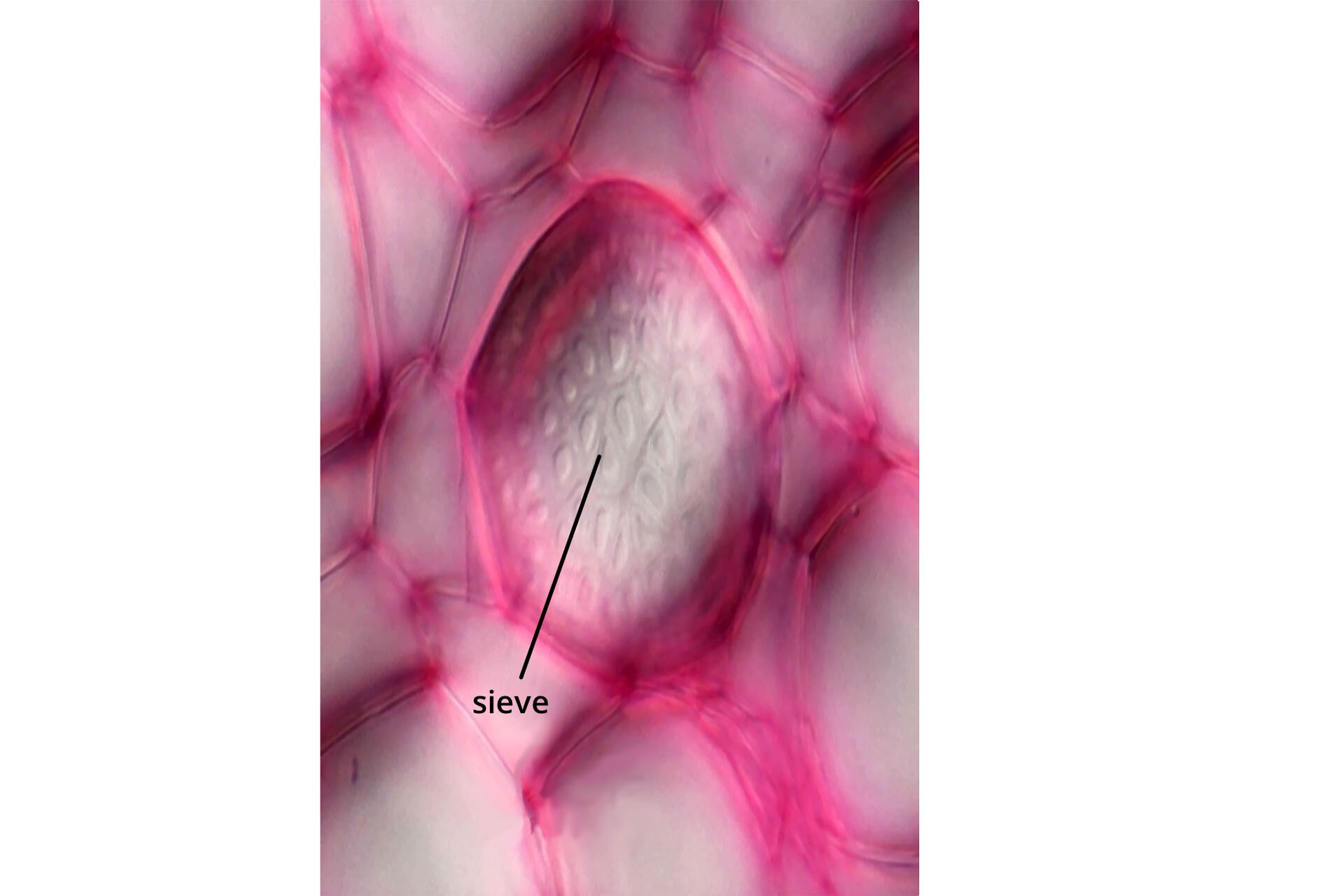
Phloem absorbs nutrients throughout the plant produced in the leaves during photosynthesis. It is made of elongated, living cells, whose transverse walls have many holes and resemble sieves. For them, the cells combine with each other to form cytoplasmic bands. The individual tubes sieve (sieve tube elements) are arranged over each other to form strings conductive, through which nutrients are transferred from cell to cell.
Summary
The body of plants is filled with tissues, i.e. assemblies of cells with a similar structure specialized to perform specific functions.
Vascular tissue is responsible for transporting water and nutrients to all parts of the plant.
Indicate the similarities and differences in the construction of wood and phloem.
Keywords
vascular tissue, wood, phloem
Match the pairs: English words with Polish definition.
tkanki roślinne, która transportują wodę z solami mineralnymi z korzeni do liści oraz przewodzą substancje pokarmowe wytworzone w liściach podczas fotosyntezy do wszystkich organów rośliny; składają się z komórek drewna (naczyń) i komórek łyka (rurki sitowe), zespół komórek o podobnym pochodzeniu i budowie, pełniących określone funkcje w organizmie
| tissue | |
| vascular tissues |
Glossary
tkanka – zespół komórek o podobnym pochodzeniu i budowie, pełniących określone funkcje w organizmie
tkanki przewodzące – tkanki roślinne, która transportują wodę z solami mineralnymi z korzeni do liści oraz przewodzą substancje pokarmowe wytworzone w liściach podczas fotosyntezy do wszystkich organów rośliny; składają się z komórek drewna (naczyń) i komórek łyka (rurki sitowe)