`
Water – the basis of life
that water is a chemical compound;
that the water molecule is composed of one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms;
that the water at room temperature is a liquid.
to describe the water cycle in nature;
to present ways to save water and justify the necessity of rational management of its resources.
The presence of water in nature
Water is one of the more widespread substances in nature. The surface of the Earth is covered with water in almost 71%. Of this, 97% is the water of the seas and oceans. The remaining part of the water is trapped in glaciers, permanent snow cover and permafrost, it forms rivers and water reservoirs, it is found in groundwater, soil, air and is a component of living organisms.
Only 2.5% of the volume of natural waters are fresh waters, which are essential for the life of all organisms. The remaining 97.5% are salty waters (seas and oceans, salt lakes and groundwater) that do not play role when it comes to providing humanity with drinking water. The name „salt water” derives from the taste of seawater, which mainly comes from the dissolved sodium chloride. It is not safe to drink, and its administration can be very dangerous – the body has to use more water to expel the substance introduced with it than it received in a drunken portion.
”Fresh water” contains much less dissolveddissolved chemicals. Drinking water is obtained from it.
Arrange the puzzle. In how many states of matter water is presented in this photograph? Name them and their examples.
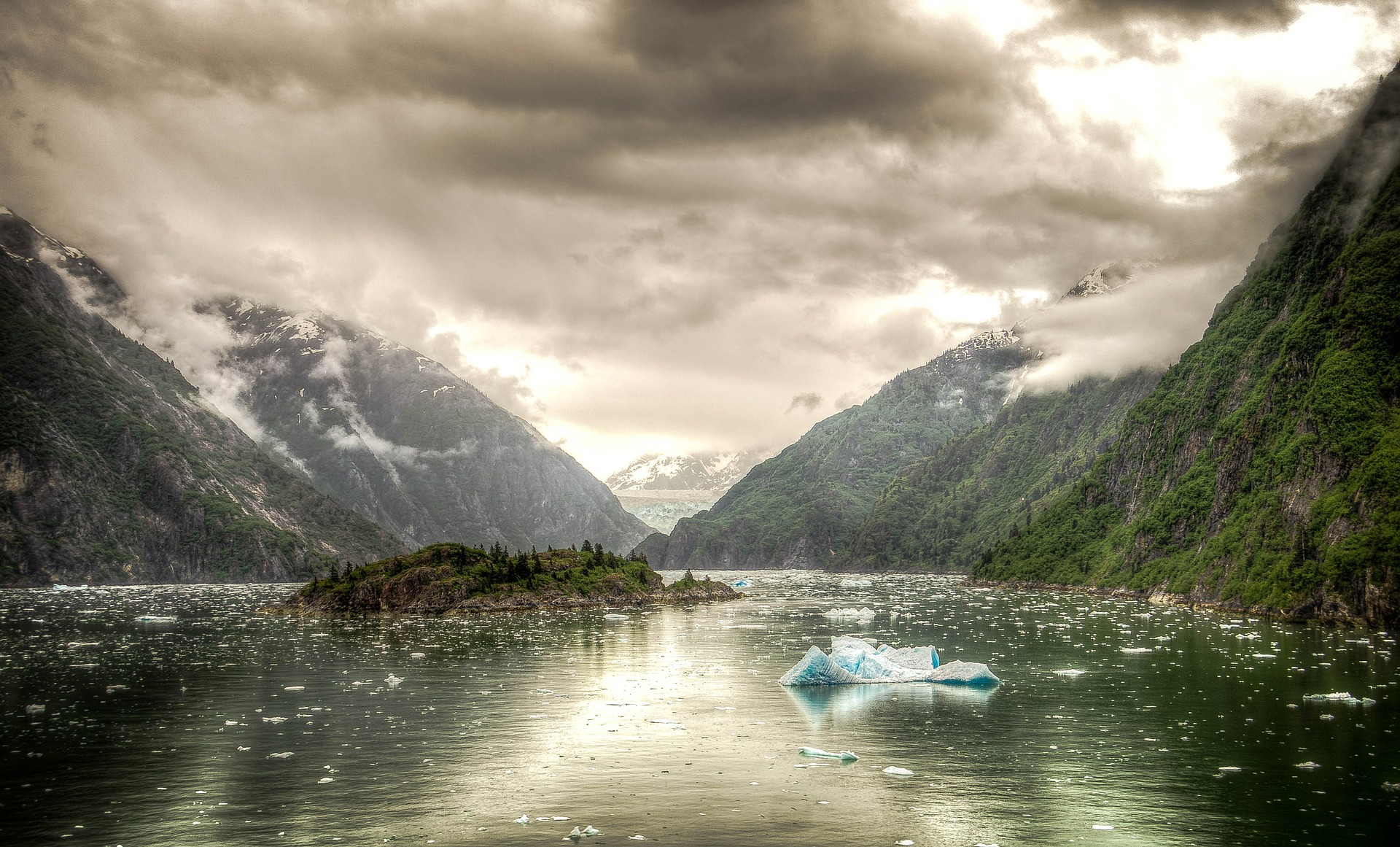

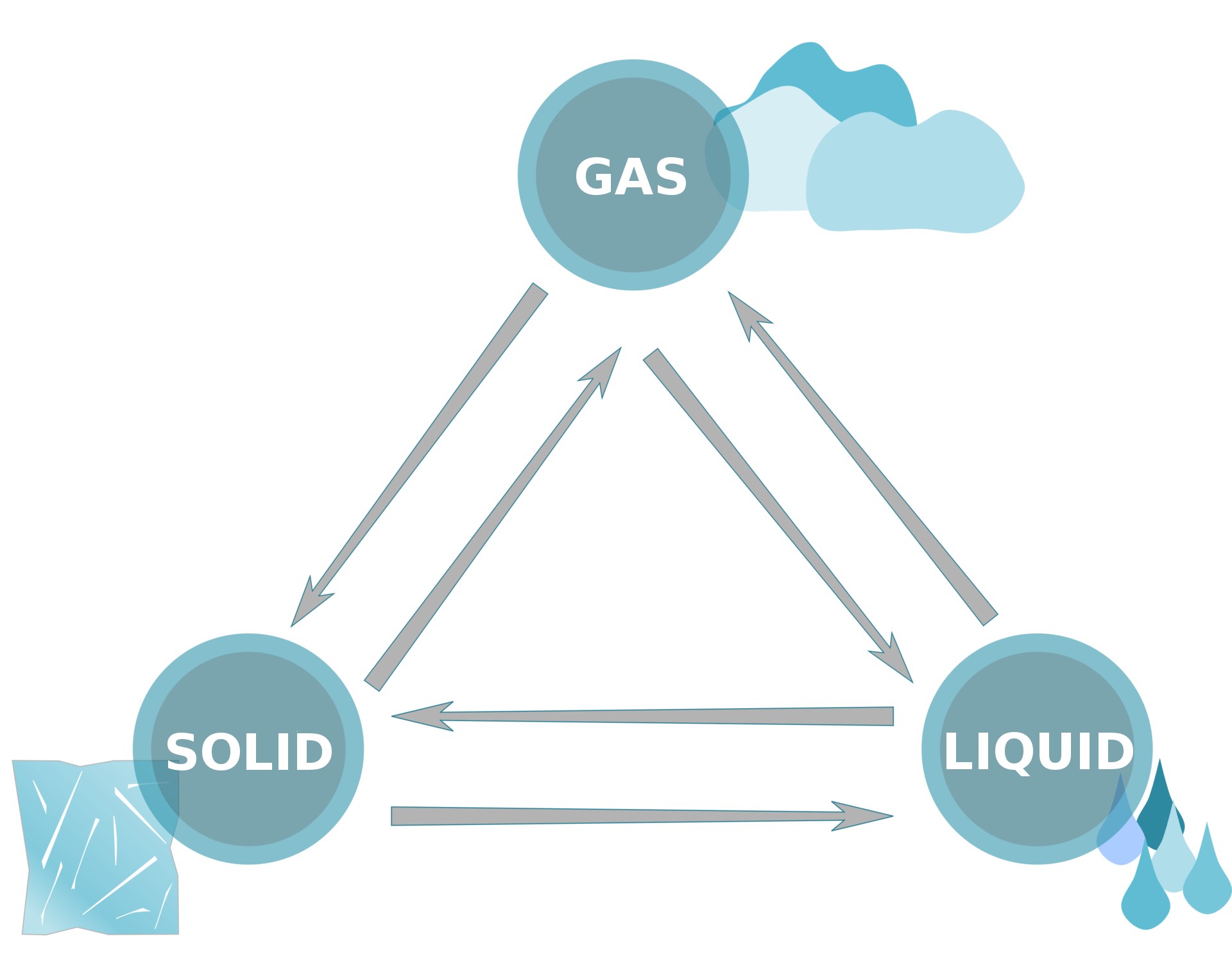
Water is the only chemical compound that occurs on Earth in three states of matter. It is liquid in surface and underground waters, in the atmosphere it is a gas, and in precipitation (snow, hail) as well as glaciers and permafrost it exists in a solid state.
Take a look how the water cycle and change of state of matter looks like in nature.
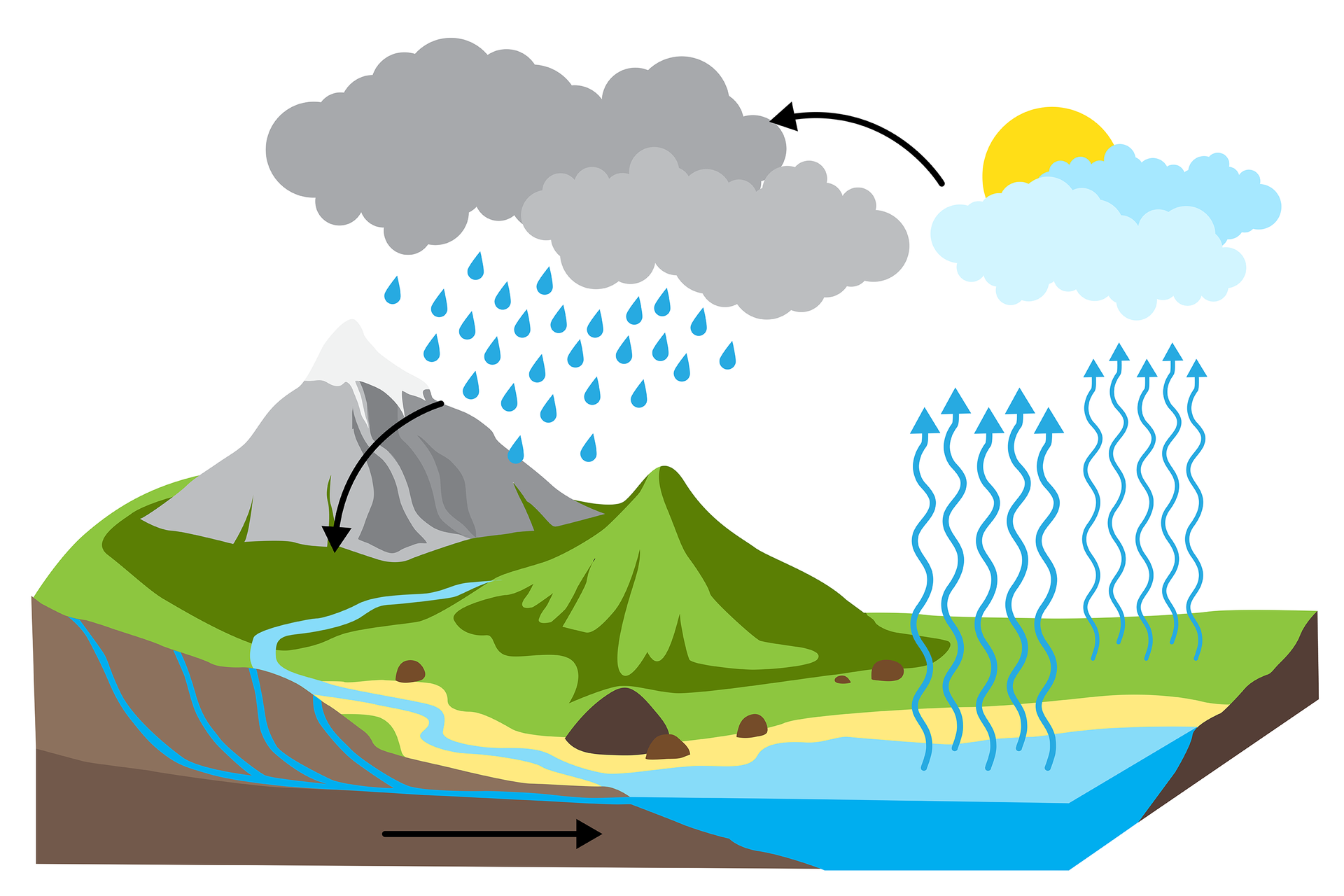
The amount of water on the globe is constant, although the water is in constant motion. Movement of water is caused by two factors – the sun and gravity. Solar energy causes evaporation of water, and the gravity - the dropping of a drop of water from the atmosphere to the surface of the Earth (condensation), and then its flow and soaking into the seas and oceans. Water in the form of ice, i.e. a solid, sublimes into gas (a vapour), and the vapour, turning into frost and snow, that is, changing the state from gas to solid, undergoes the process of resublimation.
Water as the basis of life
Water is indispensable to the life of plants, animals and people. In the hierarchy of all life needs of organisms, water is in the first place. There are even microorganisms that can live without oxygen, but they cannot live without water. Water is the most important component of organisms, for example, it constitutes about 60‑70% of human body mass. It is essential for its proper functioning: it participates in the regulation of body temperature, transport of nutrients, metabolic products and in all biochemical reactions taking place in the body.
Before you conduct experiment „Heating of the crushed cucumber”, formulate research question and hypothesis.
Does cucumber contain water?
Cucumber contains water.
raw cucumber,
test tube,
test tube claw,
gas burner.
Place a crushed slice of cucumber in a test tube.
Heat the contents of the tube until the first changes occur.
Watch a movie. Pay attention to what justifies the presence of water in the tested chemical substance. Write down your observations.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film przedstawia eksperyment - badanie obecności wody w kryształach siarczanu sześć miedzi dwa, testing of the presence of water in copper two sulfate crystals. Potrzebne będą palnik, torch, łyżka, spoon, siarczan sześć miedzi dwa, copper two sulfate, zapalniczka, lighter, probówka, test tube, szczypce, test tube clamp. Szczyptę siarczanu sześć miedzi dwa umieszczamy w probówce, a następnie probówkę podgrzewamy nad palnikiem. W wyniku ogrzewania na ścianach probówki skrapla się woda.
Drag the water processes to the right place.
evaporation, melting, solidification, sublimation, resublimation, condensation
The process of solution formation involving the mixing of particles of solute with solvent particles is called:
- dissolution
- evaporation
- combustion
Create a multiple-choice test based on today's lesson. Then exchange your questions with a friend or classmate.
Question: ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
Summary
Natural waters, found in nature, are solutions of various solid substances and gases.
Most of the substance are contained in the sea water, the least - water from precipitation.
Almost 71%of the Earth's surface is covered with water.
Water as the only compound on Earth that occurs in three states of matter.
Water is the most important component of organisms.
Due to the limited resources of available fresh water, we should save a drinking water.
Find out from which intake water is brought to your place of residence. If you can, visit this place and see if this area is really under protection. Determine whether the water is taken from a surface or underground source.
Keywords
Water, state of matter, fresh water, salt water
Glossary
rozpuszczanie – proces powstawania roztworu polegający na mieszaniu się drobin substancji rozpuszczanej z drobinami rozpuszczalnika