What is a volcano and how is it build?
what the internal structure of the Earth is;
what types of basic types of rocks and minerals can be distinguished;
what the causes and consequences of the plate are like structure of the earth's crust.
determine the relationship between the location on the boundary of lithospheric plates and the occurrence of volcanoes and earthquakes;
indicate and name the elements of a volcanic cone in a figure;
discuss the difference between a volcanic cone and a shield volcano, and the difference between an active volcano and an extinct volcano;
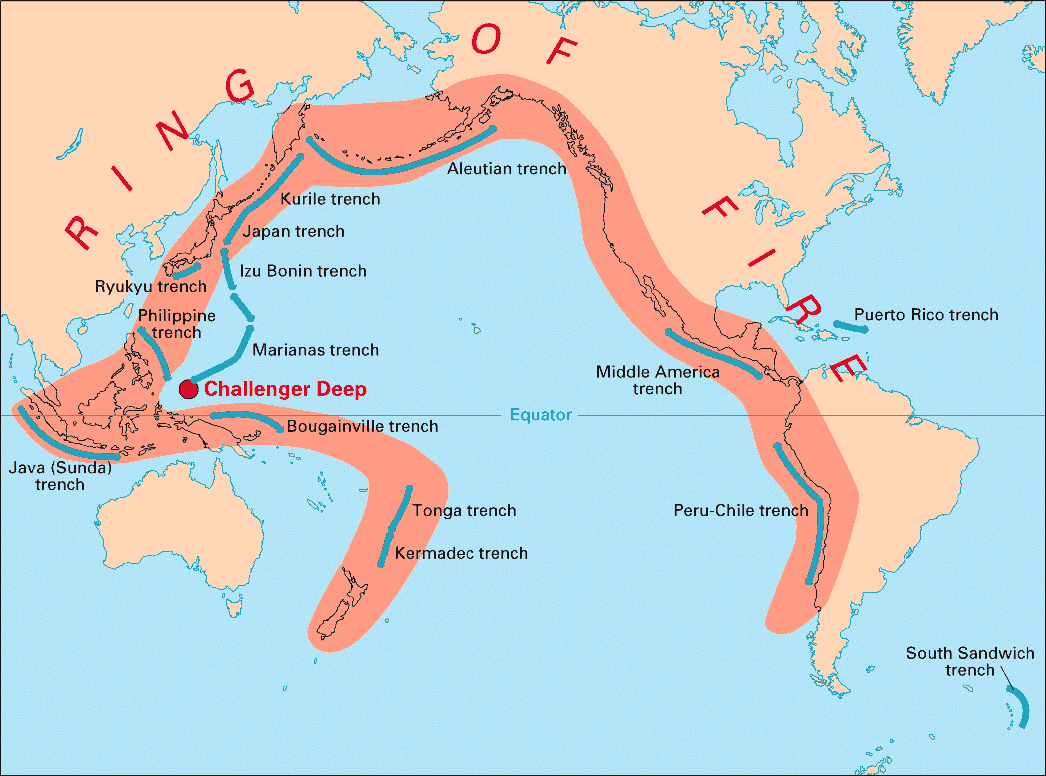
locate places on a physical world map with the largest active volcanoes;
give conclusions concerning the Pacific ring of fire;
explain what a geyser is and when it arises;
justify how volcanoes affect human life.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film przedstawia krater wulkanu. Wokół krateru płaski teren bez roślinności. Z wnętrza krateru wydobywa się jasnoszary dym.
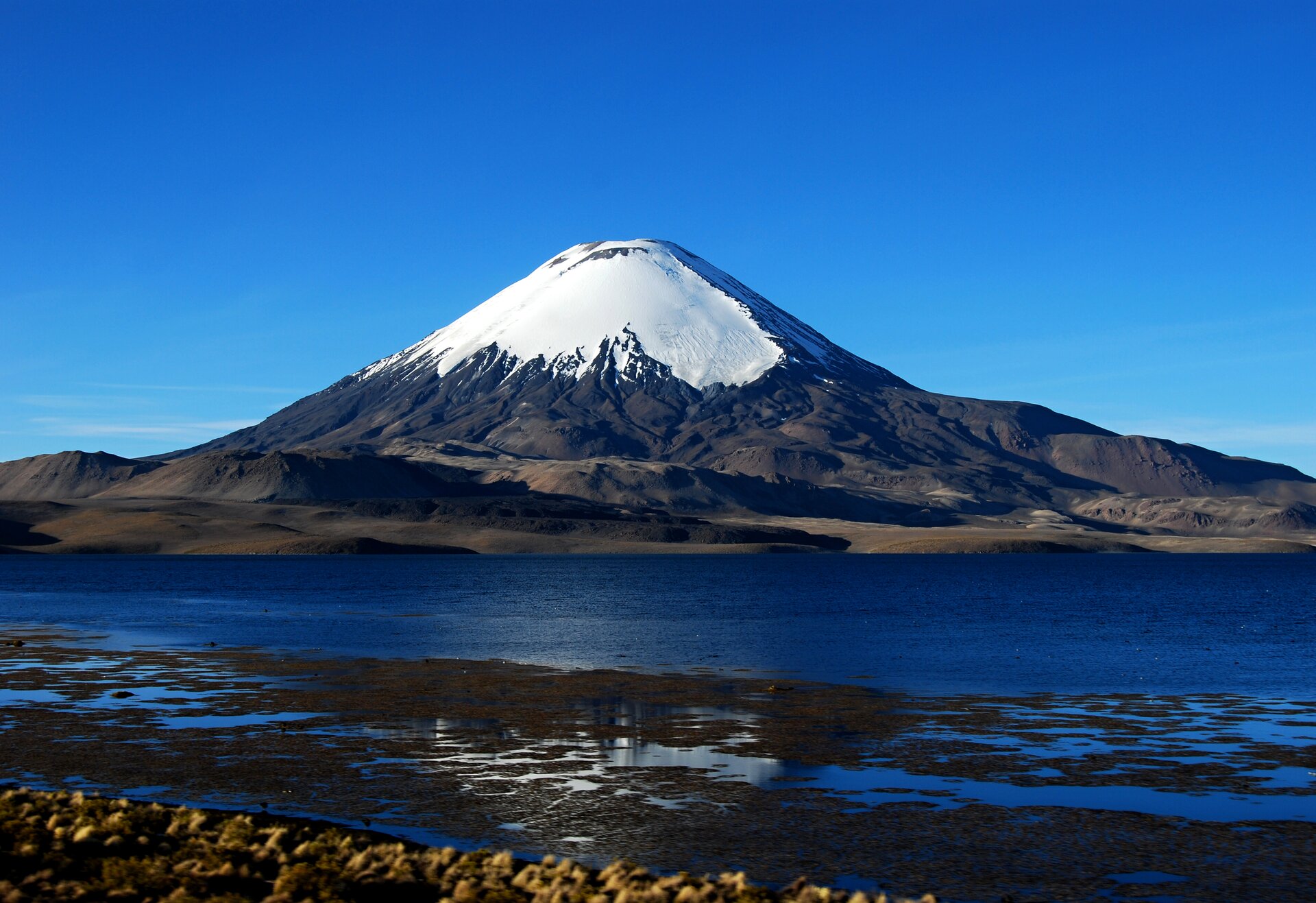
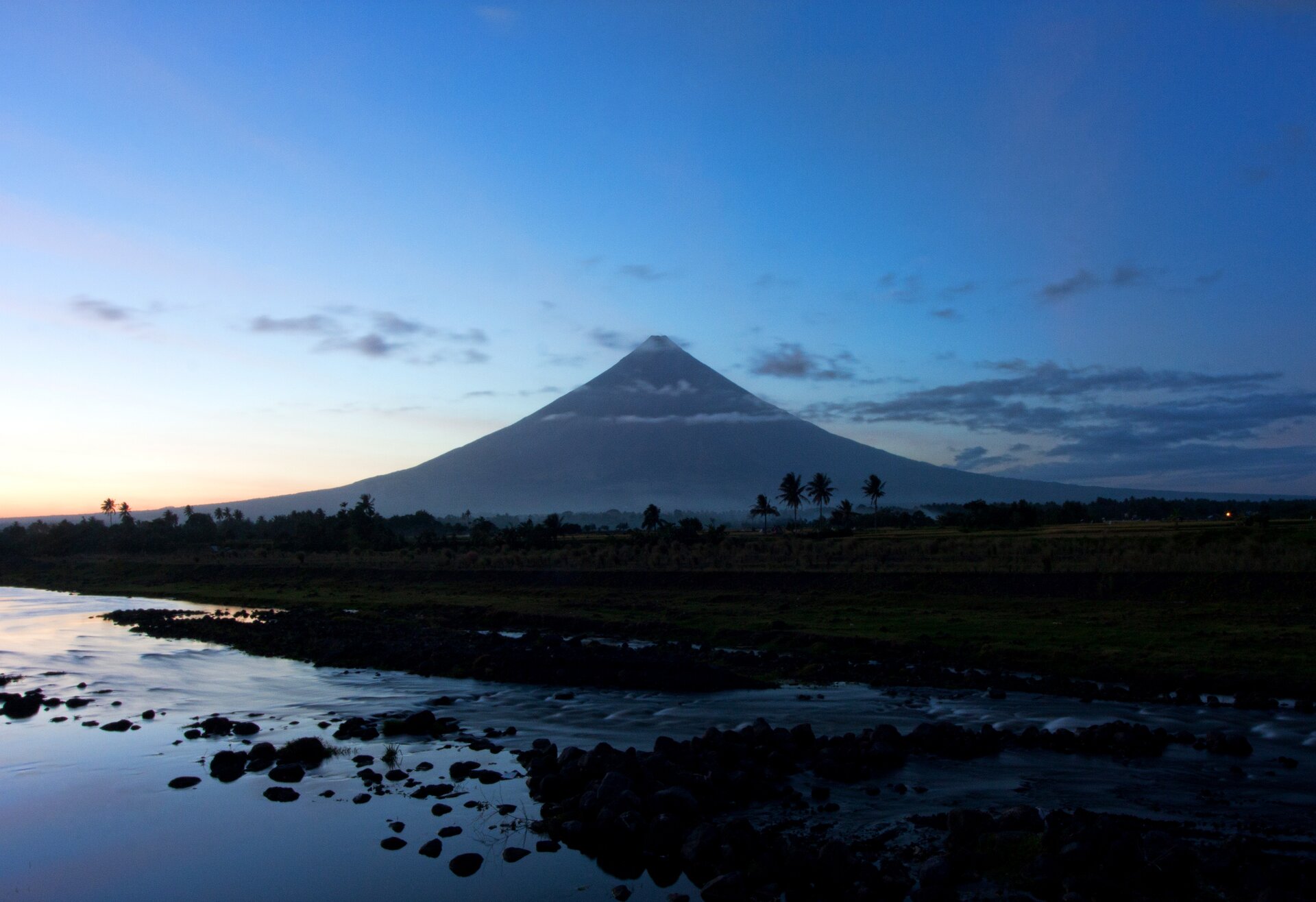
Volcanic phenomena arise as a result of the high pressure of matter that is located deep below the Earth's surface, in the Earth's crust or the mantle. MagmaMagma is formed there – a hot, molten mass of rocks, with a lot of water and gases. This pressure causes the solid, liquid and gaseous volcanic products escape to the surface of the Earth. Through cracks and openings in the Earth's crust the melted rock mass is poured, i.e. lavalava, and gases and volcanic ashes are pushed into the atmosphere. A place where lava and other volcanic products escape to the surface of the continents or to the bottom of the sea is called volcanovolcano. The course of the eruption and the shape of the volcanic cones depend on the gas pressure and the temperature and viscosity of lava.
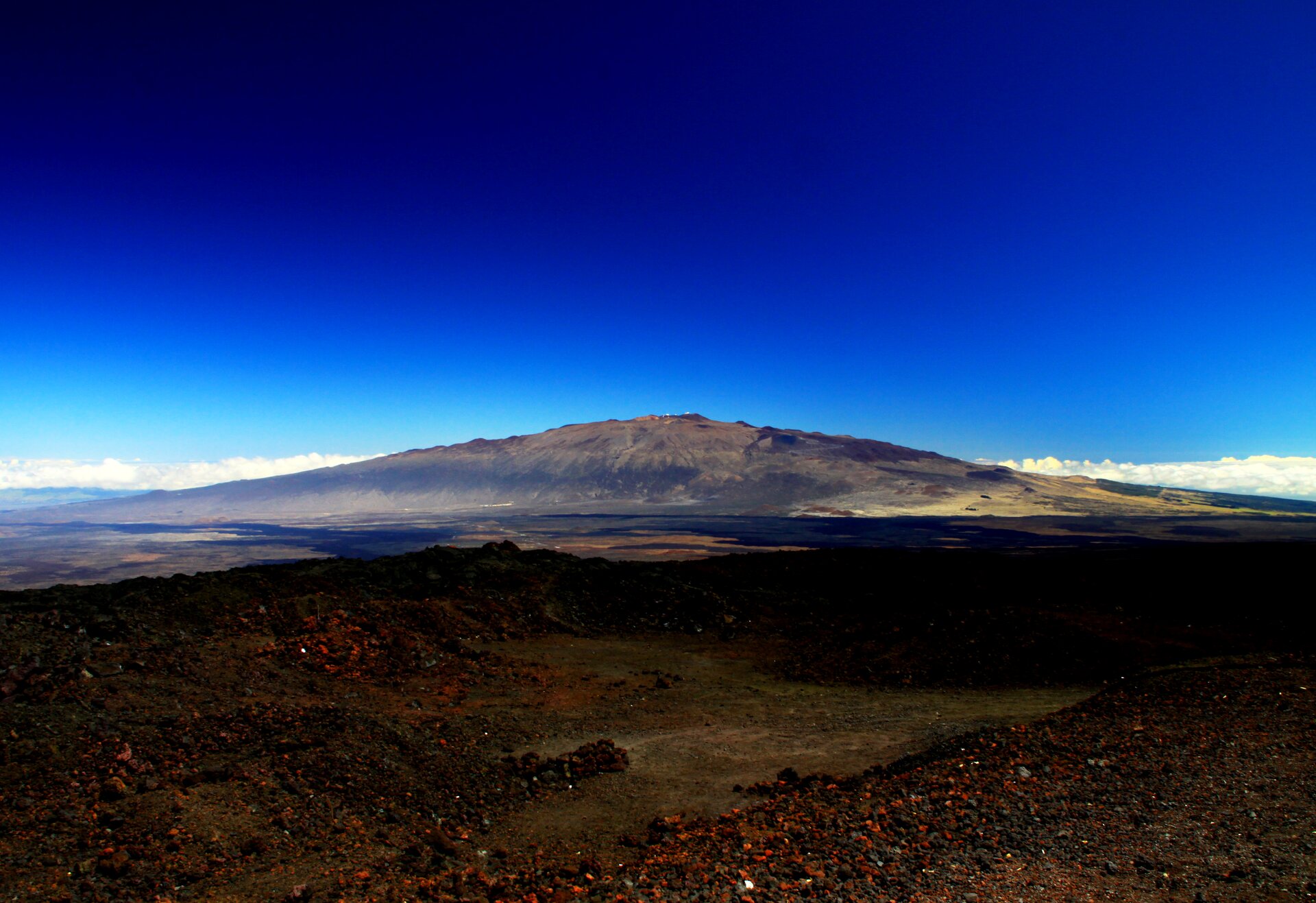
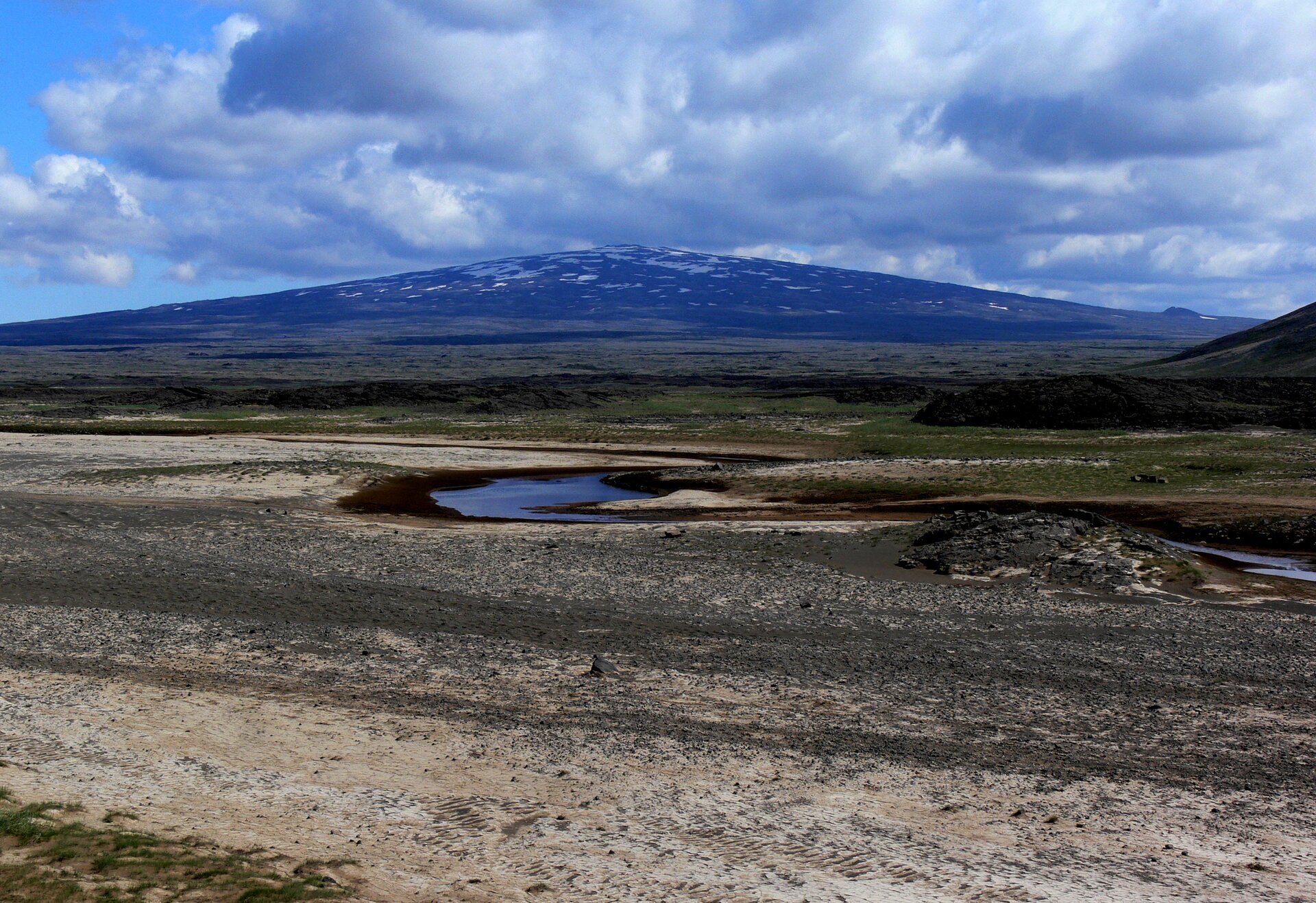
Volcanoes, from which thick lava, a lot of gases and ashes escape, usually take the shape of high cones, that is why we call them cone volcanoes. Their eruptions are violent and dangerous to people. Mild, slow eruptions of thin lava, with a small amount of volcanic gases, form flat shield volcanoes. Volcanoes are formed most often in subduction zones and then magma is formed from melted rocks of sinking lithosphere plates. Many volcanoes also occur in spreading zones (both on land and on the ocean floor), and the lava spilling out of them comes from the Earth's mantle. Volcanoes are also found far from the boundaries of the lithosphere plates, but within their range. They are formed over the so‑called hot spots, i.e. places where convection currents in the Earth's mantle provide so much heat that it can melt the lithosphere and allow the magma to travel towards the Earth's surface. One of the largest hot spots is located under the Yellowstone National Park in the USA.
Get acquainted with the elements of the volcano at the moment of the explosion (below).
During the eruption of the volcano, volcanic material escapes into the atmosphere (magma, pyroclastic materials, volatile substances: gases, various).
Familiarise yourself with the elements of volcano. Does all volcanoes look like that? Can you distinguish varius types of volcanoes?
Choose the correct name for the mixture of molten rocks and other liquid and gaseous volcanic products inside the Earth.
- magma
- pyroclastic flow
- lithosphere
- bench
Where do volcanoes most often arise? Choose the names of the two zones in which volcanoes are most often created.
- subduction zone
- Moho zone
- tropopause zone
- coastal zone
- spreading zone
- metamorphosis zone
Shapes of volcanoes. Complete the text.
The shape of volcanic cones depends on gas ................, temperature and viscosity of lava. Volcanoes from which dense ............ and a lot of gases and ............ escape are called .............. or explosive volcanoes. When the eruption is mild and slow, it is from more liquid lava with a small amount of ................ gases formed by flat ............ volcanoes, also called effusive.
Keywords
volcano, magma, lava
Glossary
lawa - roztopione, ciekłe skały wypływające na powierzchnię Ziemi w miejscach aktywności wulkanicznej
magma - stopione gorące masy skalne zmieszane z wodą i różnymi gazami
wulkan - miejsce na powierzchni Ziemi, w którym z jej głębi wydostają się: lawa, gazy i popioły wulkaniczne





