White Man’s Burden – colonialism in the 19th century
which countries took part in geographical discoveries;
what was a gold rushgold rush and what it meant;
what is colonialismcolonialism and which countries participated in it;
what the colonial policy was and what consequences it had.
Since the 16th century, the European powers have subjugated many areas outside Europe. This process intensified especially in the 19th century. The object of colonisation became, for example, countries in Africa and India. Europeans exploited the natural resources of coloniescolonies, treating the local population as a cheap labour force and buyers for their goods. Great Britain became the biggest colonial empire, with territorial possessions in almost every corner of the world. At the end of the 19th century, Germany became a new colonial state. Many people emigrated to the colony in expectation of a better life or a quick and easy income. One of such reasons was the so‑called „gold rush”, i.e. a rapid surge of new settlers to areas where valuable raw materials or minerals were discovered
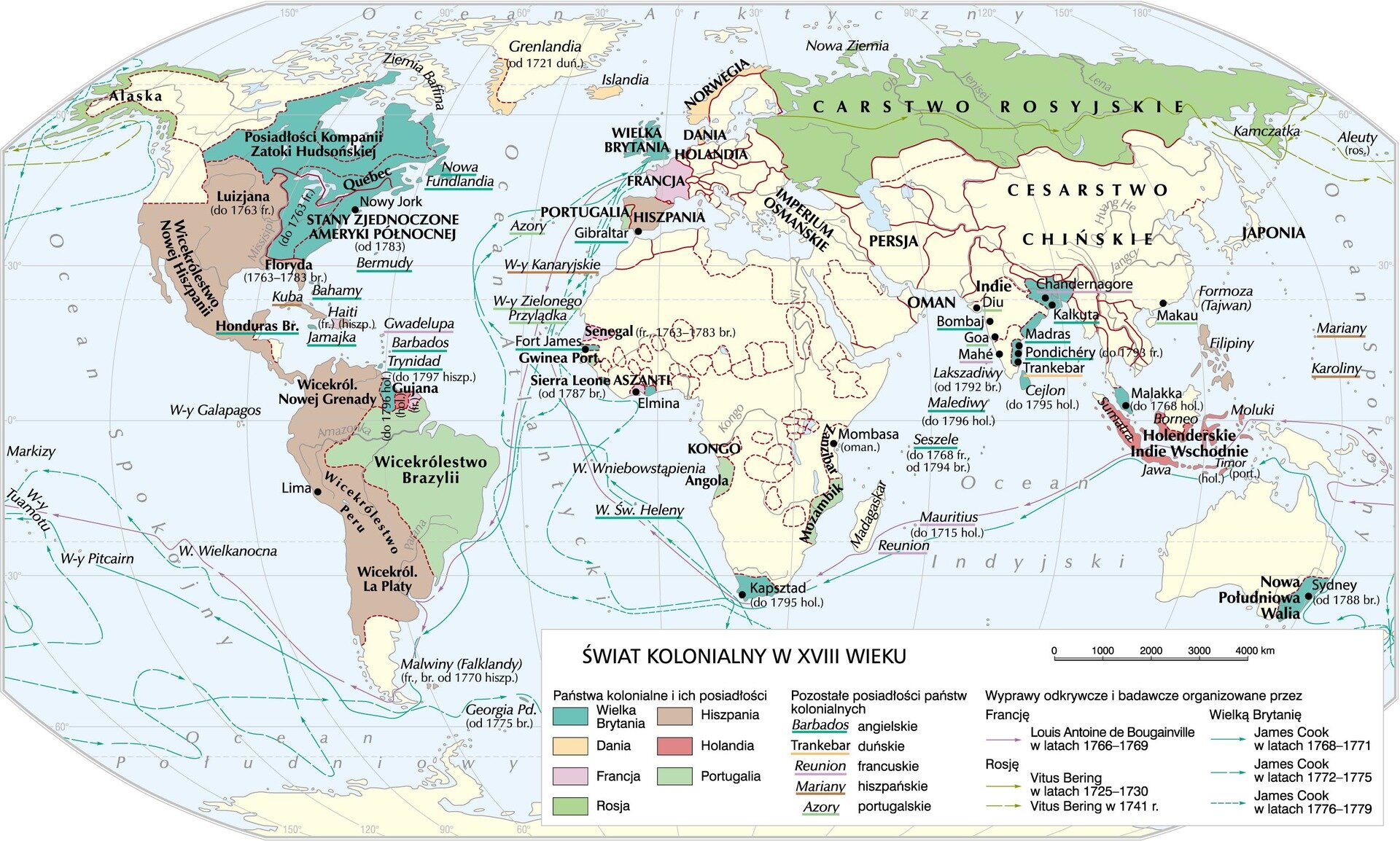
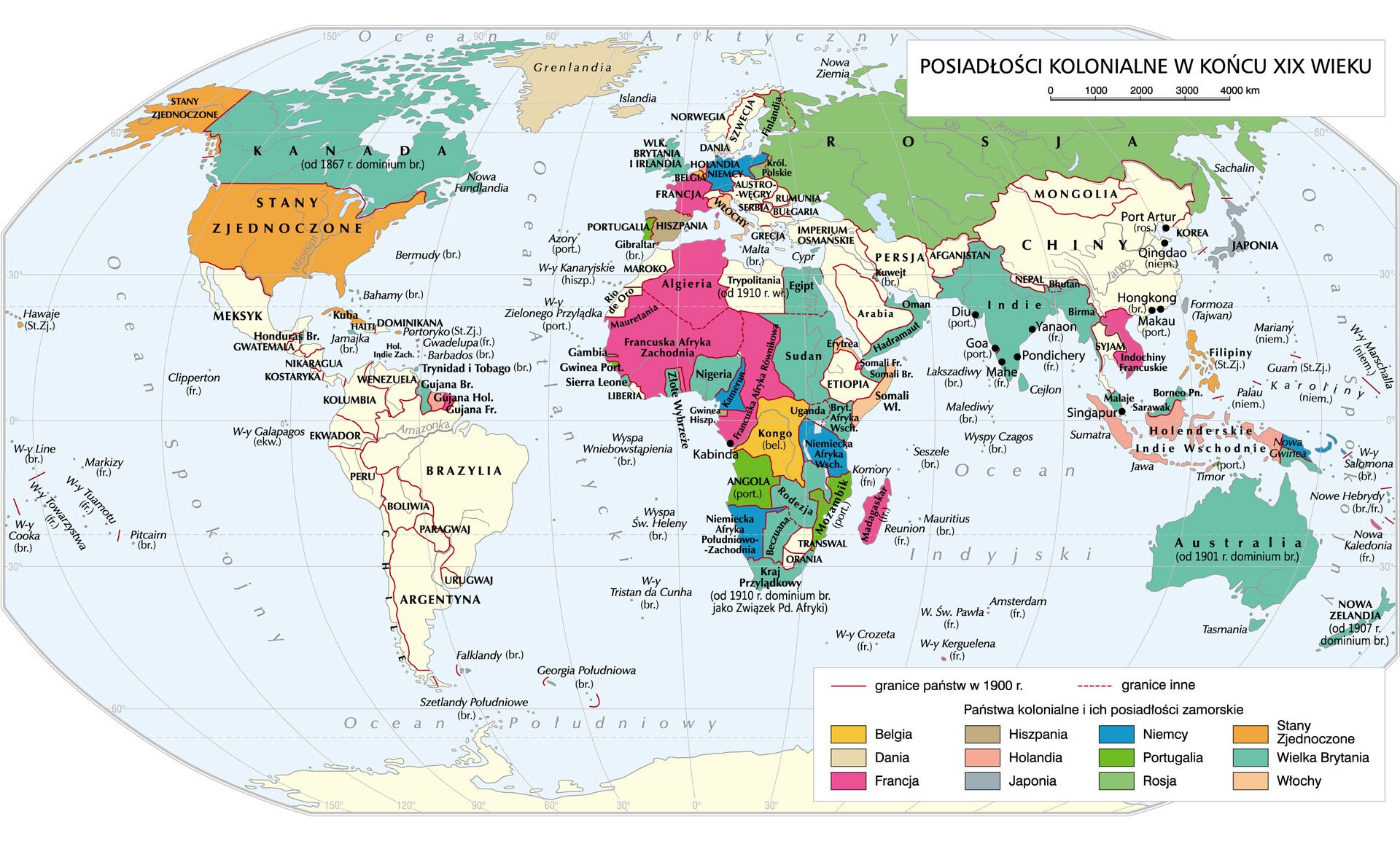
Look carefully at the maps below and tell how the countries' dominance around the world was changing. Which of them were the greatest powers in the 16th century and which in the 19th century?
Three biggest colonial empires at the beginning of the 19th century were:
- The Netherlands
- Germany
- Spain
- France
- Great Britain
- Portugal
They lost their position at the end of the 19th century:
- Germany
- Spain
- France
- Great Britain
- Portugal
They expanded their conquests:
- The Netherlands
- Germany
- Spain
- France
- Great Britain
- Portugal
Which country became a new colonial state at the end of the 19th century?
- The Netherlands
- Germany
- Spain
- Great Britain
Which country was the biggest colonial empire at the end of the 19th century?
- The Netherlands
- Germany
- Spain
- Great Britain
- Portugal
Point out the the most colonised continents in the 19th century.
- Asia
- Africa
- Australia
- North America
- South America
Familiarize yourself with the illustration and learn more about the British colonial empire
Opinions about colonisation were and are different. They often depend on the interests of the person who delivers them. Match the following effects of colonisation accordingly.
road and rail construction, the need to bear the cost of maintaining the colony, inflow of resources, education and health care development, destruction of local culture, political and military power, exploitation of the population, robbery
| Positive for colonies | |
|---|---|
| Positive for colonial powers | |
| Negative for colonies | |
| Negative for colonial powers |
Tick the true sentences.
- Gold rush is the name of a tropical disease suffered by miners working in gold mines.
- The great geographical discoveries initiated a period called colonialism.
- The discoverer of Australia's east coast was James Cook.
- Germany became a colonial state at the end of the 19th century.
- Belgium had colonies in South America and Asia.
- Colonies brought considerable economic benefits to their metropolises.
- Europeans Christianised all conquered lands.
- White settlers and natives had the same rights in colonies.
Keywords
colonialism, geographical discoveries, colonial empires
Glossary
Colonies – posiadłość państwa, która znajduje się poza jego granicami, ale bezpośrednio mu podlega.
Colonialism – polityka podbojów i przejmowania państw słabo rozwiniętych przez rozwinięte gospodarczo. Jej której celem było utrzymanie w zależności siebie tych krajów i wykorzystywanie ich zasobów ludzkich i surowcowych.
Dominion – terytorium państwa, w ramach imperium brytyjskiego, mające charakter pośredni między samorządną kolonią a niezależnym państwem. Status dominium oznaczał najwyższy stopień autonomii, które mogło osiągnąć terytorium w ramach Wielkiej Brytanii.
Native – osoba należąca do rdzennej grupy ludności zamieszkującej dany obszar, np. Aborygeni w Australii.
Gold rush – gwałtowny napływ dużej liczby osób chcących szybko się wzbogacić na tereny gdzie odkryto złoto lub inne szlachetne kruszce, np. diamenty, srebro. Przyczyniała się do zasiedlania nowych terenów, np. Australii.
Physical map – potoczna nazwa mapy hipsometrycznej (ukształtowania terenu). Przedstawia ona morza i lądy, ich ukształtowanie terenu oraz znajdujące rzeki, lasy, pustynie itp.
Political map – mapa tematyczna, której głównym celem jest pokazanie państw i terytoriów od nich zależnych. Przeważnie nie przywiązuje się na nich uwagi do uwarunkowań geograficznych terenu.