Precipitation of sediment pt 1
that salts are a group of ionic chemical compounds, composed of cations of metals and anions of an acid radical;
that there are salts which dissolve in water and those which are sparingly soluble or practically insoluble in water;
that based on the solubility table it can be determined whether ions present in the solution will react with each other, a chemical compound that is sparingly soluble in water.
to predict whether mixing of substances that undergo dissociation will (or will not) create a sparingly soluble compound;
to explain what the precipitation reaction is;
to present chemical equations for precipitation using molecular, complete ionic and net ionic formulas.
What does the precipitation reaction consist of?
Before you watch the movie, formulate the research question and hypothesis.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film pokazuje eksperyment. Problem badawczy: Porównanie przebiegu reakcji chlorku sodu z azotanem pięć potasu i azotanem pięć srebra jeden. Hipotezy: Chlorek sodu reaguje z obiema solami. Chlorek sodu nie reaguje z żadną z podanych soli. Chlorek sodu reaguje tylko z azotanem pięć potasu. Chlorek sodu reaguje tylko z azotanem pięć srebra jeden. Będziesz potrzebować: probówki, roztwory soli: chlorku sodu, azotanu pięć potasu i azotanu pięć srebra jeden. Instrukcja: Do dwóch probówek wlej takie same objętości (po około dwa–trzy centymetry sześcienne roztworów soli: do pierwszej – azotanu pięć srebra jeden, a do drugiej – azotanu pięć potasu. Do każdej z nich dodawaj kroplami jednakową objętość (pół centymetra sześciennego) roztworu chlorku sodu.
Comparison of the reaction of sodium chloride with potassium nitrate and silver(I) nitrate.
Select one of the presented hypotheses and then verify it.
Sodium chloride reacts with both salts.
Sodium chloride does not react with any of the salts.
Sodium chloride reacts only with potassium nitrate.
Sodium chloride reacts only with silver(I) nitrate.
test tubes,
solutions of the following salts: sodium chloride, potassium nitrate and silver(I) nitrate.
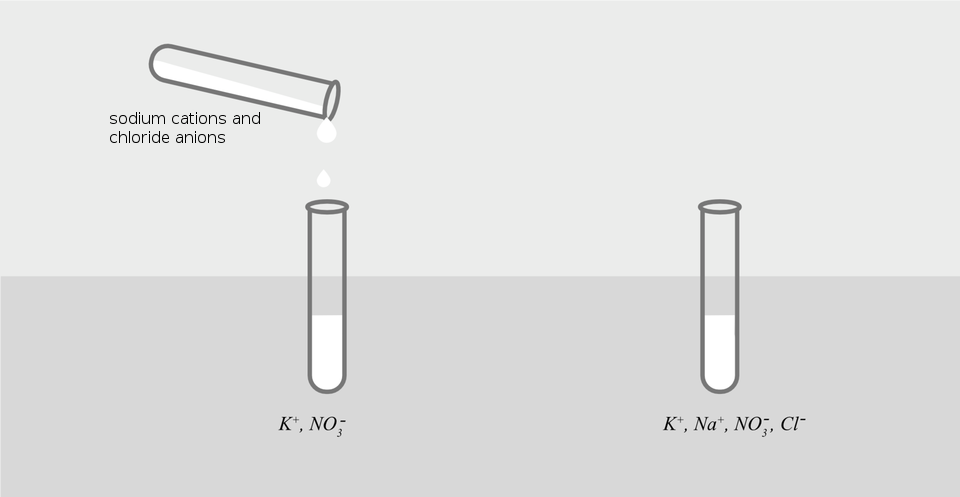
Pour the same volume of salt solutions (approx. 2–3 cmIndeks górny 33 each) into two tubes: silver(I) nitrate into the first tube and potassium nitrate into the second one.
Drop by drop, add the same volume (0.5 cmIndeks górny 33) of the sodium chloride solution to each of them.
Observe the changes that occur.
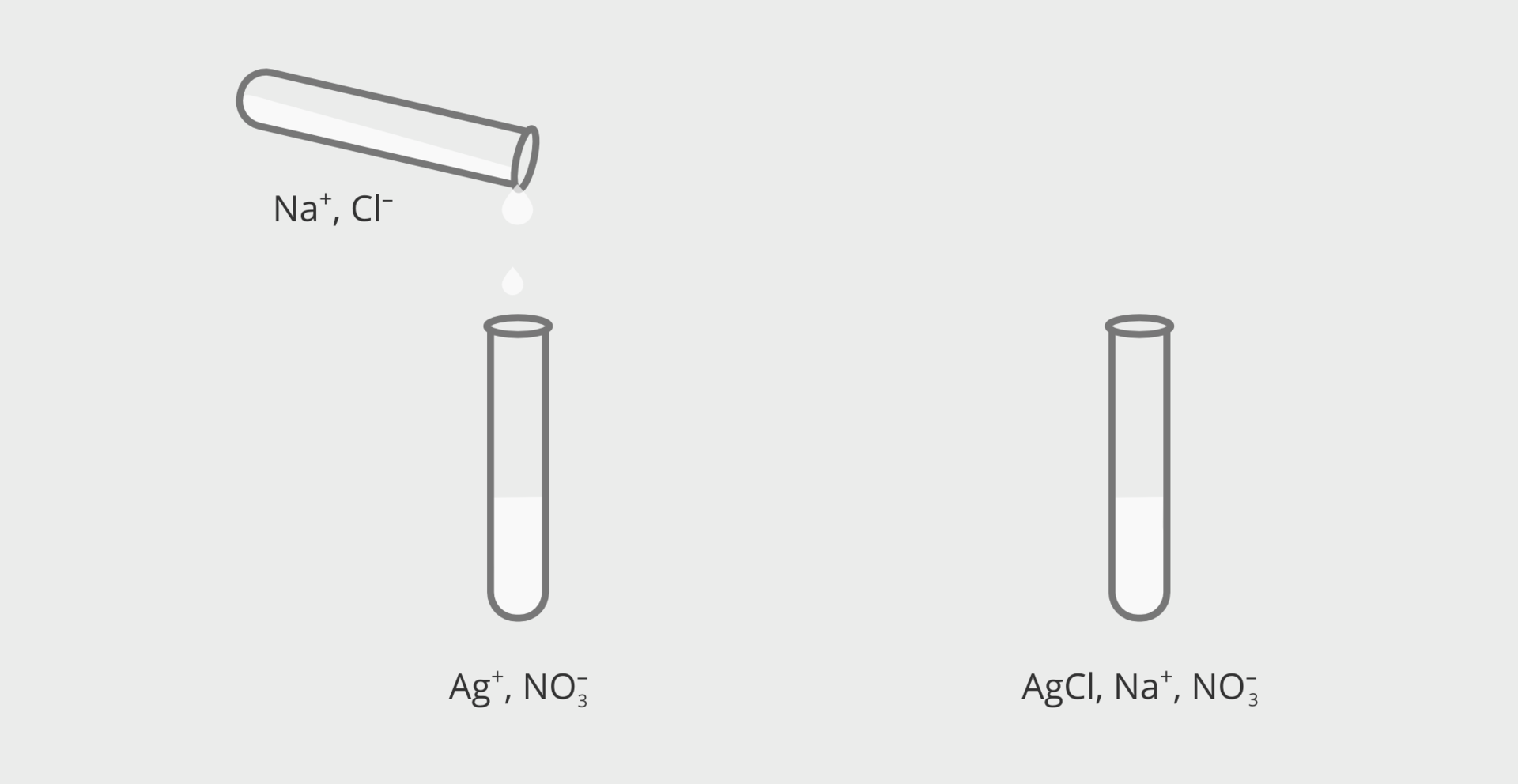
A white sediment (precipitate) appears in the tube containing silver(I) nitrate after adding the sodium chloride solution. After adding this salt to the potassium nitrate solution, no changes are visible.
Water‑soluble salts decompose into ions as a result of the process of electrolytic dissociation. When you mix the solutions of two salts, such as silver(I) nitrate and sodium chloride, the solution contains ions next to each other: . Two of them, , will form a salt that is practically water‑insoluble – silver(I) chloride. This salt precipitates from the solution in the form of sediment. In the chemical equation, this fact is indicated by an arrow pointing downwards, placed after the salt formula:
When potassium nitrate and sodium chloride are mixed together, the resulting solution will contain ions: . None of them form together insoluble compounds, therefore the solution after mixing is homogeneous.
A reaction in which a sparingly soluble compound is formed after mixing together the solutions of two soluble substances is called a precipitation reactionprecipitation reaction. Its essential element is the reaction between some ions formed from dissociation of the substances mixed together.
How do we describe a precipitation reaction?
We can present a precipitation reaction in various ways. It will be discussed using the example of the reaction taking place in experiment 1. As you remember, as a result of the reaction of silver nitrate with sodium chloride, silver(I) chloride was precipitated in the form of sediment. This transformation can be described with a chemical equation in molecular form, i.e. containing molecular formulas of compounds:
You remember that the above reaction takes place in an aqueous solution, and the substrates used for the experiment are soluble in water and occur in it in the form of ions. Two of them joined together to form a chemical compound that is sparingly soluble in water. In the equation, we can include the form in which substances occur during the reaction:
You already know that this way of expressing a chemical equation, which includes the formulas of all ions present in the reaction mixture, is called a complete ionic equation. In a chemical equation presented in this way, we do not use arrows that symbolize the formation of sediment, because the method of writing (molecular formula for salt) already informs about the formation of a product that is sparingly soluble (no free ions).
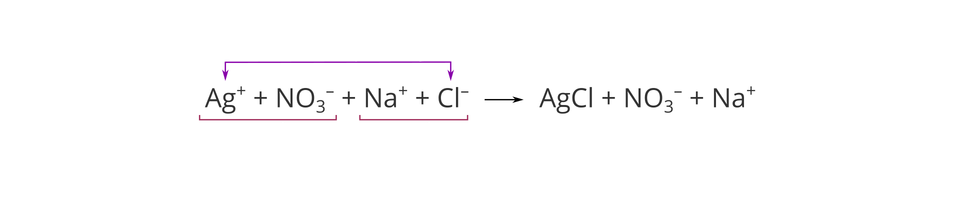
1. formation of sparingly soluble salt
2. silver(I) nitrate solution
3. sodium chloride solution
Note that there are identical ions on the sides of both substrates and products, and that the presented reaction happens only between two types of ions: silver cation and chloride anion. In the complete ionic equation, we can cross out recurring ions on both sides of it:
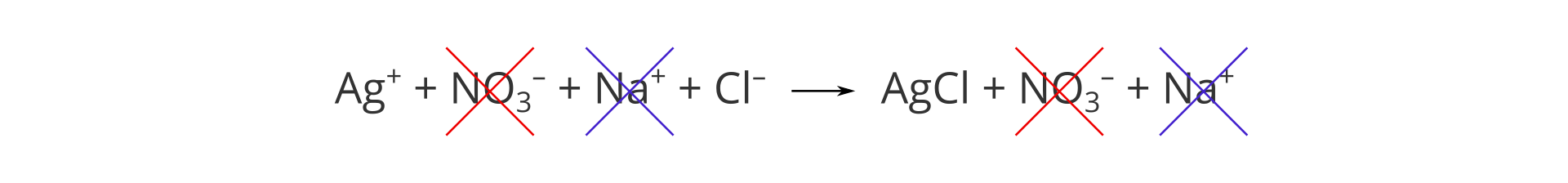
We can therefore write down an equation that contains only symbols of ions that react with each other:
This is a net ionic equation.
Can substances other than salts participate in precipitation reactions?
Do sodium hydroxide and copper(II) sulfate solutions react with each other? If so, what is the effect of this reaction?
Select one of the presented hypotheses and then verify it.
Sodium hydroxide and copper(II) sulfate solutions do not react with each other.
Mixing the two solutions: sodium hydroxide and copper(II) sulfate will result in a sparingly soluble compound (sediment will be precipitated).
test tubes,
solutions of the following substances: sodium hydroxide, copper(II) sulfate.
Pour 2–3 cmIndeks górny 33 of the salt solution – copper(II) sulfate into a test tube.
Add the sodium hydroxide solution to it.
Observe the changes that occur.
A gelatinous blue gelatinous sediment (precipitate) was formed in the tube with the solution of copper(II) sulfate after the addition of the sodium hydroxide solution.
In the solutions of the substances used for the experiment, there were ions formed as a result of dissociation. In the salt solution, these were: cations of copper(II) and anions of sulfate . In the hydroxide solution, these were the following ions: cations of sodium and hydroxide anions .
After mixing the two solutions, copper(II) cations and hydroxide anions formed the sparingly water‑soluble copper(II) hydroxide:
The above reaction takes place between ions, so it can be described with the following complete ionic equation:
The net ionic equation for this reaction is as follows:

Complete the definition.
aqueous, sparingly soluble, is precipitated, ions
Precipitation reaction - a chemical reaction in an .................................. solution between .................................. from substances mixed together, resulting in the creation of a .................................. compound, which .................................. from the solution in the form of sediment
Complete the sentences.
solubility table, react with other salts and hydroxides, salt, Reactions between salts as well as between salts and hydroxides, produces sparingly soluble products, precipitation reactions, will combine into a compound that is sparingly soluble in water
Salts can ................................................................................................................................ in an aqueous solution, on condition that this reaction .................................................................................................................................
If there is a reaction between two salts, the sparingly soluble product is also a .................................................................................................................................
Reactions occurring in an aqueous solution between ions from two different substances, which together form a sparingly soluble compound, are called .................................................................................................................................
Precipitation reactions can be predicted on the basis of the ................................................................................................................................ by checking whether the ions that will be found in the solution after mixing of two soluble substances .................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................ are examples of an exchange reaction.
Chemical reaction taking place in an aqueous solution between the ions coming from the mixed substances, leading to the formation of a sparingly soluble compound that precipitates from the solution in the form of a sediment is called:
- precipitation reaction
- synthesis reaction
- sedimentation reaction
Conclusion
Salts can react with other salts and hydroxides in an aqueous solution, provided that this reaction produces sparingly soluble products.
If there is a reaction between two salts, the sparingly soluble product is also a salt.
Keywords
precipitation reaction, precipitation reaction of sediments, sediment, salt, hydroxide, salts and hydroxides solubility table
Glossary
reakcja strąceniowa – reakcja chemiczna zachodząca w roztworze wodnym między jonami pochodzącymi od zmieszanych ze sobą substancji, prowadząca do powstania trudno rozpuszczalnego związku, który wytrąca się z roztworu w postaci osadu