Solubility of substances
that a solution is obtained as a result of dissolution;
that the dissolution rate is influenced by mixing, fragmentation of the dissolved substance, increase of the temperature.
to list and discuss factors affecting the solubility of the substance.
Before you watch the movie „Are all substances dissolved in water to the same extent?”, write down the research question and the hypothesis. During the screening, pay attention to what happens to the dissolved substances. Write down the observations and conclusions.
1. In the same volume (mass) of water, dissimilar masses of different substances dissolve.
2. In the same volume (mass) of water, the same masses of different substances dissolve.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Eksperyment prezentujący roztwory nasycone i nienasycone. Do wykonania eksperymentu wykorzystane są: cukier, sól, siarczan sześć miedzi dwa, jodek potasu, bagietka, 4 zlewki z wodą. Laborant wsypuje do kolejnych zlewek cukier, sól, siarczan sześć miedzi dwa, jodek potasu i miesza każdą z substancji do momentu rozpuszczenia substancji w wodzie. Nie wszystkie substancje udaje się rozpuścić całkowicie. Na dnie zlewki z roztworem siarczanu sześć miedzi dwa pozostają nierozpuszczone kryształy.
Do the experiment „The influence of temperature on the dissolution of a solid in water on the example of sodium chloride”. Before doing the experiment, look at the research question and the hypothesis. During the show, pay attention to what happens to the dissolved substance. Write down the observations and conclusions.
Does the temperature affect the amount of solid (sodium chloride) that can be dissolved in a given volume of water?
The higher the temperature of the water, the more substance (sodium chloride) can be dissolved in it.
beakers,
burner (kettle),
ceramic plate,
water,
sodium chloride (NaCl).
Pour 10 cmIndeks górny 33 of water with varying temperature (e.g. 20 and 50°C) into two beakers.
Put 5g of sodium chloride into each of them.
Thoroughly mix the contents of both beakers.
Compare the amount of dissolved substance in water of different temperature.
Do the experiment “The influence of temperature on the dissolution of gases in water on the example of carbon dioxide”. Before doing the experiment, write down the research question and the hypothesis. During the show, pay attention to what happens to the gas bubbles in the beakers. Write down the observations and conclusions.
What effect does temperature have on the dissolution of gas in water?
Select one of the presented hypotheses and verify it.
The higher the water temperature, the less amount of gas dissolves in it (the amount of gas dissolved in water decreases with increasing temperature).
The higher the water temperature, the more amount of gas dissolves in it (the amount of gas dissolved in water increases with increasing temperature).
beaker,
room temperature water,
boiling water,
sparkling water cooled in the fridge,
sparkling water in room temperature.
Add the same volume of sparkling water cooled in the fridge (several dozen cmIndeks górny 33) to the three beakers of the same volume.
Into each of them, add the same volume of „normal” water in different temperature: to the first beaker – water cooled in a fridge, to the second beaker – water at room temperature, to the third beaker – water at temperature about 100°C (boiling water).
Observe the appearance of gas bubbles in the beakers. Compare the number of bubbles.
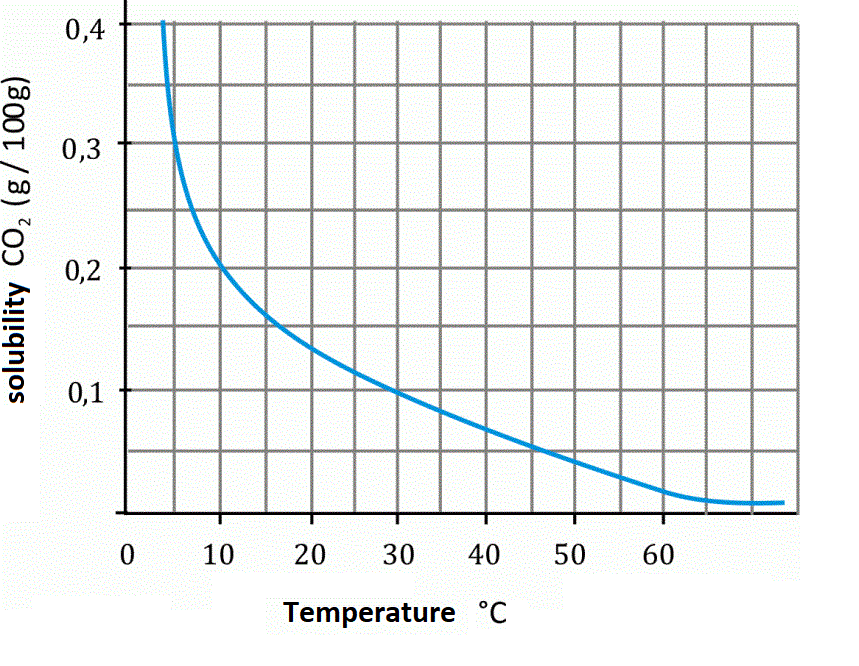
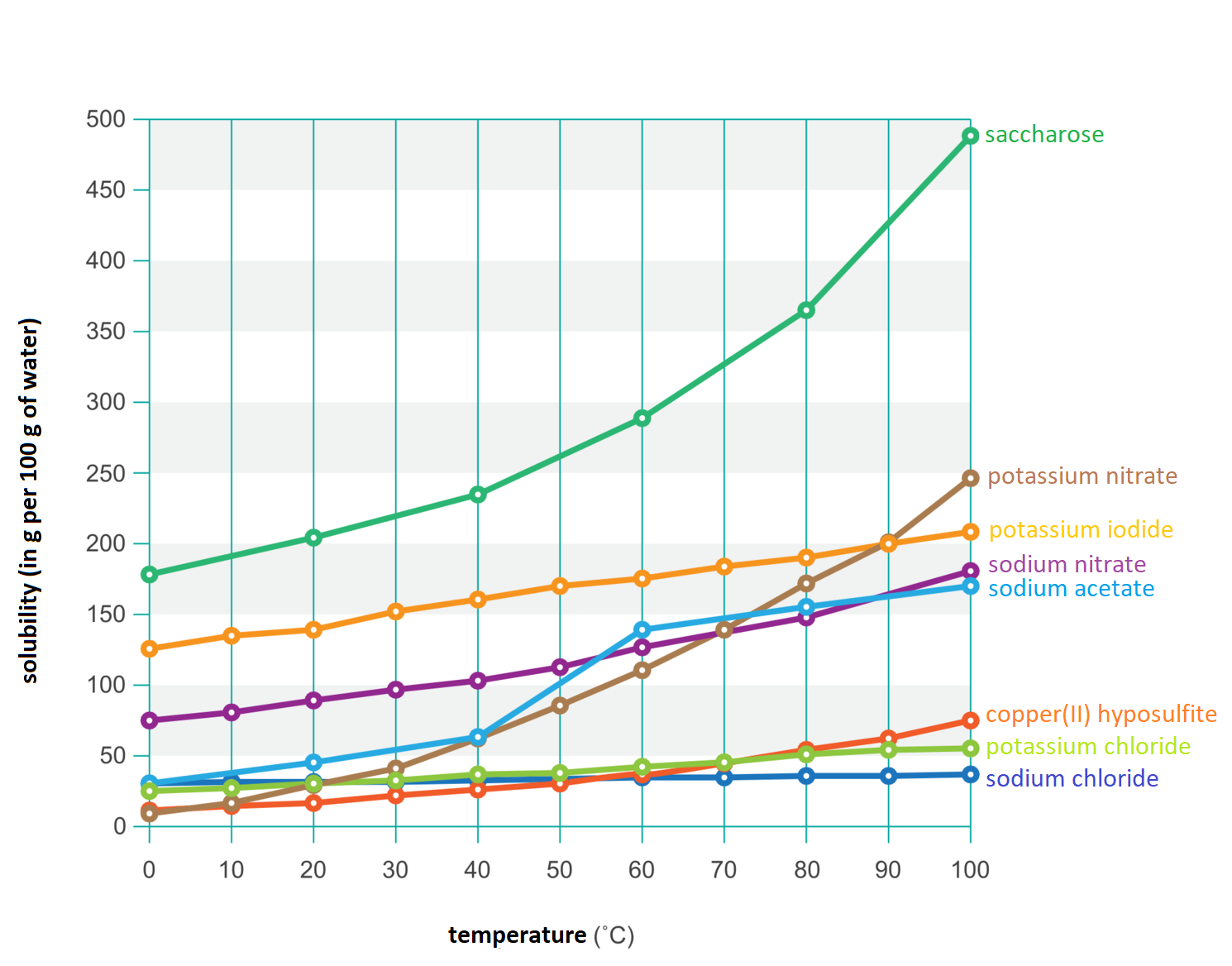
The amount of substance that can be dissolved in water depends on the temperature. In the case of gases, this quantity decreases with the increase of temperature, while for solids the amount generally increases.
Select the true sentences.
- The number of grams of substances that can be dissolved in 100 g of water to form a saturated solution at a given temperature is called the solubility of a given substance
- The dependence of solubility of substance on pressure is presented by means of a solubility curve
- With the drop of the temperature, the solubility of solids decreases and the solubility of gases increases
- The solubility of gases in water increases with increasing pressure
Group the factors affecting the solubility of the substance in water and the rate of dissolution of the substance
temperature, temperature, fragmentation of a solute, mixing, type of substance
| The solubility depends on: | |
|---|---|
| The rate of dissolution of a substance depends on: |
Summary
Different amounts of various substances dissolve in the same volume of water.
The amount of solid dissolved in water depends on the temperature and usually increases with the rise of temperature.
As the temperature rises, the amount of gas dissolved in the water decreases.
Keywords
Solubility, solvent, solute
Glossary
krzywa rozpuszczalności – wykres przedstawiający zależność rozpuszczalności danej substancji od temperatury
rozpuszczalność – określa maksymalną ilość substancji, jaka może rozpuścić się w 100 g rozpuszczalnika w danej temperaturze i pod stałym ciśnieniem
roztwór nasycony – roztwór, który w danej temperaturze zawiera maksymalną ilość substancji rozpuszczonej, a dodana kolejna do niej porcja substancji nie ulega rozpuszczeniu
roztwór nienasycony – roztwór, który w danej temperaturze nie zawiera maksymalnej ilości substancji rozpuszczonej i w którym można rozpuścić dodatkową porcję tej substancji
roztwór rozcieńczony – roztwór, który zawiera co najmniej kilkakrotnie mniej substancji rozpuszczonej niż roztwór stężony
roztwór stężony – roztwór, w którym ilość substancji rozpuszczonej jest taka sama jak w roztworze nasyconym lub niewiele mniejsza