Europe rebels. Revolutions of 1848 - Spring of Nations
the areas covered by revolutionary actions;
the most important events of the Spring of Nations;
the political demands of the Spring of Nations, the achievements of its participants and the causes of its failure.
In the years 1848‑1849, revolutionary riots called the Spring of Nations took place all over Europe (except for Russia and Great Britain). In France, as a result of the French RevolutionRevolution of 1848, the monarchy was overthrown and the Second Republic was established. Its president was Louis Napoleon Bonaparte. Within the area of the Austrian Empire, there were riots on the streets of Vienna, while the Hungarians began their struggle for independence. Despite their efforts, they were pacifiedpacified by the Austrian and Russian armies. Revolutionary movements reached also the German and Italian countries, wherein both cases attempts were made to unite the nation into one state. Revolutionary activities occurred also on Polish lands. An uprising was caused by the residents of the Grand Duchy of Posen, as well as Cracow and Lviv. Both riots were suppressed, but thanks to them Polish people from Wielkopolska gained representatives at the Prussian estates, and the Austrian authorities carried out an enfranchisement reform in Galicia.
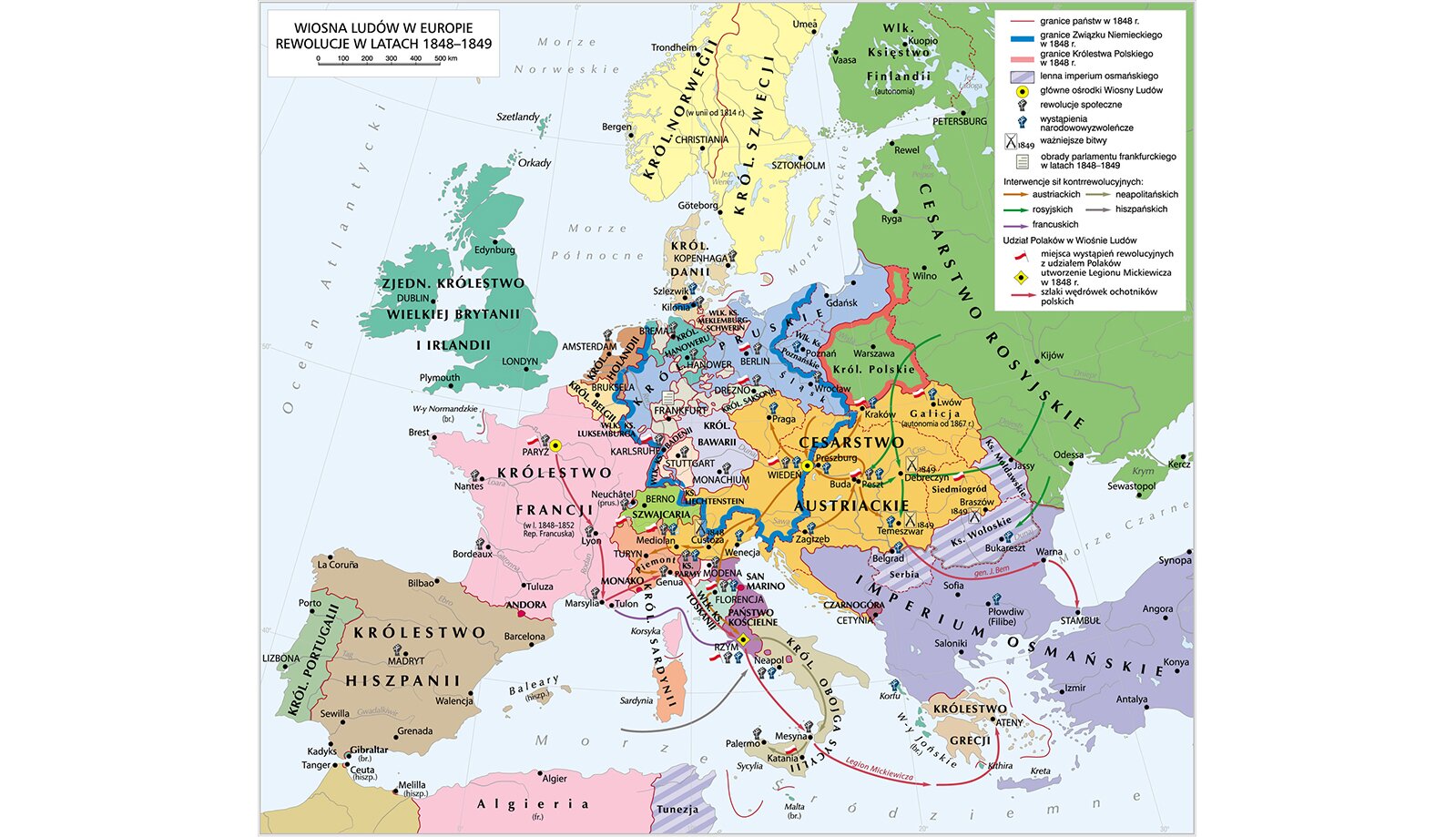
Look at the map of Europe in 1848-49. In which of the following states the revolutions of the Spring of Nations did not happen? Why?
- France
- Germany
- Great Britain
- Austria
- Russia
Familiarize yourself with the most important events of the Spring of Nations and organize your knowledge. Which of the events were the most important and why?
Fill the SWOT sheet in placing the following terms in correct fields.
Possibility of conducting liberal social-political reforms, Bloody suppression of activities (lives lost), Different nature of revolution in different countries, which hindered the trans-national cooperation., Simultaneous revolutionary actions on the European continent, Increase of the national awareness of people, Different interests of participants in the revolution (e.g. workers and bourgeoisie), Greater chances of success for reform supporters, Protests of numerous social groups against the order established during the Congress of Vienna., Fueling the nationality-oriented conflicts by the House of Habsburg within the territory of the Austrian monarchy, The rulers, surprised with the revolution, are more willing to make concessions, Repressions and return to the old system after the failure of revolution, Wide reform agenda, Threat to the position of monarchs, forcing them to make reforms, Cooperation of monarchs in suppression of revolutionary movements, Possibility to remove the remains of feudalism
| Strengths: | |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses: | |
| Opportunities: | |
| Threats |
Keywords
Spring of NationsSpring of Nations, proclamationproclamation, rebellion, pacificationpacification, revolution, abdicationabdication
Glossary
Wiosna Ludów – seria zrywów rewolucyjnych i narodowych w Europie w latach 1848–1849.
abdykacja – zrzeczenie się władzy przez panującego
proklamacja – ogłoszenie czegoś, obwieszczenie
pacyfikacja – brutalne tłumienie buntów i powstań narodowych siłą zbrojną
Święte Przymierze - sojusz zawarty w 1815 roku po zakończeniu wojen napoleońskich przez Imperium Rosyjskie, Królestwo Prus i Cesarstwo Austriackie. Z czasem dołączyły do niego kolejne państwa. Celem sojuszu była obrona ustaleń kongresu wiedeńskiego oraz przeciwdziałanie ruchom rewolucyjnym.
detronizacja - pozbawienie urzędującego władcy tronu, najczęściej za pomocą siły.
rewolucja - gwałtowna i znacząca zmiana ale także zbrojne wystąpienie społeczeństwa mające na celu obalenie istniejącej władzy.