Major vegetation types
what the relation between the illumination of Earth”s surface and the diversification of environmental conditions is;
what climate zones are found on Earth;
how atmospheric circulation and general azonal factors affect the availability of water in various parts of the planet;
what the characteristic features of each climate type is and how climate types differ from one another.
about some types of vegetation found on Earth;
to show major vegetation types on the map of the world;
to name the altitudinal zones of the Tatra Mountains.
The factors affecting the occurrence of different types of vegetation on Earth are: climate, availability of water, terrain and soil type. This is why vegetation varies depending on the climate zone, climate type and even on the conditions prevalent in a specific area. In each vegetation region, you can find characteristic forms of vegetation as well as their distinct local subtypes.
Descriptions of vegetation regions of the world
Major vegetation types
Tropical forest
- Climate: hot and humid all year round
- Examples of plants: palms, orchids, lianas, banana trees, tree ferns, mangroves
- Examples of animals:
gorillas, hippopotamuses, hummingbirds, chameleons, piranhas, butterflies
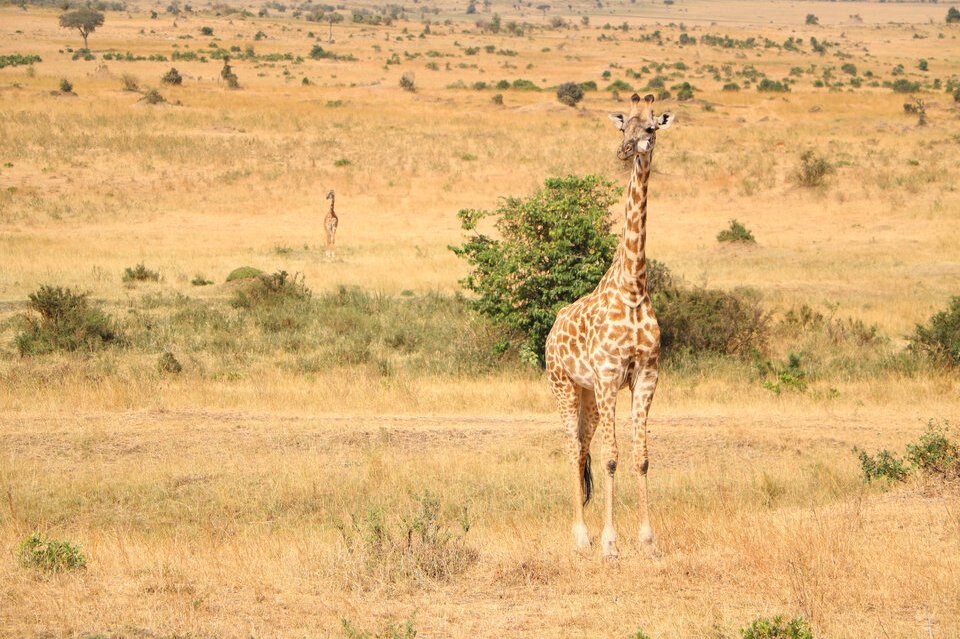
Savannah
- Climate: hot all year round but with two distinct seasons: dry and rainy
- Examples of plants: acacias, baobabs, eucalyptuses, thorny bushes, grasses
- Examples of animals: elephants, giraffes, antelopes, lions, hyenas, ostriches, vultures, snakes, grasshoppers, thermites
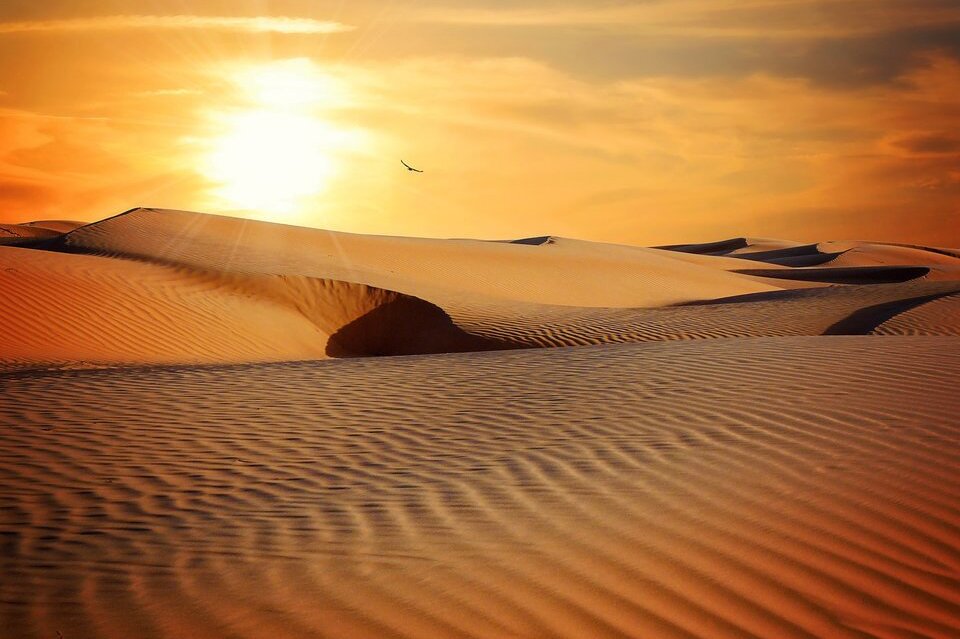
Hot deserts and semi-deserts
- Climate: hot during the day and cold at night, little precipitation only in summer
- Examples of plants: agaves, stonecrops, cacti, aloes, date palms in oases
- Examples of animals: camels, gerbils, lizards, rattlesnakes, scorpions, ants, flies
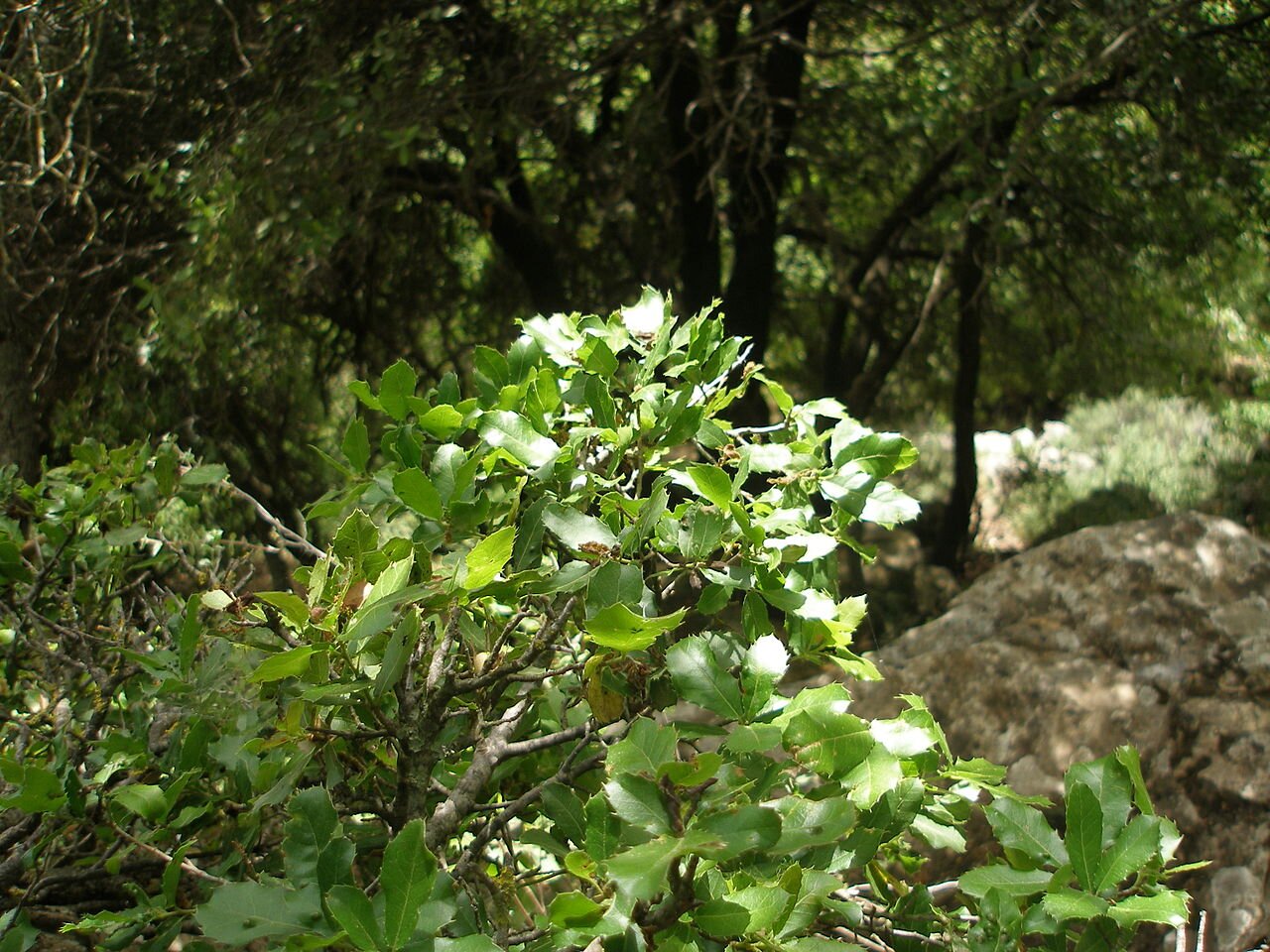
Mediterranean vegetation (maquis)
- Climate: hot and dry in summer, warm and rainy in winter
- Examples of plants:cedars, kermes oaks, wild olive trees, pistachio trees, myrtle, heath, cypress, juniper, laurel, lavender
- Examples of animals: fallow deer, mouflons, porcupines, bats, flamingoes, geckos, turtles
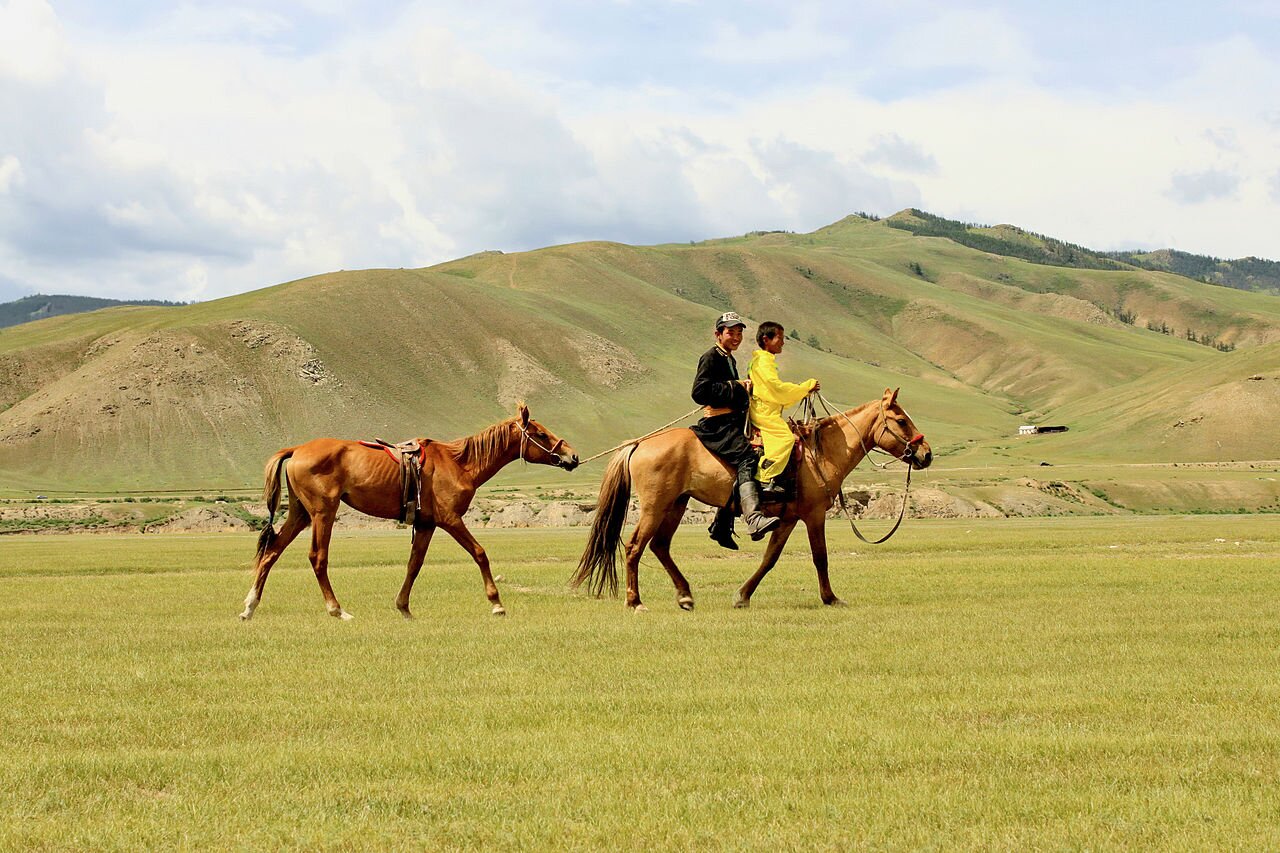
Steppes and cold deserts
- Climate: hot and dry summers, frosty winters
- Examples of plants: grasses, wormwood, hyacinths, tulips, garlic
- Examples of animals: saiga antelopes, donkeys, shrews, ground squirrels, bobak marmots, quails, bustards, locusts
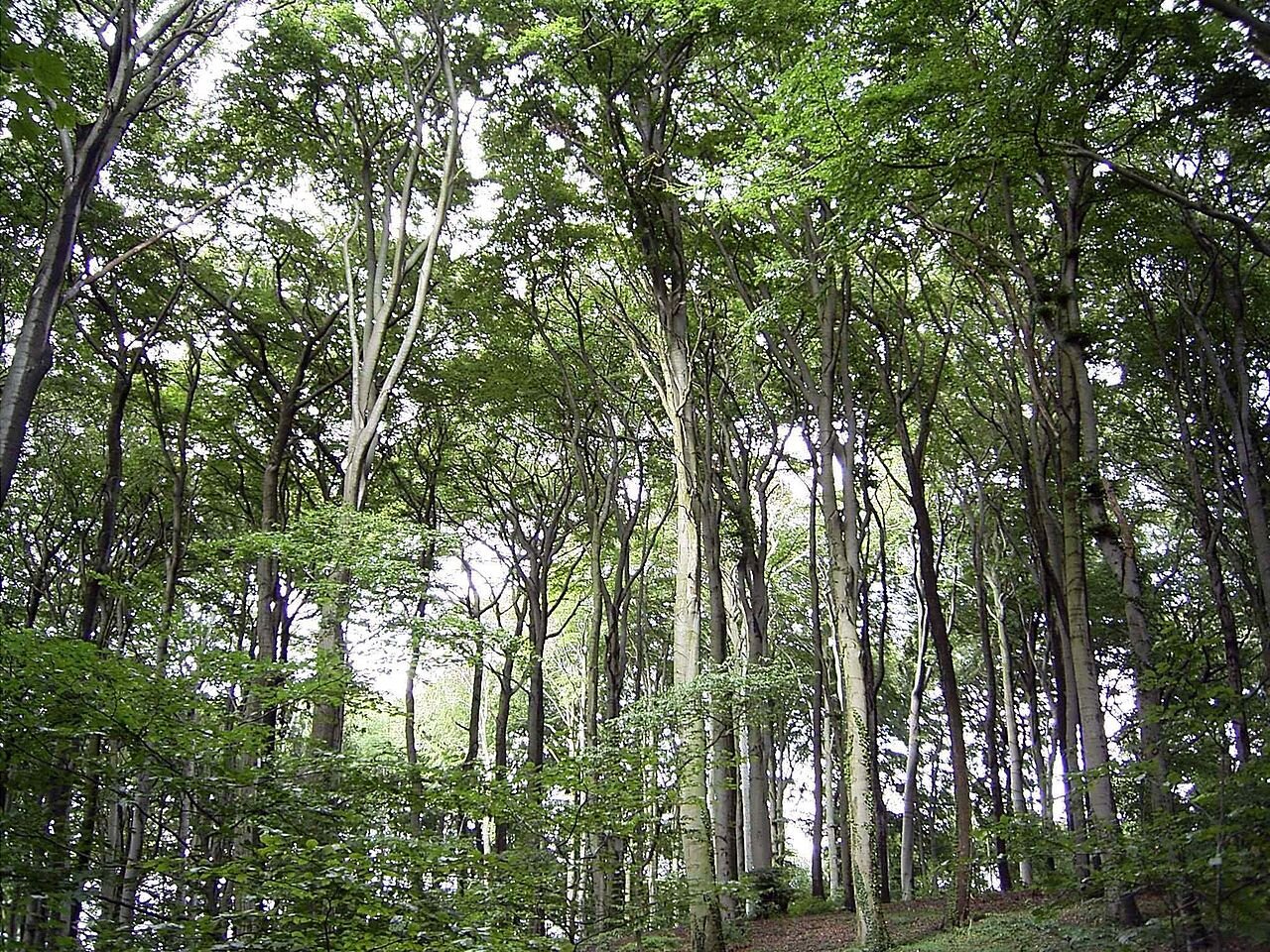
Broadleaf and mixed forest
- Climate:warm and rainy summers, cool and humid winters
- Examples of plants: beech, oak, maple, lime tree, ash, pine
- Examples of animals: wisent (European bison), roe deer, deer, boars, wolves, storks, sparrows
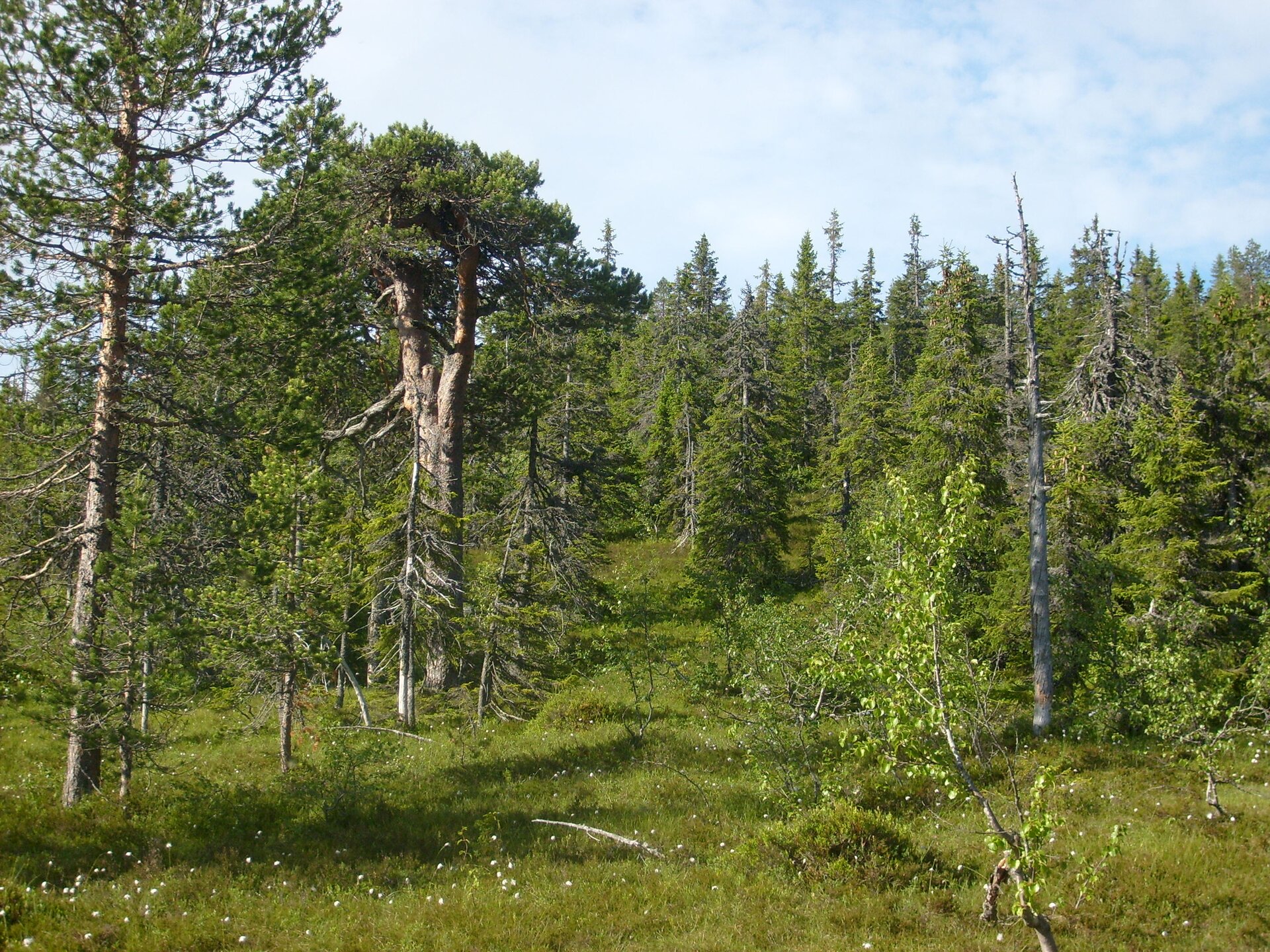
Taiga
- Climate: short, warm summers and frosty winters
- Examples of plants: pine, spruce, fir, larch, yew, birch, alder, juniper, moss
- Examples of animals: elks, bears, wolves, foxes, stoats, tits, waxwings, mosquitoes
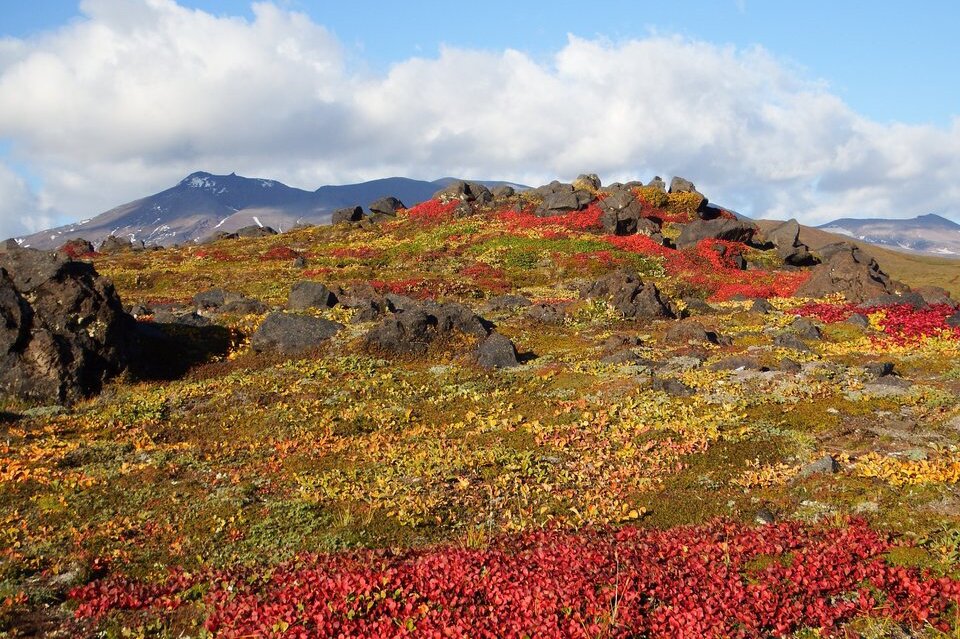
Tundra
- Climate: very short, cool summers and long, frosty winters
- Examples of plants: dwarf birch, dwarf willow, heather, bilberries, reindeer lichen
- Examples of animals: reindeer, wolves, arctic foxes, mountain hares, lemmings, buzzards, ptarmigans, snowy owls
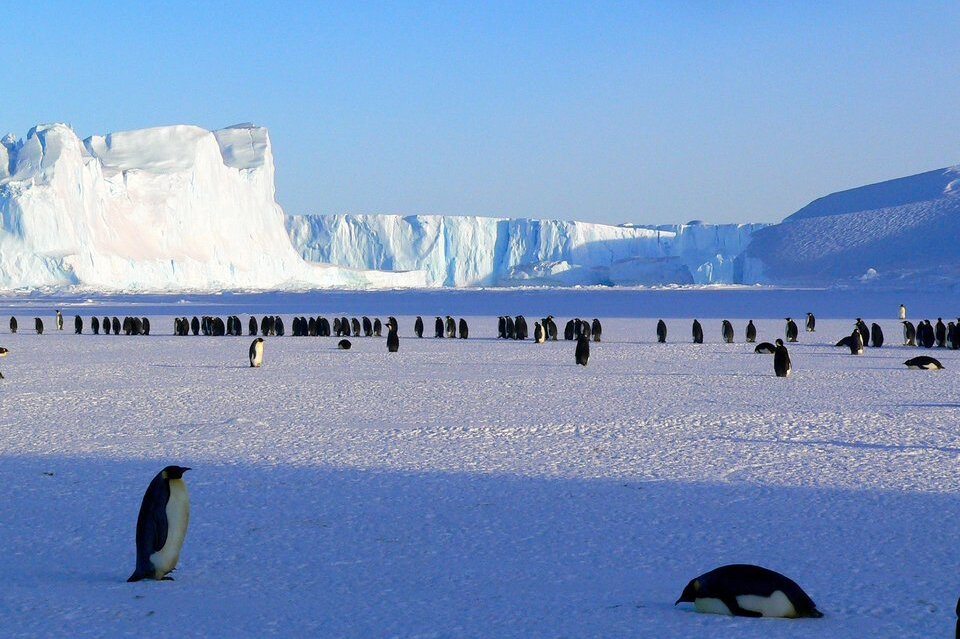
Arctic and Antarctic desert
- Main Climate:freezing all year long with very short and cool summers occurring only in coastal areas
- Examples of plants: moss, liverwort, very rarely grasses
- Examples of animals: The Arctic: polar bears, walruses, seals The Antarctic: penguins, elephant seals, seals
Vegetation regions of the Earth are shown on the map below.
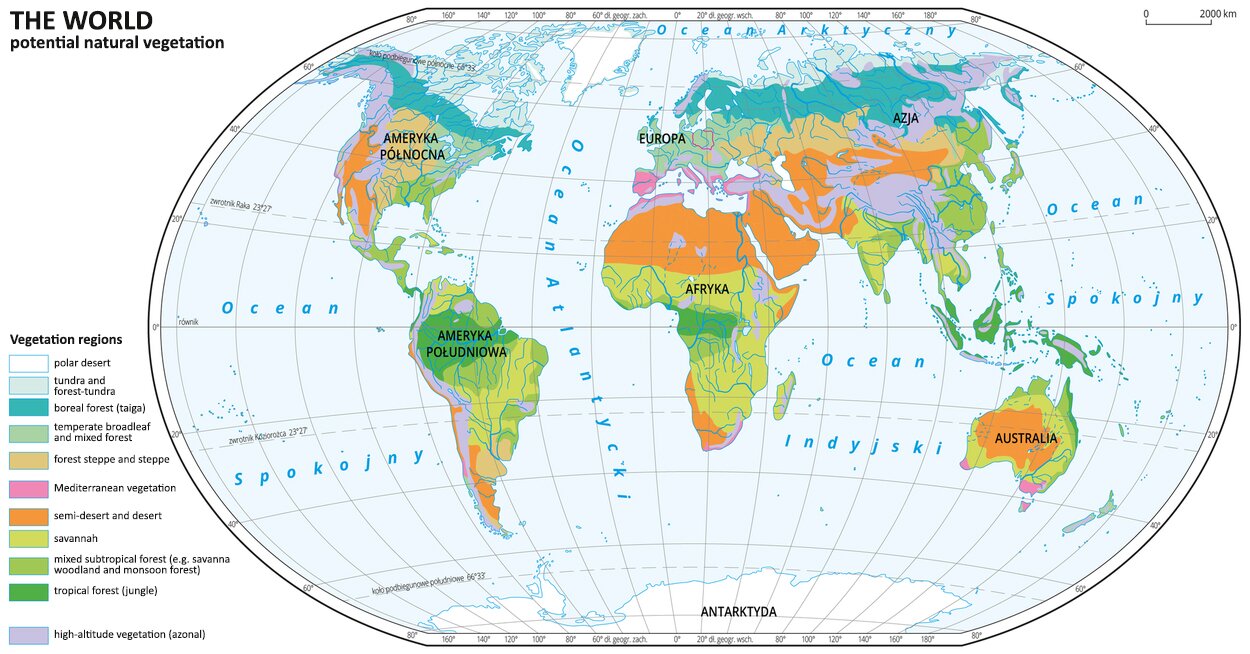
The climat of the environment is sometimes called vertical zonation due to the arrangement of floors in order resembling the arrangement of landscape zones (climatic and soil‑plant). Apart from desert and polar areas, where there is almost no vegetation in the mountains, in other zones, for example in the temperate zone, similarities can be found between the lower regula and the deciduous and mixed forest zone, between the upper regla floor and the taiga zone, between the mountain pine and halls and the tundra, and between the crags and the outskirts of the ice desert.
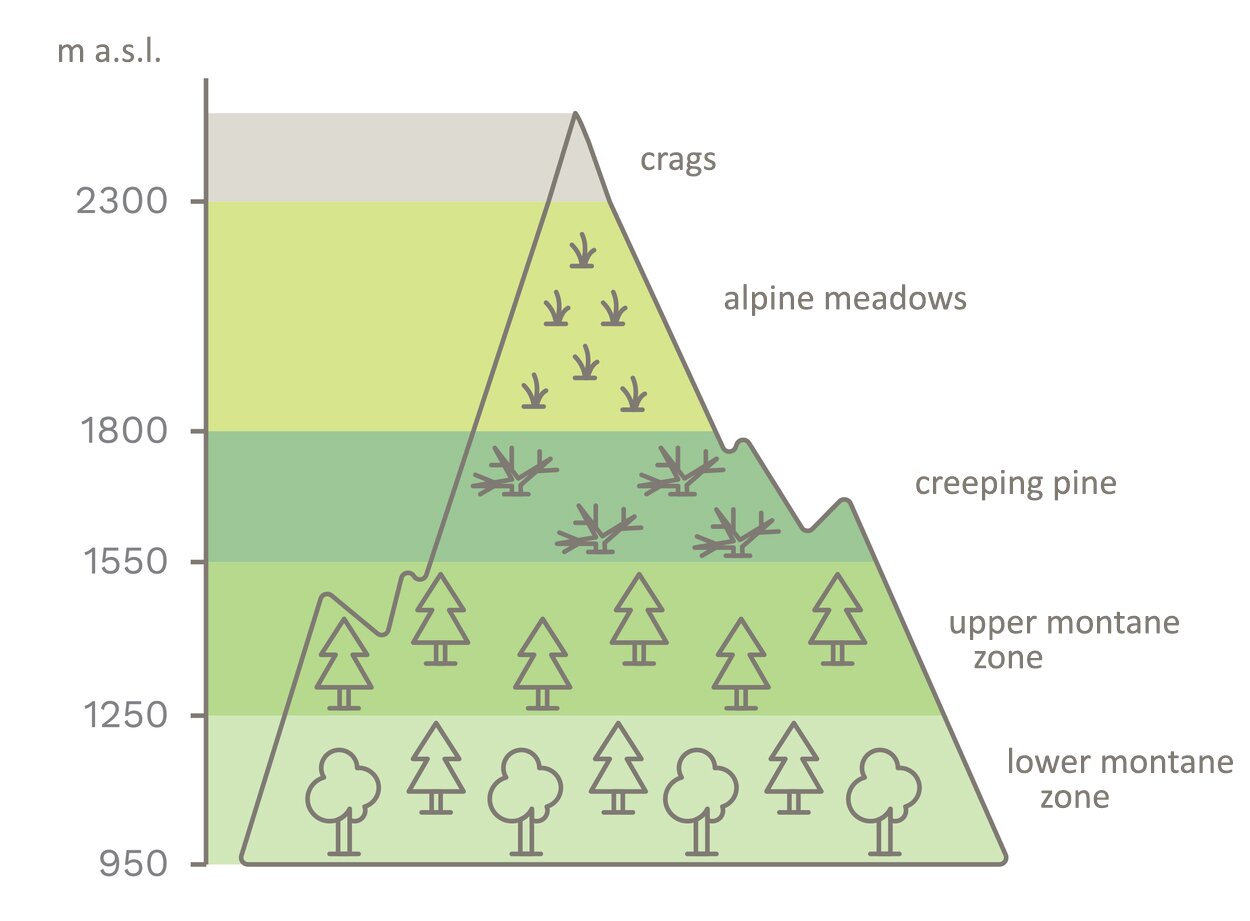
Put the images showing the altitudinal zones of the Tatra Mountains in the correct order, starting with the highest one.
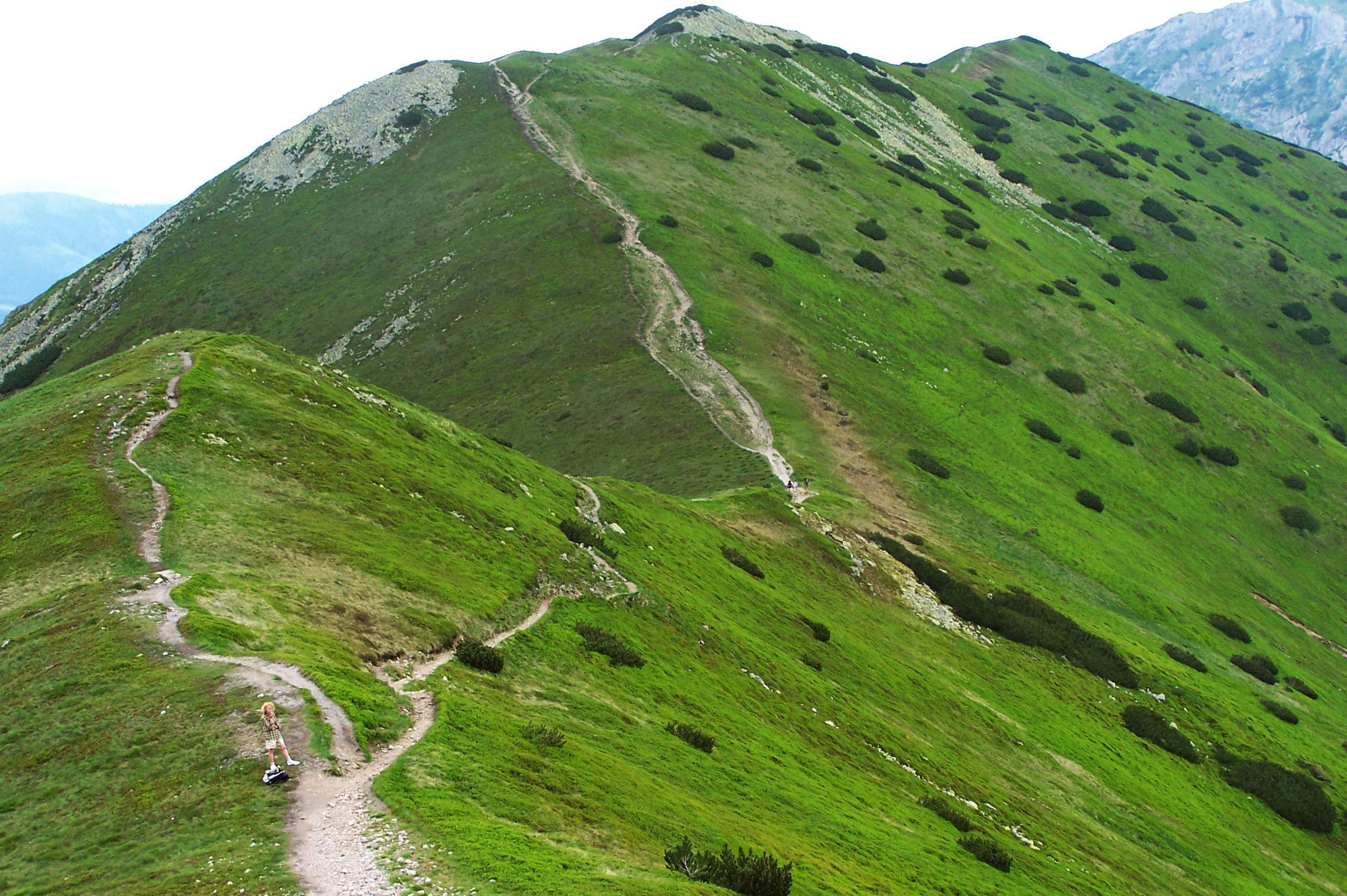
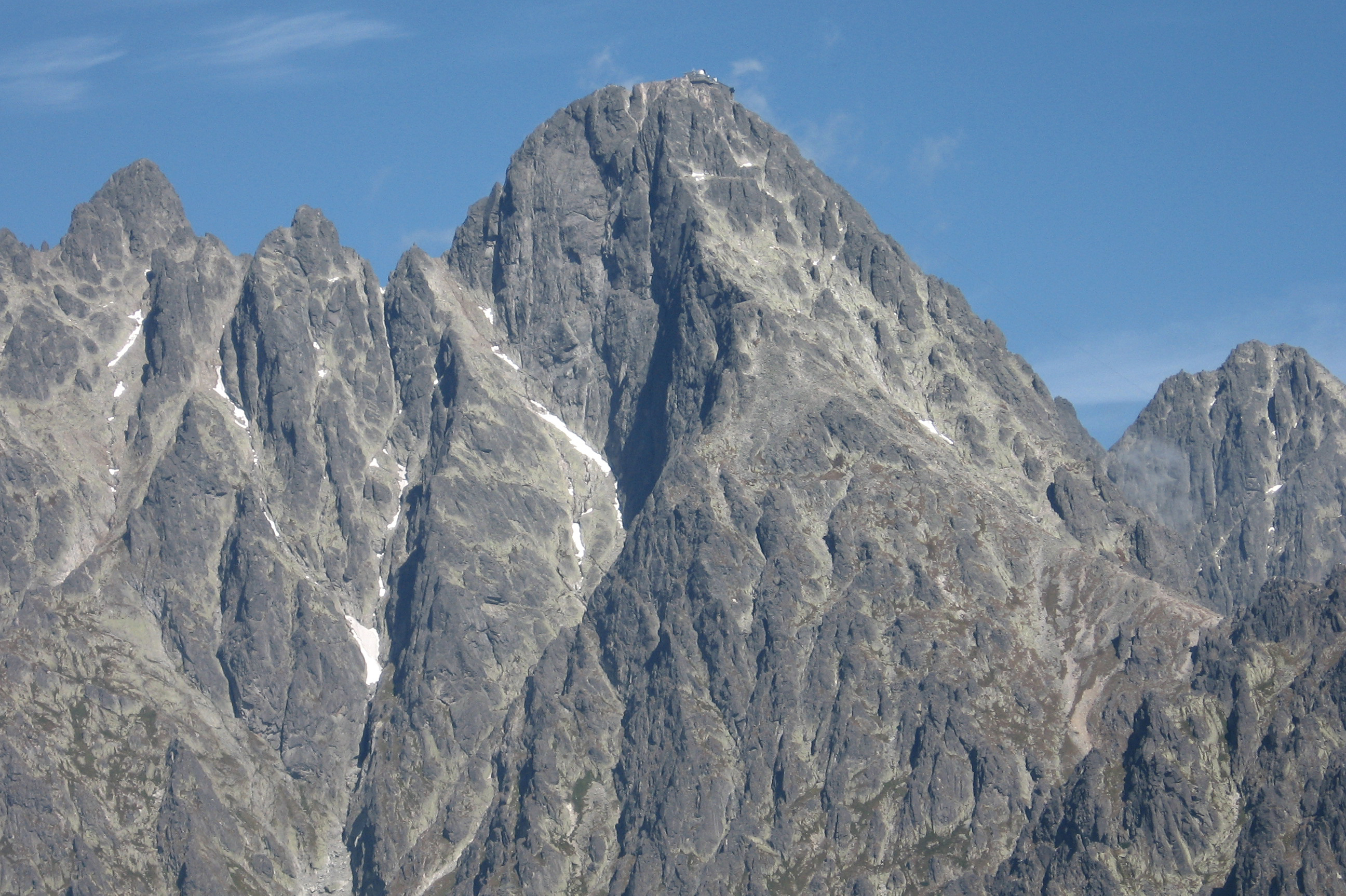





Summary
The lighting zones of the Earth and the associated climate zones influenced the formation of plant zones.
Geographical factors cause that there are also astrephic plant formations.
Variability of climatic, water and terrain conditions together with altitude means that plant floors can be distinguished in the mountains.
Keywords
altitudinal zones, lower montane zone, upper montane zone, Tatra Mountains, plant zones
Match the pairs: English words with Polish definition.
piętro w górach, powyżej piętra hal, obszar stromych ścian skalnych i głazów, łąki wysokogórskie w wysokich partiach polskich gór powyżej piętra kosodrzewiny; obszar, w którym występują, nazywany jest piętrem hal, piętro lasów iglastych występujące w górach powyżej regla dolnego, piętro lasów liściastych i mieszanych występujące w górach powyżej terenów uprawnych, gatunek drzewa (lub krzewu) iglastego, który tworzy piętro kosodrzewiny powyżej regla górnego, charakterystyczna dla wielu obszarów górskich zmienność roślinności wraz z wysokością nad poziomem morza, uwarunkowana występowaniem pięter klimatycznych, typ roślinności charakterystyczny dla danego obszaru; rośliny wchodzące w skład formacji roślinnej mają podobne wymagania w stosunku do gleby i klimatu, duży obszar z odrębną roślinnością przystosowaną do szczególnych warunków panujących w tej strefie
| vegetation type | |
| alpine meadows | |
| creeping pine | |
| altitudinal zones | |
| lower montane zone | |
| upper montane zone | |
| vegetation region | |
| crag |
Glossary
formacja roślinna – typ roślinności charakterystyczny dla danego obszaru; rośliny wchodzące w skład formacji roślinnej mają podobne wymagania w stosunku do gleby i klimatu
hale – łąki wysokogórskie w wysokich partiach polskich gór powyżej piętra kosodrzewiny; obszar, w którym występują, nazywany jest piętrem hal
kosodrzewina – gatunek drzewa (lub krzewu) iglastego, który tworzy piętro kosodrzewiny powyżej regla górnego
piętra roślinne (piętra klimatyczno‑roślinne) – charakterystyczna dla wielu obszarów górskich zmienność roślinności wraz z wysokością nad poziomem morza, uwarunkowana występowaniem pięter klimatycznych
regiel dolny – piętro lasów liściastych i mieszanych występujące w górach powyżej terenów uprawnych
regiel górny – piętro lasów iglastych występujące w górach powyżej regla dolnego
strefa roślinna – duży obszar z odrębną roślinnością przystosowaną do szczególnych warunków panujących w tej strefie
turnie – piętro w górach, powyżej piętra hal, obszar stromych ścian skalnych i głazów







