Non-inherited variation
that genetic variation is brought about by sexual reproduction,
that some diseases are caused by DNA mutations.
to tell the difference between and provide examples of inherited and non‑inherited variation.
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie dźwiękowe abstraktu dotyczące zmienności dziedzicznej
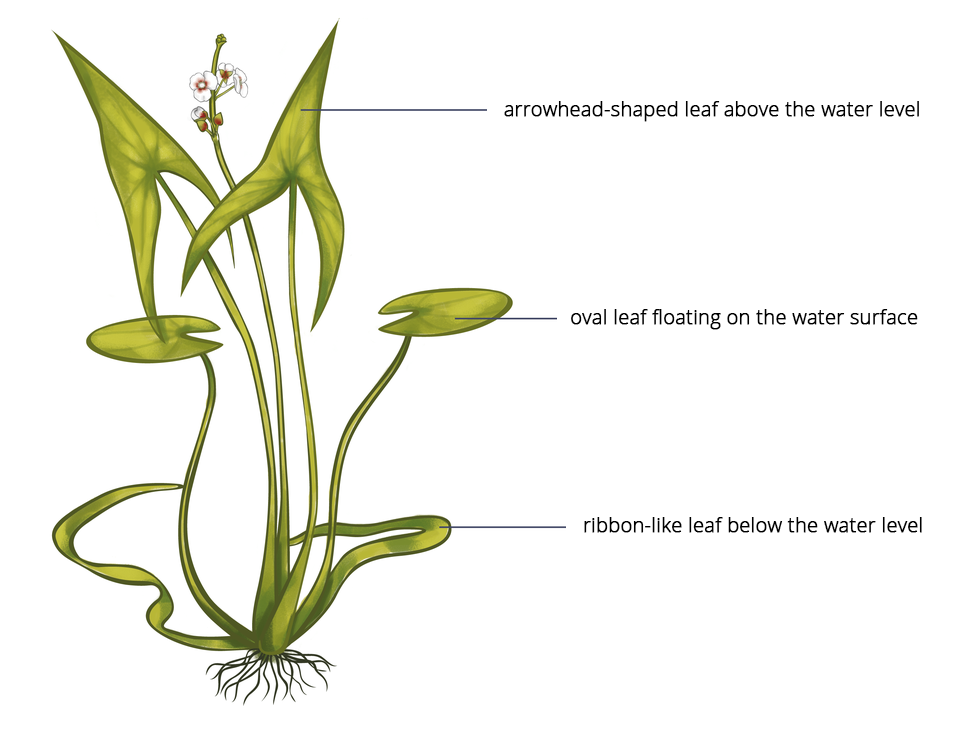
Apart from genetic variation, there is also non‑inherited variationnon‑inherited variation i.e. environmental variation. It accounts for all the changes in the organism’s phenotype during its lifespan that are caused by various external factors. These traits are not passed on to the offspring. One example of environmental variation is the heterophylly of the arrowhead plant (Sagittaria sagittifolia). The shape of its leaves is determined by its surroundings. The leaves of a fully submerged arrowhead are ribbon‑like, and those that grow above the water are arrowhead‑shaped.
When planting the seeds of an arrowhead plant with ribbon‑like leaves, the leaves of new generations will be ribbon‑shaped, oval‑shaped, arrow‑shaped or in all shapes, depending on the depth of the water reservoir.
Search the available resources for examples of non‑inherited variation of organisms other than those in the reader.
What is environmental variation? Select the correct answer.
- Inherited variation related to the fact that organisms better adjusted to a particular environment survive and pass their genes on to new generations
- Inherited variation related to the fact that two organisms of the same phenotype can have different genotypes
- Non-inherited variation related to the fact that organisms of the same species must change environment
- Non-inherited variation related to the fact that the environment causes diversity between specimens in a population
Categorise each element appropriately.
different shapes of arrowhead leaves, different habits of pines growing in two different areas of the same forest, different colours of pea plant flowers, different eye colour of people of different nationalities, different coat colour of puppies from the same litter, different number of teeth in adults, different body size of the queen bee and worker bees
| inherited variation | |
|---|---|
| non-inherited variation |
Indicate all the factors that may cause differences between specimens of the same potted plant obtained by dividing the parent plant.
- amount of light
- size of the flowerpot
- soil quality
- plant care
- genetic recombination
- somatic cell mutations
A remarkably large mouse specimen was bred in a laboratory. Match the potential determining factors of such a mouse phenotype with their descriptions.
access to the right nutrition, impact of DNA-altering substances, genes that determine the size of the adult specimen
| environmental factor | |
| genetic factor | |
| mutagenic factor |
Summary
Non‑inherited (environmental) variation accounts for all the changes in the organism’s phenotype during its lifespan that are caused by various external factors.
Keywords
environmental factor, non‑inherited variation, pine
Glossary
zmienność niedziedziczna – zróżnicowanie cech osobników jednej populacji zachodzące pod wpływem środowiska; nie jest dziedziczona