Physical phenomenon and chemical transformation
that the substances have specific physical properties;
we divide substances into simple (elements) and complex (chemical compounds);
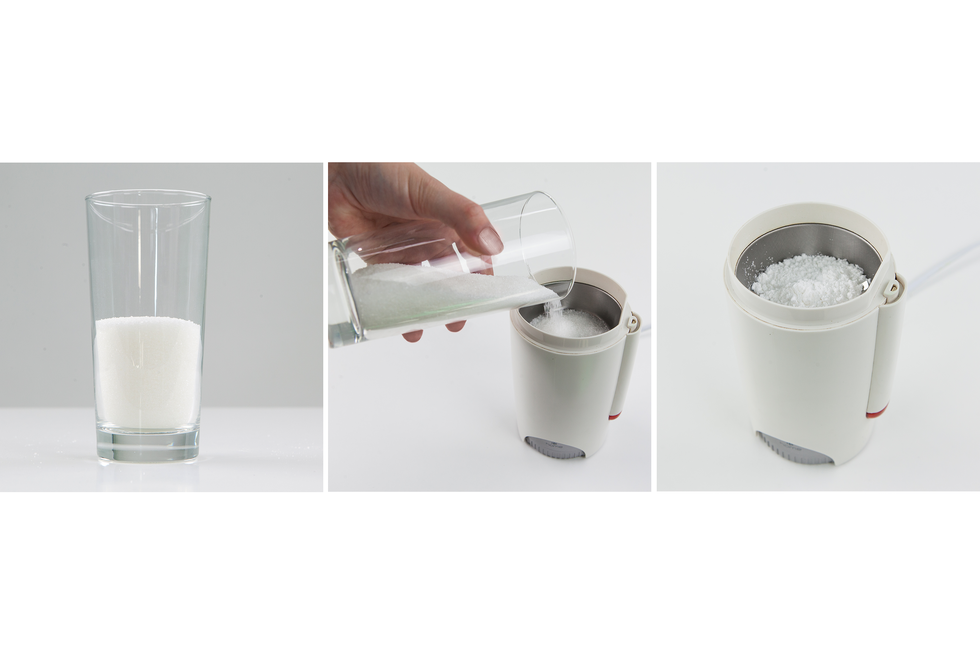
substances can be mixed together to form homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures;
mixtures can be separated into components.
to describe the differences between physical phenomenon and chemical transformation;
to give examples of physical phenomena and chemical transformations taking place in the human environment;
to design and perform a simple experiment illustrating physical phenomena and chemical reactions;
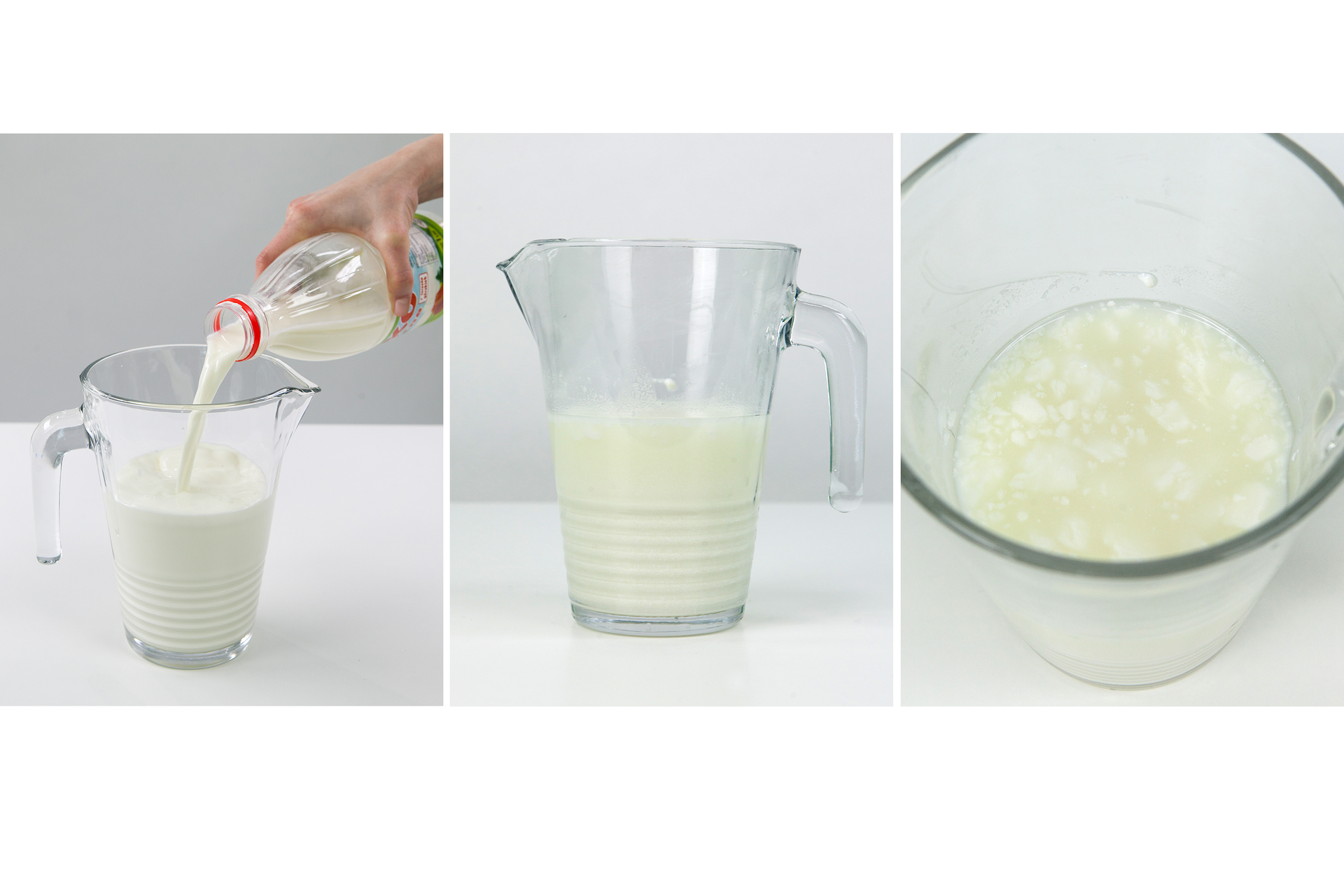
What transformation is associated with a change in the physical properties of a substance?
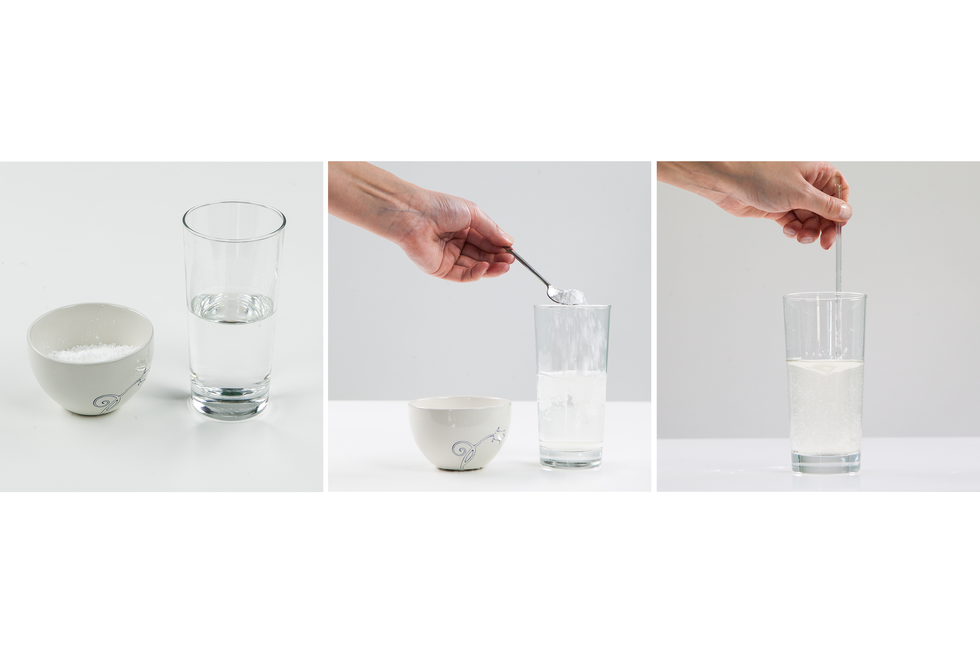
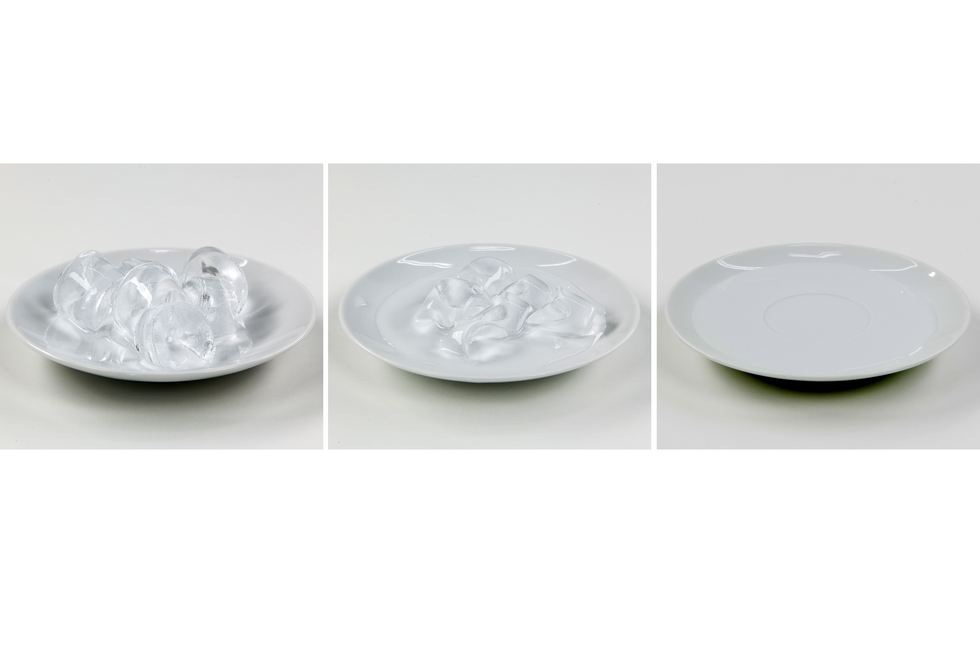
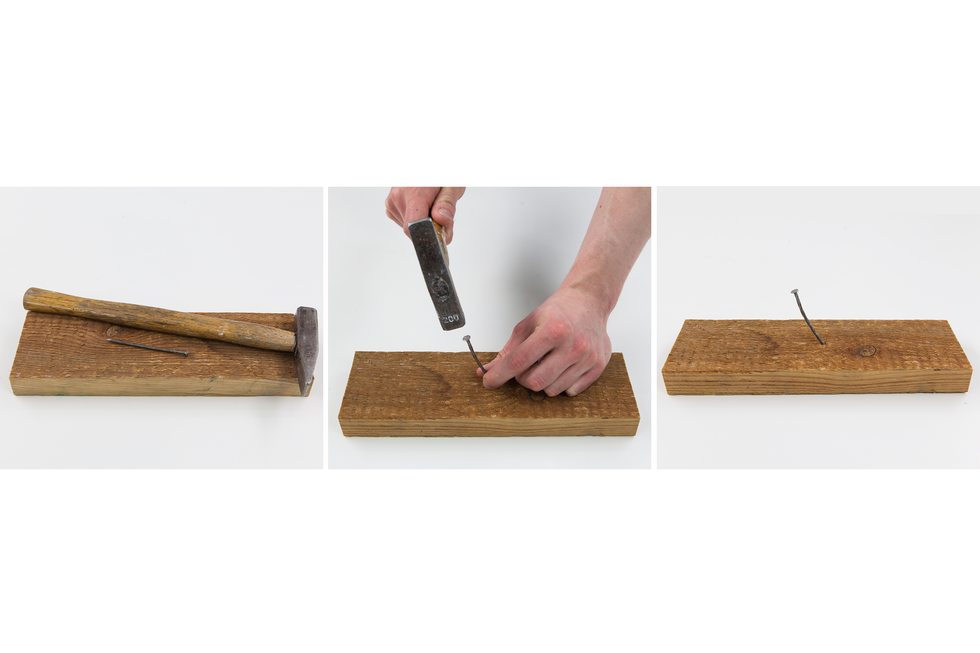
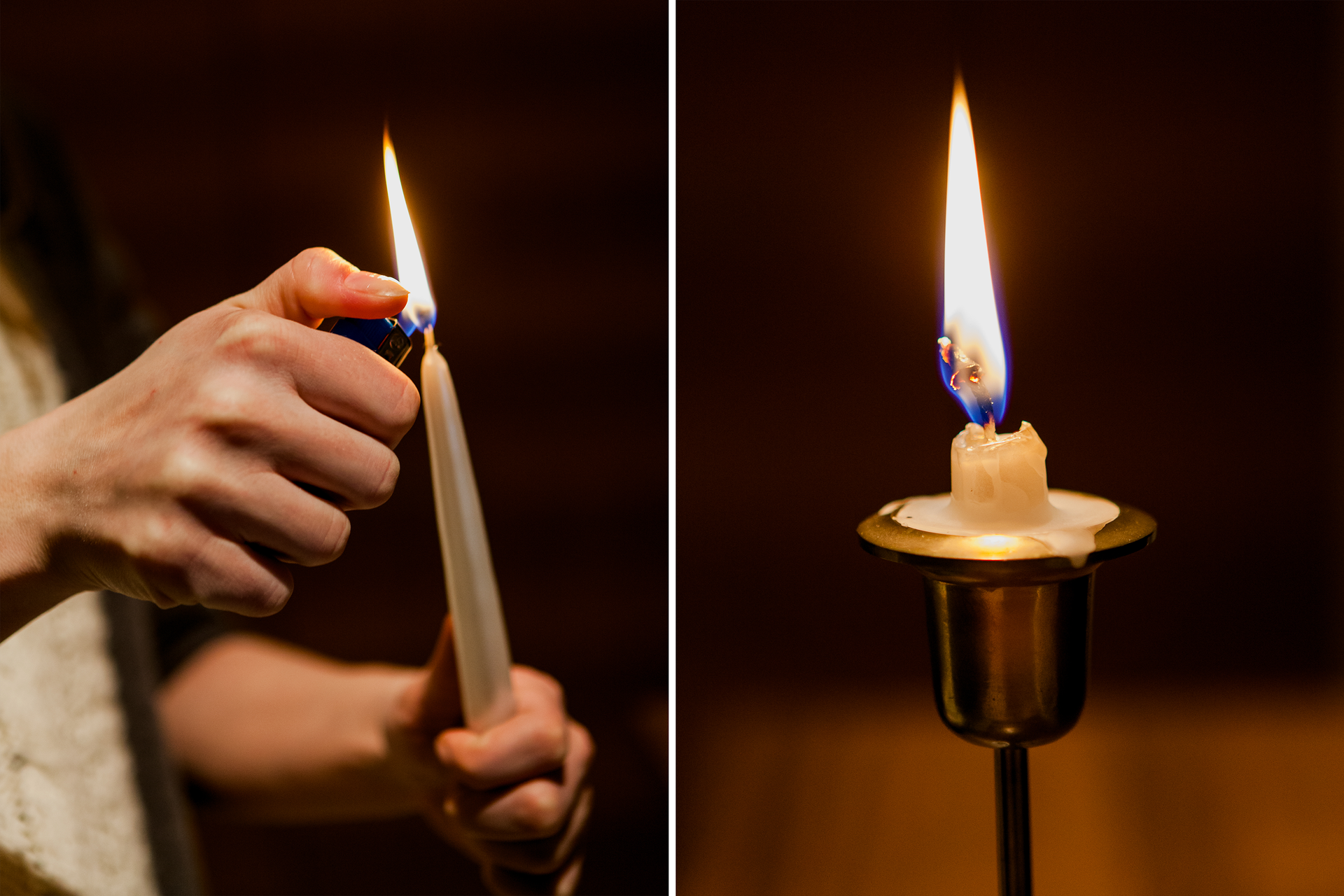
In our environment we can observe many tranformations in which the physical properties of matter change, but not itself. An example of this is freezing of water. The ice that is produced as a result of this process is not a new material but still water. As a result of the temperature decrease, only physical state (physical property) of the substance changes. Such process, as a result of which matter only changes its physical properties, we call physical transformationphysical transformation or physical phenomenonphysical phenomenon.
Before watching the movie “Obtaining plastic sulfur”, formulate a research question and hypothesis. Write down your observations and concluding remarks.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Prezentacja przedstawia eksperyment, polegający na otrzymywaniu siarki plastycznej. Do przeprowadzenia tego eksperymentu potrzebujemy: siarki, szpatułki, palnika, zlewki z zimną wodą oraz uchwytu do probówki. Probówkę z siarką umieszczamy nad palnikiem. Siarka z żółtego koloru staje się brązowa. Zawartość probówki wlewamy do wody. Wyciągamy z wody plastyczną substancję.
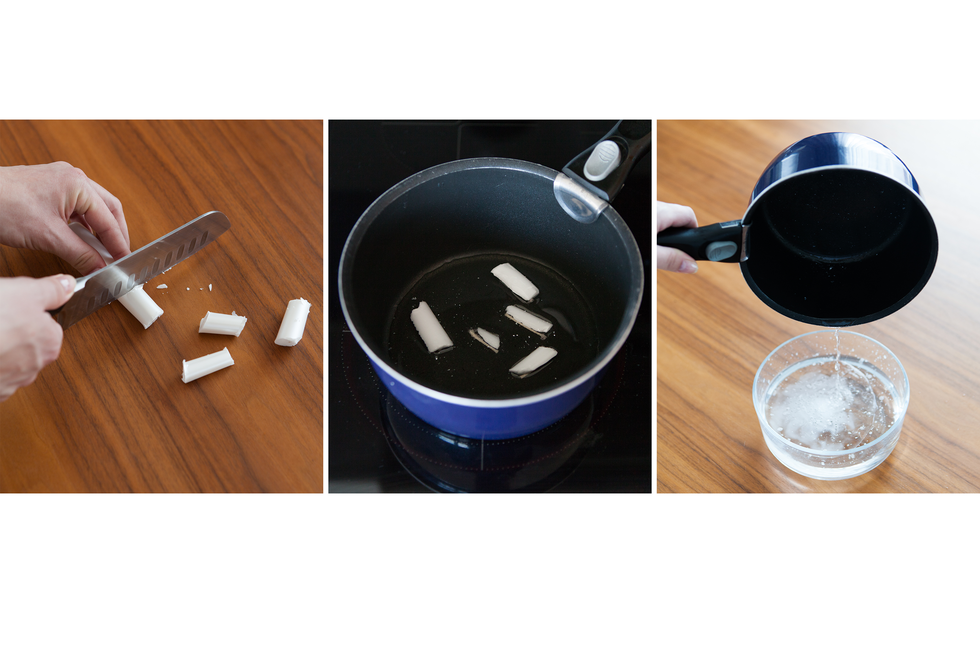
What transformation (physical or chemical) occurs when heating and then cooling down sulfur?
Sulfur subjected first to high and then low temperature undergoes physical transformation.
heat‑resistant test tube,
burner,
wooden clamp for test tubes,
a teaspoon,
beaker,
sulfur.
Fill the tube with a sulfur of its height.
The contents of the tube should be gently warmed in the flame of the burner until the sulfur for the second time obtains a smooth consistency.
With vigorous movement pour over liquid sulfur into a beaker filled halfway with cold water.
When the sulfur has cooled down, take it out using a glass rod and put it on a watch glass. Using glass rod examine the plasticity of sulfur – try to stretch it, bend it, etc.
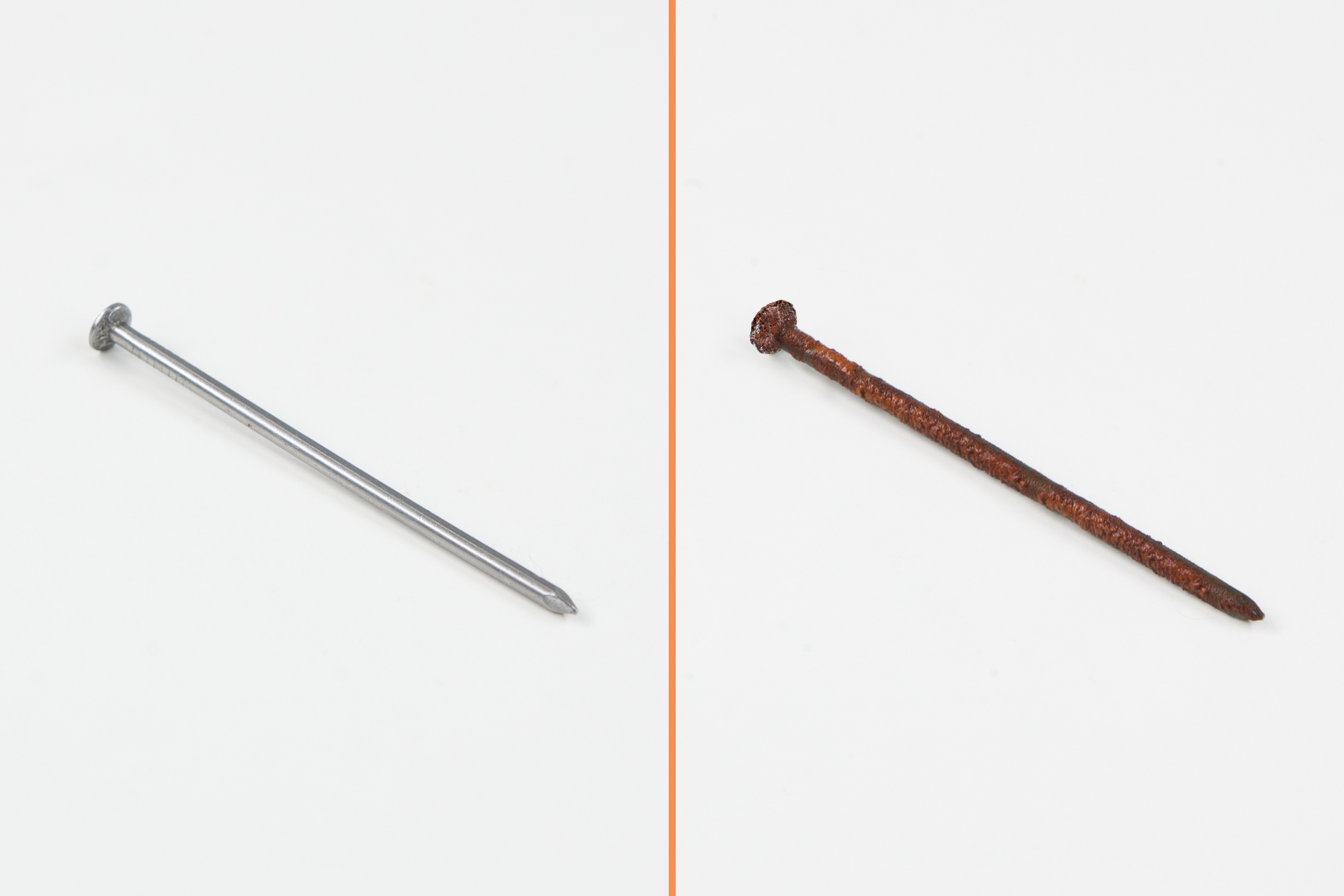
What transformations make one substance transform into another?
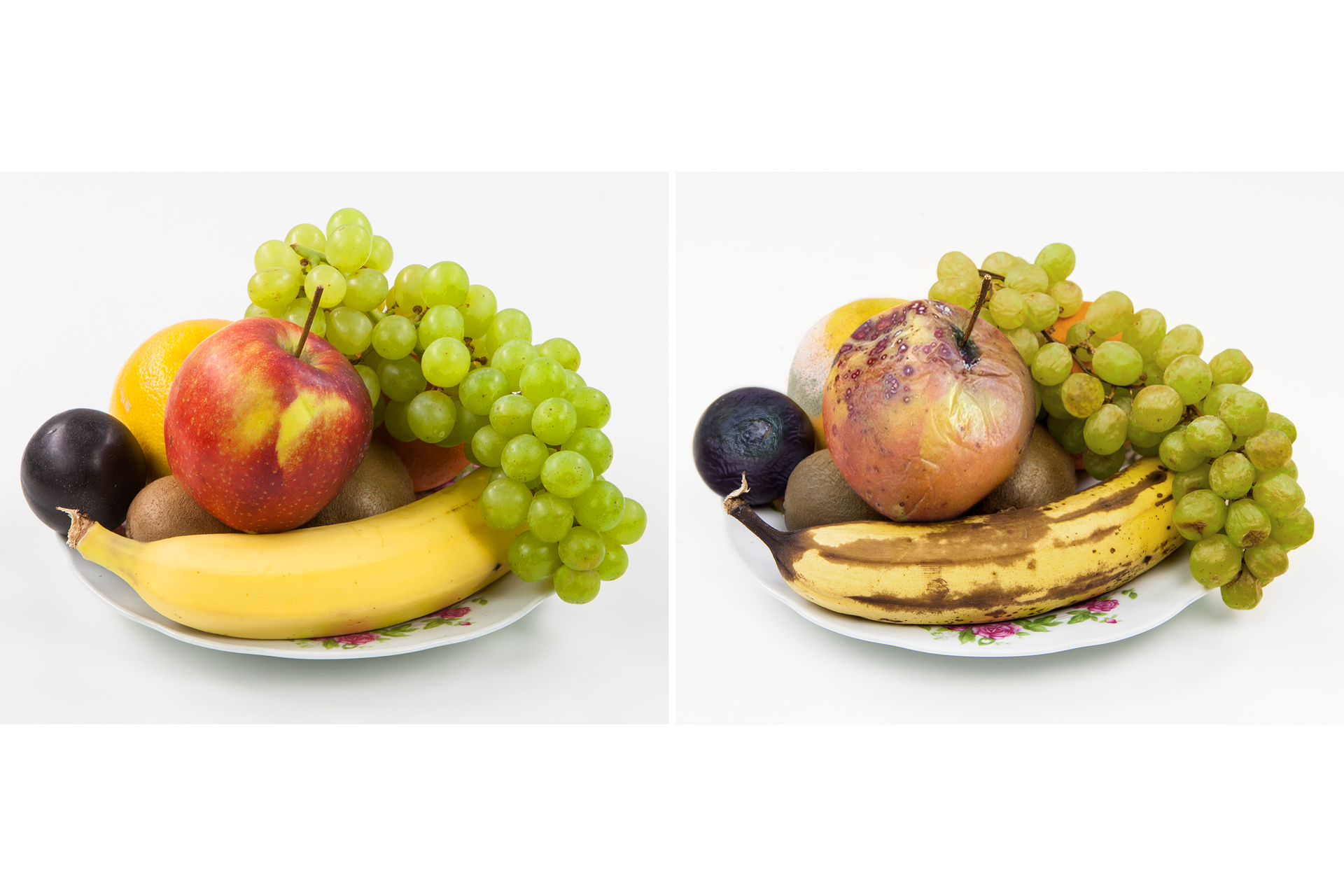
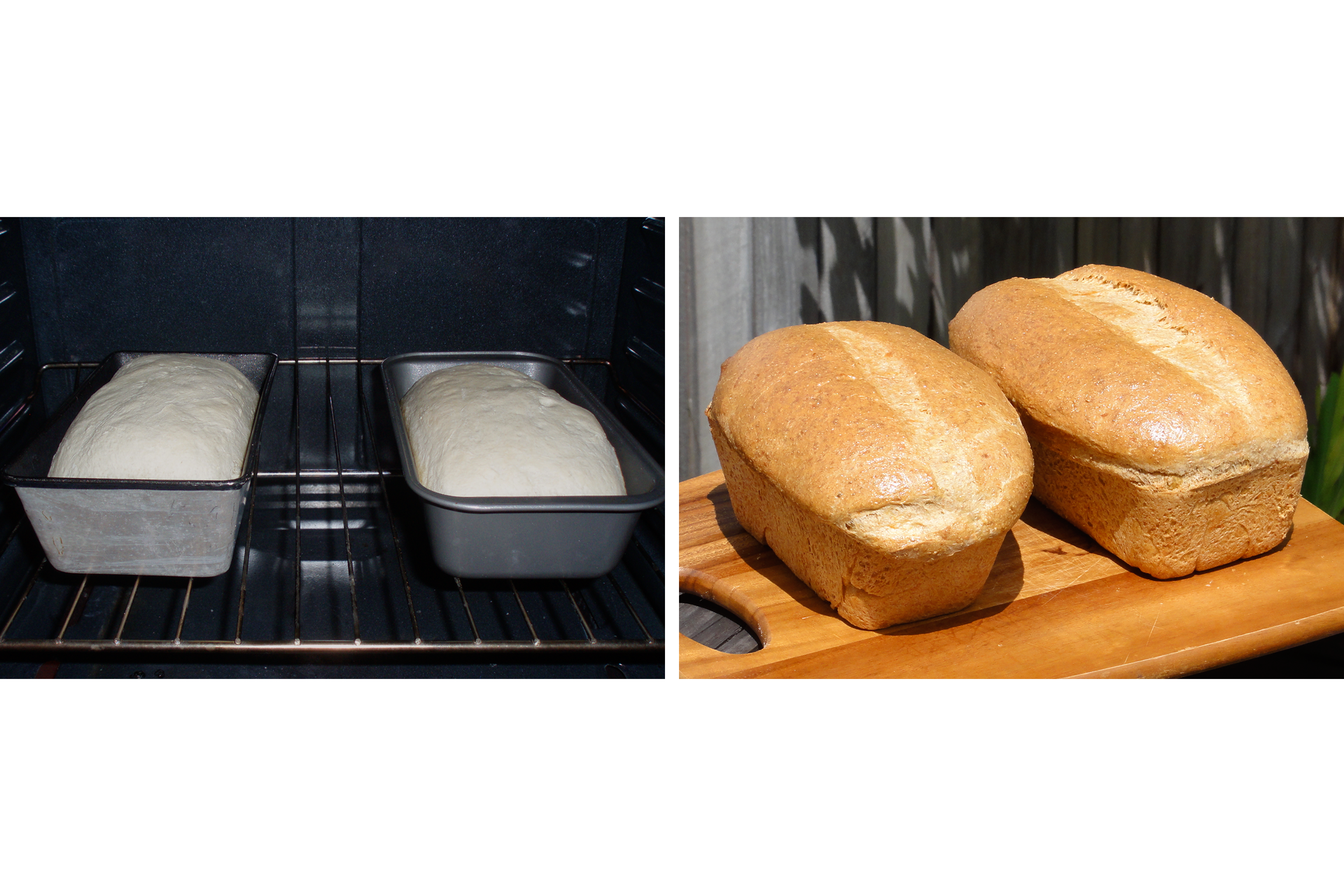
In our environment, many transformations can be observed, during which substances undergo constant changes and transform into other substances.
Transformations presented in above photographs take place under the influence of various factors: high temperature action, microorganisms, interaction of various substances. They have one thing in common – they result in new substances with different properties. Such processes are said to be chemical transformationschemical transformations or chemical reactionschemical reactions.
Consider and answer the following questions:
Are hair cutting and dyeing the same type of transformation? Specify these processes.
Are carving in wood and firing patterns in it transformations of the same type? Name them.
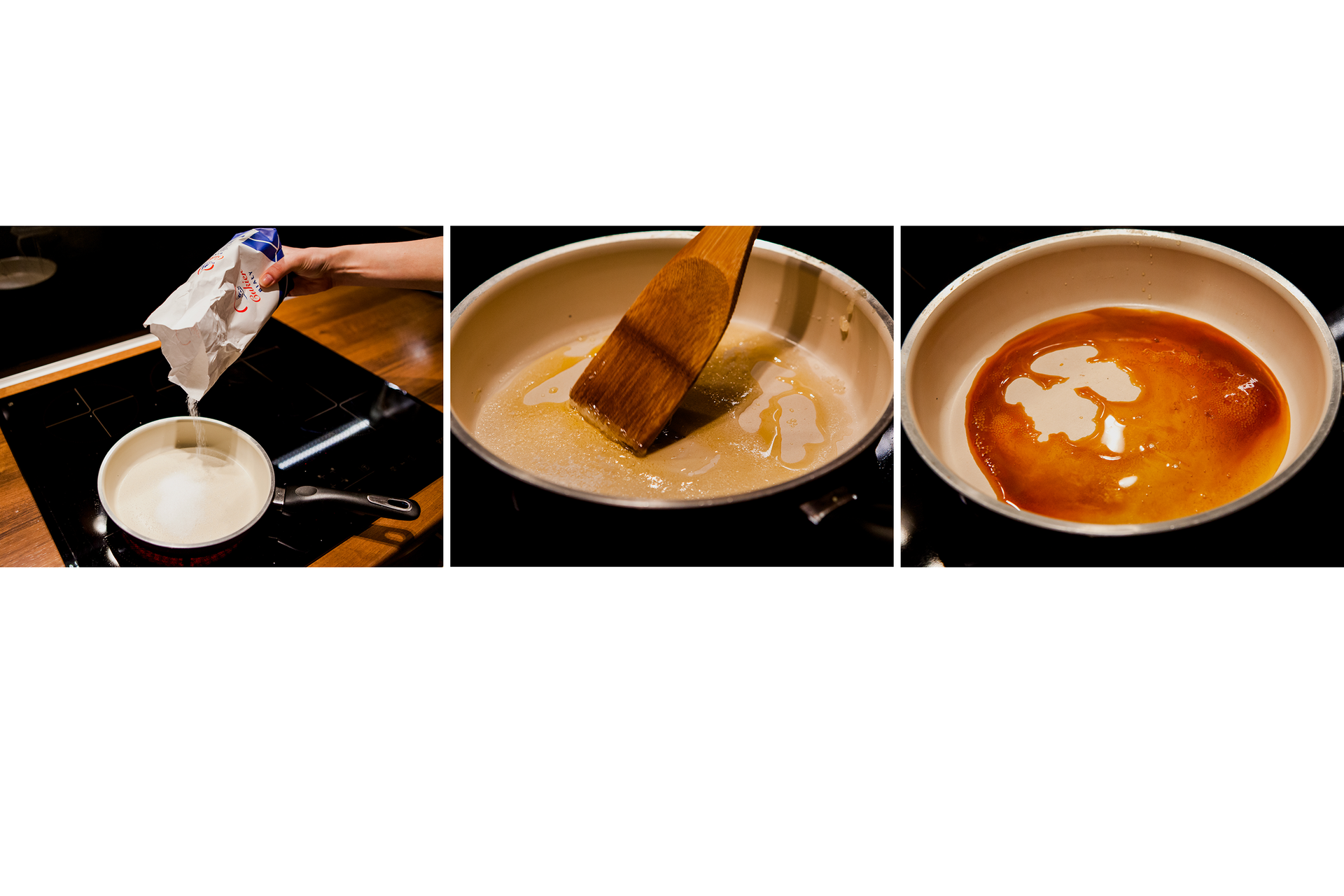
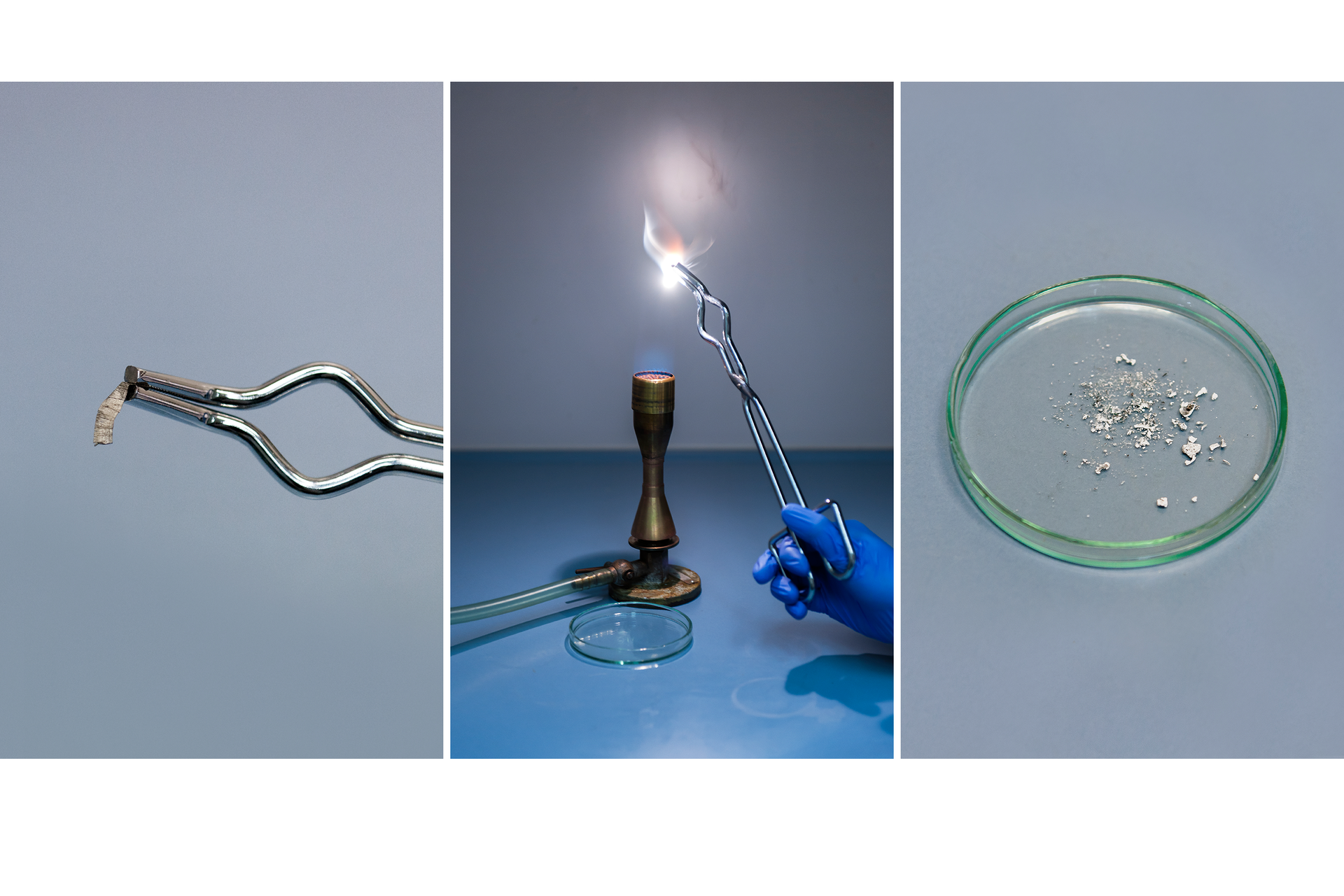
What transformation sulfur undergo during combustion?
Burning sulfur undergoes chemical transformation.
combustion spoon,
burner,
combustion cylinder,
sulfur.
Apply a small amount of sulfur to the combustion spoon.
Place the spoon in the flame of the burner and wait for the sulfur on it will ignite.
Place the combustion spoon with burning sulfur in a high cylinder.
Observe the sulfur combustion process, the flame color and other effects that accompany it.
Sulfur placed in the flame of the burner first melts and then ignites. Burns with a blue flame.
The combustion of sulfur produces a colorless substance with a gaseous state – sulfur dioxide. This transformation is an example of chemical reaction (transformation).
What is the difference between physical and chemical reaction?
Physical phenomenaPhysical phenomena and chemical transformations accompany us every day. It is not always easy to assess their type. In many cases, just process observation is not enough to determine whether a new substance was created as a result of it, or only the physical properties (e.g. state of aggregation) of the substance undergoing this transformation have changed. The factors used also do not determine the type of transformation. As a result of heating, the substance may either change physically or take part in a chemical reaction.
As a result of mixing two different substances, their mixture may be formed (physical phenomenon) or a chemical reaction may occur. This depends on properties of substances themselves and on conditions in which they are placed. In predicting the type of transformations under influence of various factors, knowledge about properties of substances is very useful.
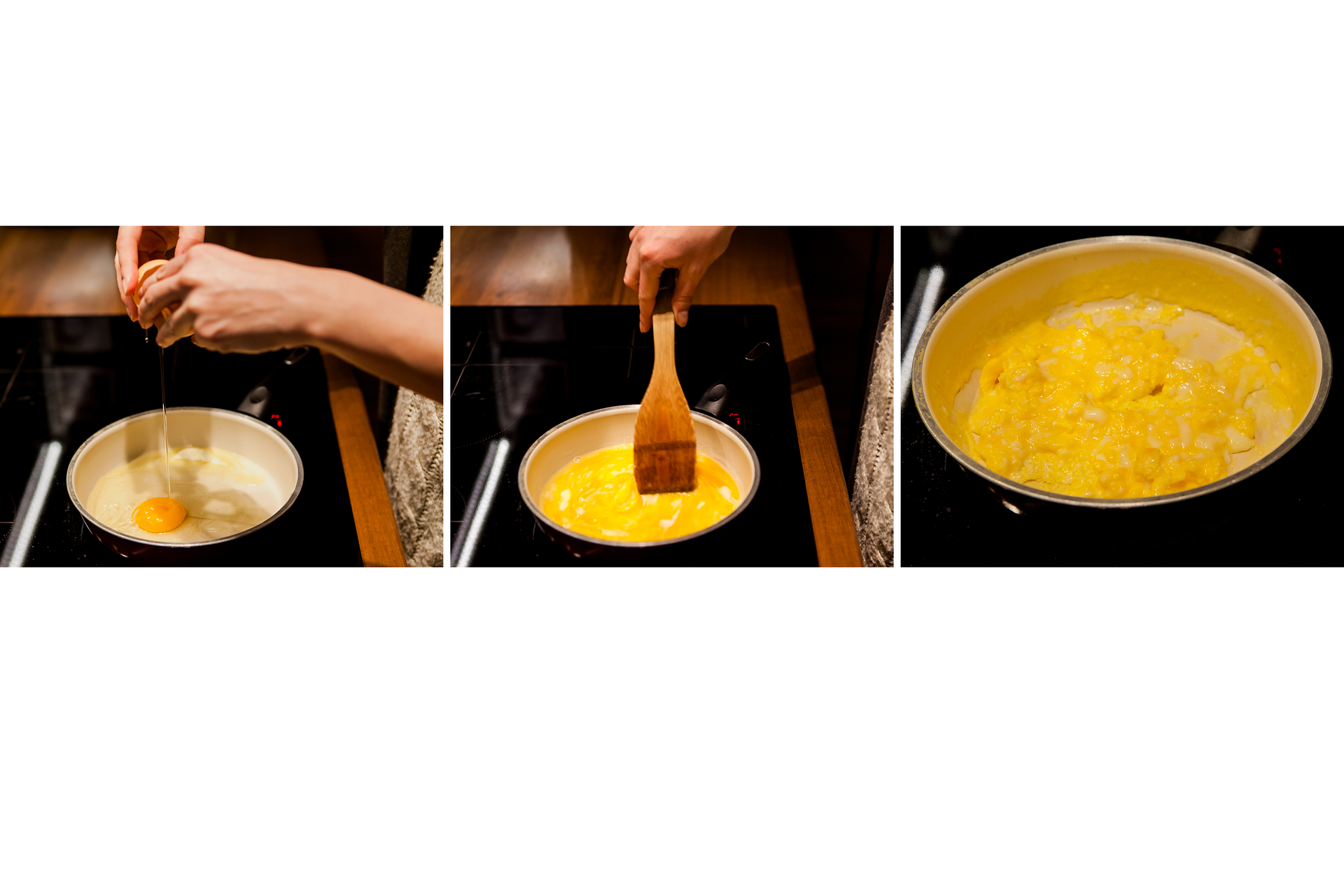
What transformations occur when mixing with one another and then heating up sulfur and iron?
Mixing sulfur with iron is a physical transformation and as a result of their heating a chemical reaction takes place.
sulfur,
iron in the form of dust (so‑called iron powder),
mortar,
spatulas,
ceramic tile,
gas burner.
Weigh 2 g of sulfur and 3.5 g of iron.
Transfer the weighed amount of elements to the mortar and mix thoroughly.
Check if the iron is still in the mixture – place the magnet close to it.
Transfer the mixture of sulfur and iron to the ceramic tile.
Place the plate on the tripod and heat it from the bottom using burner.
Keep heating until the mixture is glowing.
After the end of any transformations check presence of iron in resulting mass using the magnet.
Sulfur mixed with iron forms a gray mixture. The magnet close to its surface attracts iron powder. After heating to a high temperature, the mixture ignites. The heat covers the entire mixture. After finishing glowing, a black‑colored mass is formed. The magnet does not attract any of its components.
Iron powder can be extracted from its mixture with sulfur using a magnet. During the heating, a chemical reaction occurs in the mixture – sulfur reacts with iron. A new substance is created which, in contrast to iron – does not exhibit magnetic properties.
How can we describe chemical reactions?
Chemists have found a universal way of describing chemical transformations, during which one substance is transformed into another. With the help of arrow they indicate the direction of the transformation – from substances that took part in the chemical reaction to substances that were created:
Substances that undergo chemical transformation are called substratessubstrates, and substances resulting from it are called productsproducts. The record, in which using arrows and molecular formulas transition from substrates to products is shown, is called chemical reaction equationchemical reaction equation. The general scheme is as follows:
In the chemical reaction equation, substrates are always on the left side of the arrow, and the products – are on the right. The arrow is directed from the substrates to the products.
In experiment 2 from sulfur and oxygen we obtained sulfur dioxide. Sulfur has reacted with the oxygen presented in the air. This reaction can be described by the following equation:
Experiment 3, based on heating of sulfur with iron, led to the formation of iron(II) sulfide. This chemical transformation can be presented by the following equation:
Another chemical reaction, in which magnesium oxide is formed as a result of magnesium, can be described by the equation:
Chemical reaction equation | Substrates | Products |
sulfur, iron | iron(II) sulfide | |
sulfur, oxygen | sulfur dioxide | |
magnesium, oxygen | magnesium oxide | |
hydrogen, oxygen | water | |
sodium, chlorine | sodium chloride | |
carbon, oxygen | carbon dioxide | |
calcium, oxygen | calcium oxide | |
hydrogen, chlorine | hydrogen chloride |
Which of the above-mentioned activities do you attribute to physical phenomena, and which to chemical reactions (transformations)?
Salting potatoes, Dissolving juice in water, Cooling water, Dissolving sugar, Heat up the oil, Rinsing potatoes, Fryed meat, Peeling potatoes, Gas ignition, Acidification of cream with citric acid, Boiled potatoes, Boiling water, Burning butter, Dissolving butter, A burning match
| Physical phenomena | |
|---|---|
| Chemical transformation |
Create a multiple-choice test based on today's lesson. Then exchange your questions with a friend or classmate.
Question: ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
Summary
Physical phenomena are based on changing the physical properties of a substance. During these processes new elements and new chemical compounds are not created.
Chemical transformation is a process during which one substance is transformed into another.
Substances that undergo transformations in chemical reaction are substrates, and those that result from them are products;
The chemical reaction equation is a symbolic record of chemical reaction course. Substrates are written on the left side of the reaction equation, on the right – products. The arrow indicates the direction of the reaction from substrates to products.
Key words
products, chemical reaction equation, substrates
Glossary
produkty – substancje, które powstają w wyniku reakcji chemicznej
reakcja chemiczna (przemiana chemiczna) – proces, w którym z jednej substancji lub większej ich liczby powstaje jedna lub więcej nowych substancji o odmiennych właściwościach
równanie reakcji chemicznej – zapis przebiegu reakcji chemicznej za pomocą symboli i wzorów chemicznych; przedstawia substraty i produkty reakcji oraz często warunki zachodzenia danej reakcji
substraty – substancje, które biorą udział w przemianie chemicznej
zjawisko fizyczne (przemiana fizyczna) – proces, w wyniku którego zmieniają się właściwości fizyczne substancji