How is the Earth's crust built?
what the lithosphere is and what it consists of;
the internal structure of the Earth;
that the Earth's mantle is semi‑liquid and the lithosphere is rigid.
haracterize the Earth's crust;
the structure of the Earth's crust;
discuss the basaltic and granite zones of the Earth's crust;
show the largest tectonic plates on the map of world.
Think about how the Earth is physically changing. In what way it does? Why? Discuss this topic with other students.
Recall the construction of the interior of the Earth. Do you remember the order of its layers? Set the Earth's interior layers in the correct order. Start with the outer one.
- inner core
- outer core
- crust
- stiffer mantle
- rigid mantle

Plate tectonics
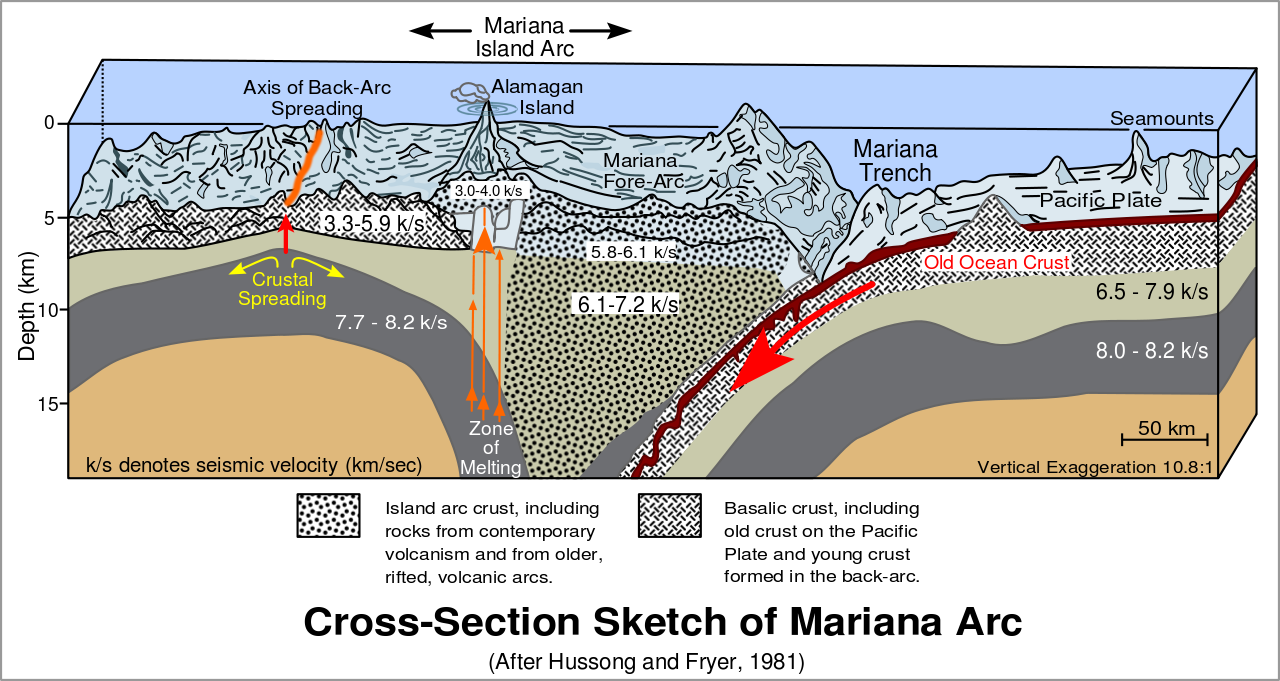
From the very beginning of its existence, geology has asked questions about how the mountains were created, why volcanoes erupt, what causes earthquakes. Not more than 100 years ago, in 1912, a revolutionary hypothesis was born known as the continental driftthe continental drift, now called from the surname of its creator - Wegener's theoryWegener's theory. At the time, he was unable to explain the cause of the slow movement of continental and oceanic plates, but this concept gained more and more recognition over time. It was only when the ocean floor was studied several dozen years later that the validity of Wegener’s hypothesis was confirmed and developed into a scientific theory of tectonics of the lithospheric platestheory of tectonics of the lithospheric plates. This theory gives answers to most questions asked by modern geology. It assumes that the lithospherelithosphere zone is divided into huge plates that cover the entire planet and float on a plastic mantle. They can move apart, creating places called the spreadingspreading zones (proliferation). If two plates collide with each other, usually one of them (usually the oceanic one) slides under the other (most often the land‑based one), and the line of such a collision is called the subductionsubduction zone. The lithospheric plates can also move parallel to each other along the line of faultsfaults.

In the place where the oceanic ridge runs, there is a zone of spreading, i.e. the growth of the oceanic crust. Ocean ridge forms a network around the entire Earth. Volcanic phenomena and frequent earthquakes can be observed in this zone.
Element | Percentage by weight |
oxygen | 47.00 |
silicon | 29.50 |
aluminium | 8.05 |
iron | 4.65 |
calcium | 2.96 |
sodium | 2.50 |
potassium | 2.50 |
magnesium | 1.87 |
titanium | 0.45 |
hydrogen | 0.145 |
manganese | 0.10 |
phosphorus | 0.093 |
Let's check what you already know about tectonic plates. Match the tectonic plates that border with each other.
borders with the South American Plate, borders with the Australian Plate, borders with the Indian Plate, borders with the Pacific Plate, borders with the African Plate, borders with the North American Plate, borders with the Antarctic Plate
| Philippine Sea Plate (oceanic plate) | |
|---|---|
| Scotia Plate (oceanic plate) | |
| Arabian Plate (continental plate) |
Put the elements that build the Earth's crust in the correct order taking into account their largest percentage.
- silicon
- aluminium
- calcium
- iron
- oxygen
Pair the words: English and Polish terms.
teoria wędrówki płyt tektonicznych, rozsuwanie się płyt litosfery, ruch kontynentów, wciąganie płyt litosfery w głąb płaszcza ziemskiego, teoria Wegnera, deformacja mas skalnych
| continental drift | |
| plate tectonics theory | |
| Wegener’s theory | |
| spreading | |
| fault | |
| subduction |
Keywords
Earth's crust, subduction, Earth's layers, continental drift
Glossary
litosfera - składa się ze skorupy ziemskiej oraz górnej części płaszcza Ziemi. Grubość litosfery waha się od 10 km pod grzbietami oceanicznymi do nawet 200 km w obrębie prekambryjskich platform kontynentalnych.
dryf kontynentalny - ruch kontynentów względem siebie i względem powierzchni globu pod wpływem ruchu płyt litosfery, który wywołany jest prądami konwekcyjnymi w płaszczu Ziemi
teoria tektoniki płyt litosferycznych - teoria, która tłumaczy przyczyny i skutki ruchu płyt litosfery, w tym także zjawisko dryfu kontynentów
Teoria Wegenera - inna nazwa teorii dryfu kontynentówdryfu kontynentów
tektonika płyt - proces rozsuwania się płyt litosfery i tworzenia nowych powierzchni skorupy ziemskiej, najczęściej w dnie oceanicznym
defekt - deformacja mas skalnych powstająca w wyniku pionowego lub poziomego przesunięcia masywu skalnego wzdłuż rozdzielającej je płaszczyzny
subdukcja - proces wciągania fragmentów płyt litosfery w głąb płaszcza ziemskiego; zwykle jest to wciąganie płyty oceanicznej pod kontynentalną